
In the above reaction product is
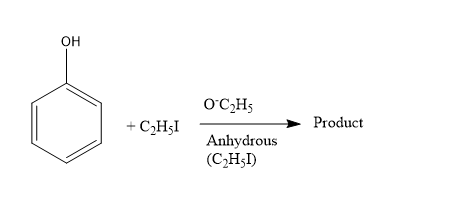
(A) \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}\]
(B) \[{{\rm{C}}_2}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}\]
(C) \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_6}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}\]
(D) \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{I}}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: An ether is a functional group in which two alkyl groups are attached to the oxygen atom. In a chemical reaction, ether is written as R-O-R. There are many methods of preparation for ether. One such method is Williamson ether synthesis.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's first understand what a Williamson ether synthesis is. In this reaction, deprotonated alcohol undergoes a reaction with an alkyl halide to give ether as a product.
Here, also the reaction is a Williamson ether synthesis. The first step of the reaction is the deprotonation of phenol to form a phenoxide ion.
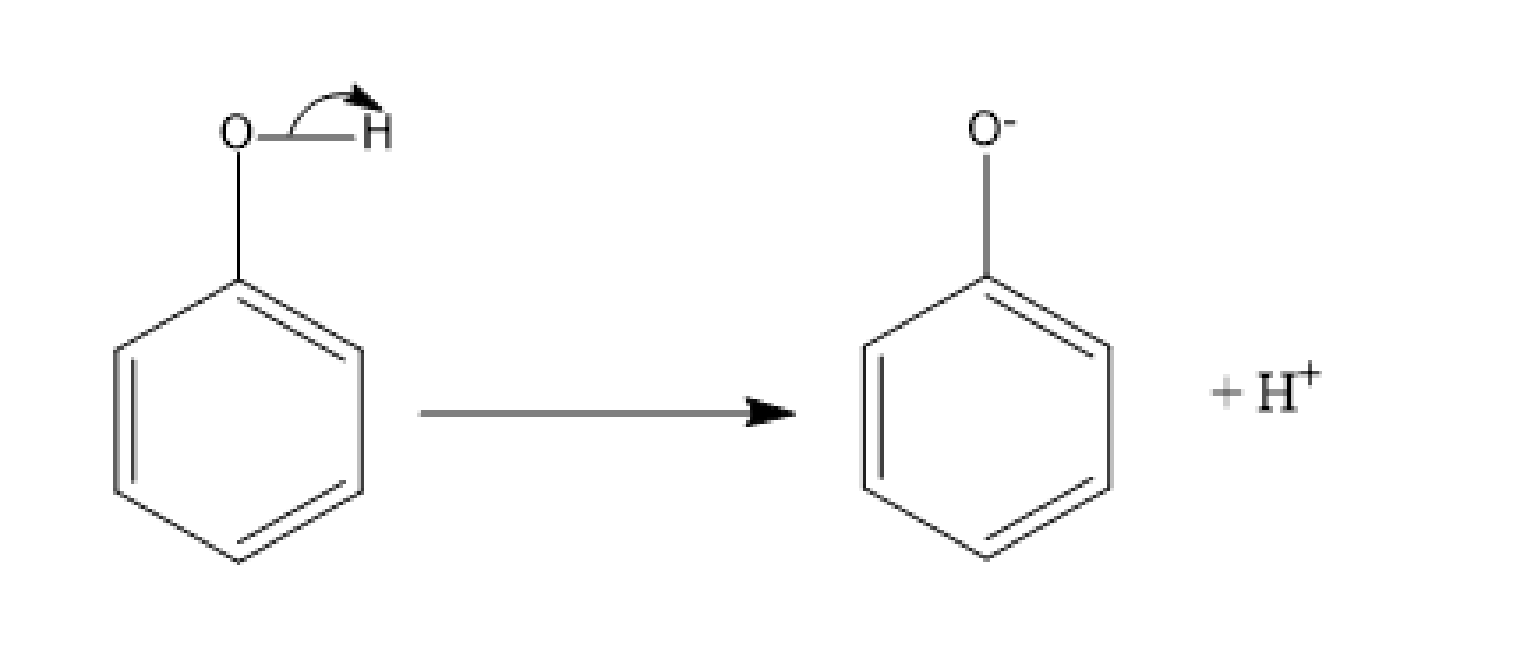
Fig: Deprotonation of phenoxide ion
In the next step, the electrophilic carbon of the ethyl chloride is attacked by the phenoxide ion and the iodine separates.
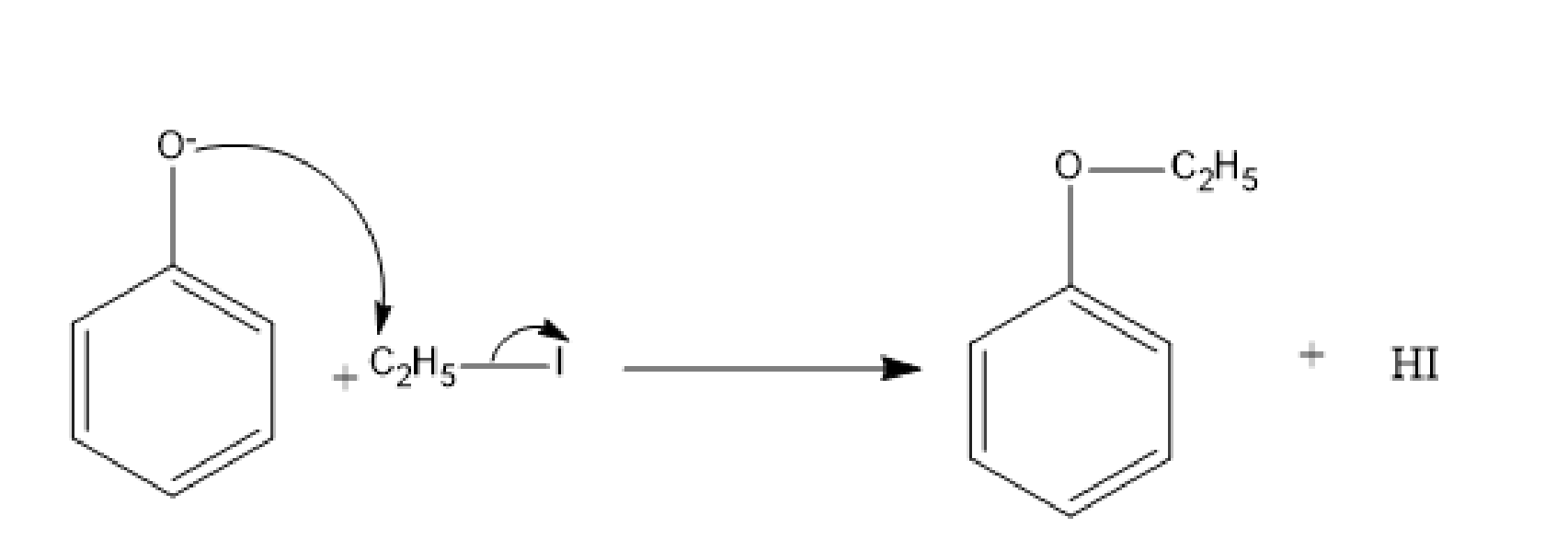
Fig: Nucleophilic attack of phenoxide ion
The product formed is \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}\] and the hydrogen iodide separates as a by-product.
Therefore, option A is right.
Additional Information: Let's discuss some properties of ether. It is a liquid whose nature is volatile. It has no colour and a pleasant odour. The boiling of ether is comparable with alkanes but less than alcohols. The solubility of ether in water is because of the hydrogen bond formation by the oxygen of ether with the water molecules. But there is a decrease in solubility when the hydrocarbon chain increases.
Note: Ether is a very important compound in many industries. Its use in the manufacturing of hydrocarbons, gums, oil, dyes, resins, and paints is significant. They are also used in lubricating oils. The nature of ether is toxic.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's first understand what a Williamson ether synthesis is. In this reaction, deprotonated alcohol undergoes a reaction with an alkyl halide to give ether as a product.
Here, also the reaction is a Williamson ether synthesis. The first step of the reaction is the deprotonation of phenol to form a phenoxide ion.

Fig: Deprotonation of phenoxide ion
In the next step, the electrophilic carbon of the ethyl chloride is attacked by the phenoxide ion and the iodine separates.

Fig: Nucleophilic attack of phenoxide ion
The product formed is \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{O}}{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}\] and the hydrogen iodide separates as a by-product.
Therefore, option A is right.
Additional Information: Let's discuss some properties of ether. It is a liquid whose nature is volatile. It has no colour and a pleasant odour. The boiling of ether is comparable with alkanes but less than alcohols. The solubility of ether in water is because of the hydrogen bond formation by the oxygen of ether with the water molecules. But there is a decrease in solubility when the hydrocarbon chain increases.
Note: Ether is a very important compound in many industries. Its use in the manufacturing of hydrocarbons, gums, oil, dyes, resins, and paints is significant. They are also used in lubricating oils. The nature of ether is toxic.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




