
In presence of \[AlC{l_3}\], benzene and n - propyl bromide react in Friedel - Craft's reaction to form:
A. N-propyl benzene
B. 1,2-Dinormal propyl benzene
C. 1,4-Dinormal propyl benzene
D. Isopropyl benzene
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Friedel-Crafts reaction in consideration here is an alkylation reaction. It proceeds via an electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism where the n-propyl bromide provides the electrophile intermediate.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Friedel-Crafts reactions are a set of reactions which involve the attaching of a substituent to an aromatic ring. Friedel-Crafts reactions are of two types, alkylation reactions, in which an alkyl group (\[ - R\]) gets attached to a ring, and acylation reactions involving the attaching of an acyl group (\[ - RC = O\]) to a ring. In this reaction, the catalyst employed is aluminium chloride (\[AlC{l_3}\]) which is a strong Lewis acid. The alkylating agents have traditionally been alkyl halides.
Let’s have a look at how benzene and n-propyl bromide undergo Friedel-Craft’s reaction in presence of aluminium chloride.
In the first step, the n-propyl bromide loses its bromine atom with the help of aluminium chloride as shown. Since aluminium chloride is a strong Lewis acid, it accepts electrons from the bromine atom of n-propyl bromide, and it leads to the formation of an n-propyl carbocation.
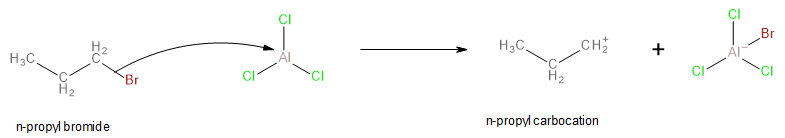
Image: Formation of n-propyl carbocation
The n-propyl carbocation formed is primary. We know that primary carbocations are the least stable (order of stability of carbocations: \[1^\circ < 2^\circ < 3^\circ \]). Since secondary carbocations are more stable, if the n-propyl carbocation can somehow become a secondary carbocation, it would become more stable. The n-propyl carbocation does indeed turn into a secondary carbocation through the rearrangement of an alpha-hydrogen. This process is called a 1,2-hydride shift since the hydrogen rearranges as a hydride and it occurs from the alpha-carbon (locant 2) to the cationic carbon (locant 1).
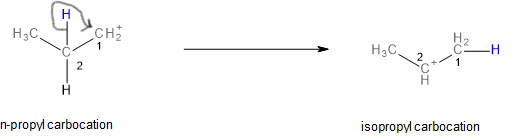
Image: Rearrangement into a more stable, secondary carbocation
The product is a more stable, secondary, isopropyl carbocation.
The isopropyl carbocation is then attacked by a \[\pi \]electron pair of benzene followed by the liberation of hydrogen bromide (\[HBr\]) to form isopropyl benzene which is commonly known as cumene.
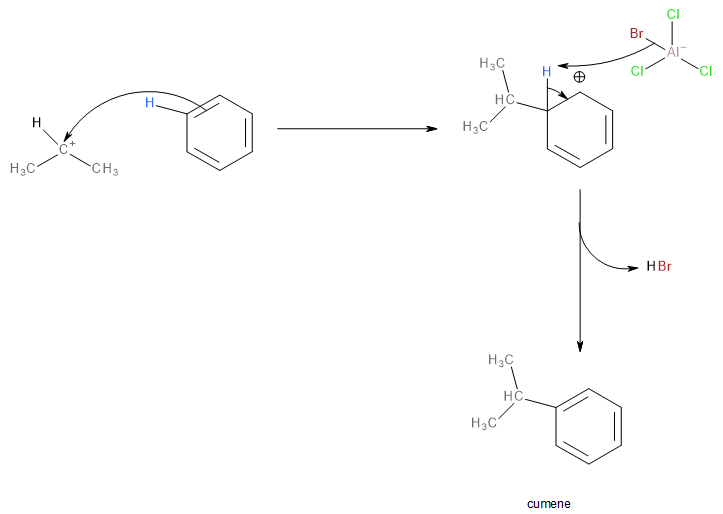
Image: Nucleophilic attack of a benzene ring on the carbocation.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: The rearrangement of the primary n-propyl carbocation into a more stable, secondary, isopropyl carbocation via 1,2-hydride shift is a very crucial step in this reaction. This is where quite a few students may go wrong. If they are unaware of this rearrangement step, they might mark option A as the answer to this question. They would be wrong.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Friedel-Crafts reactions are a set of reactions which involve the attaching of a substituent to an aromatic ring. Friedel-Crafts reactions are of two types, alkylation reactions, in which an alkyl group (\[ - R\]) gets attached to a ring, and acylation reactions involving the attaching of an acyl group (\[ - RC = O\]) to a ring. In this reaction, the catalyst employed is aluminium chloride (\[AlC{l_3}\]) which is a strong Lewis acid. The alkylating agents have traditionally been alkyl halides.
Let’s have a look at how benzene and n-propyl bromide undergo Friedel-Craft’s reaction in presence of aluminium chloride.
In the first step, the n-propyl bromide loses its bromine atom with the help of aluminium chloride as shown. Since aluminium chloride is a strong Lewis acid, it accepts electrons from the bromine atom of n-propyl bromide, and it leads to the formation of an n-propyl carbocation.

Image: Formation of n-propyl carbocation
The n-propyl carbocation formed is primary. We know that primary carbocations are the least stable (order of stability of carbocations: \[1^\circ < 2^\circ < 3^\circ \]). Since secondary carbocations are more stable, if the n-propyl carbocation can somehow become a secondary carbocation, it would become more stable. The n-propyl carbocation does indeed turn into a secondary carbocation through the rearrangement of an alpha-hydrogen. This process is called a 1,2-hydride shift since the hydrogen rearranges as a hydride and it occurs from the alpha-carbon (locant 2) to the cationic carbon (locant 1).

Image: Rearrangement into a more stable, secondary carbocation
The product is a more stable, secondary, isopropyl carbocation.
The isopropyl carbocation is then attacked by a \[\pi \]electron pair of benzene followed by the liberation of hydrogen bromide (\[HBr\]) to form isopropyl benzene which is commonly known as cumene.

Image: Nucleophilic attack of a benzene ring on the carbocation.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note: The rearrangement of the primary n-propyl carbocation into a more stable, secondary, isopropyl carbocation via 1,2-hydride shift is a very crucial step in this reaction. This is where quite a few students may go wrong. If they are unaware of this rearrangement step, they might mark option A as the answer to this question. They would be wrong.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




