
In a full wave rectifier in which input voltage is represented by $V$ = ${V_m}\sin \omega t$, then what will be the peak inversion voltage of the non-conducting diode?
A) $ - {V_m}$
B) $\dfrac{{{V_m}}}{2}$
C) $2{V_m}$
D) $0$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The maximum value of the reverse voltage of a diode when it is reverse biased is called the peak inverse voltage of the diode. In the center tapped full wave rectifier, one diode is in reverse bias in each half cycle, so the whole voltage $V_m$ is developed across the resistance.
Complete step by step solution:
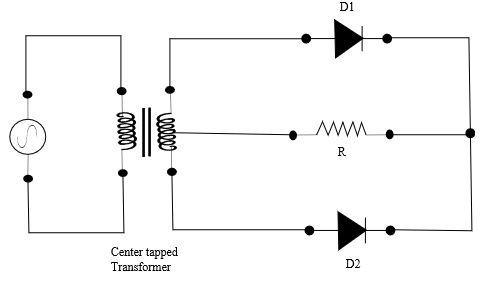
Full wave rectifier is of two types: center tapped and bridge. The center tapped full wave rectifier is constructed with a center tapped transformer, two diodes and a resistor, which taps the transformer at the center. In the first half cycle, the diode $D_1$ is forward biased, hence, conducts, and diode $D_2$ is in reverse bias, and acts as an open switch. In the second half cycle, the diode $D_2$ is forward biased and diode $D_1$ is in reverse bias.
The peak inverse voltage is the maximum reverse voltage of a diode when the diode is reverse biased. During the first half cycle of the AC power supply, the top of the secondary winding of the transformer is positive, and the diode $D_1$ conducts, offering almost zero resistance. Therefore, the whole voltage $V_m$ of the upper half winding is developed across the load or resistance. In this case, the voltage across the non-conducting diode $D_2$ is the sum of the voltage across the lower half of the transformer secondary winding and the voltage across the load connected to the center tapped transformer. The peak inverse voltage of diode can be written as,
$PIV = {V_m} + {V_m} = 2{V_m}$
Hence, the peak inverse voltage is twice the maximum voltage, that is $2{V_m}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The full wave rectifier gives a steady and smooth DC current supply. It uses both the half cycles of the AC current as opposed to the half wave rectifier, which only utilizes the positive half cycle of the AC current.
Complete step by step solution:

Full wave rectifier is of two types: center tapped and bridge. The center tapped full wave rectifier is constructed with a center tapped transformer, two diodes and a resistor, which taps the transformer at the center. In the first half cycle, the diode $D_1$ is forward biased, hence, conducts, and diode $D_2$ is in reverse bias, and acts as an open switch. In the second half cycle, the diode $D_2$ is forward biased and diode $D_1$ is in reverse bias.
The peak inverse voltage is the maximum reverse voltage of a diode when the diode is reverse biased. During the first half cycle of the AC power supply, the top of the secondary winding of the transformer is positive, and the diode $D_1$ conducts, offering almost zero resistance. Therefore, the whole voltage $V_m$ of the upper half winding is developed across the load or resistance. In this case, the voltage across the non-conducting diode $D_2$ is the sum of the voltage across the lower half of the transformer secondary winding and the voltage across the load connected to the center tapped transformer. The peak inverse voltage of diode can be written as,
$PIV = {V_m} + {V_m} = 2{V_m}$
Hence, the peak inverse voltage is twice the maximum voltage, that is $2{V_m}$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Note: The full wave rectifier gives a steady and smooth DC current supply. It uses both the half cycles of the AC current as opposed to the half wave rectifier, which only utilizes the positive half cycle of the AC current.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




