
If in a triangle \[ABC\], the altitudes from the vertices \[A,B,C\] on opposite sides are in H.P. then \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\], are in
A. A.G.P.
B. H.P.
C. G.P.
D. A.P.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
In the given question, we need to check whether \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\] are in A.G.P., H.P, G.P., or A.P. For this, we have to draw a figure using the given information. Also, we need to find the area of triangle \[ABC\]. So that we will get the values of \[AD, BE, CF\]. After that, we will show \[a,b,c\] are in A.P. Finally, we will use the sine rule to get the desired result.
Formula Used:
The following formula is used for solving the given question.
In a right-angled triangle, \[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Also, the sine rule is given by
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} = k\]
Here, \[k\] is a constant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider the following figure.
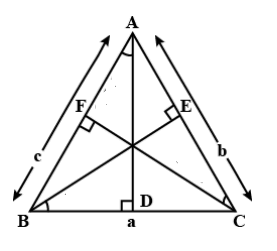
Here, \[AD, BE\] and \[CF\] are the altitudes of a triangle \[ABC\], and also they are in H.P.
Now, we will find the area of triangle \[ABC\].
\[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
\[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AD \times BC\]
But \[BC = a\]
So, we get \[AD = \dfrac{{2A}}{a}\]
Similarly, we get \[BE = \dfrac{{2A}}{b}\] and \[CF = \dfrac{{2A}}{c}\]
This indicates that \[\dfrac{{2A}}{a}\], \[\dfrac{{2A}}{b}\] and \[\dfrac{{2A}}{c}\] are in H.P.
Thus, we can say that \[\dfrac{1}{a}\], \[\dfrac{1}{b}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{c}\] are in H.P.
Hence, \[a\], \[b\] and \[c\] are in A.P.
Now, we will use the sine rule here.
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} = k\]
This gives, \[a = k\sin A,b = k\sin B,\]and \[c = k\sin C\]
But we know that \[a\], \[b\] and \[c\] are in A.P.
So, \[2b = a + c\]
Thus, we get \[2k\sin B = k\sin A + k\sin C\]
By simplifying, we get
\[2\sin B = \sin A + \sin C\]
Hence, \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\], are in A.P.
Thus, if in a triangle \[ABC\], the altitudes from the vertices \[A, B, C\] on opposite sides are in H.P. then \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\], are in A.P.
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Additional Information :
A Harmonic Progression (HP) is a series of real numbers formed by calculating the reciprocals of the arithmetic progression that does not include zero. Any element in the sequence is termed the harmonic mean of its two neighbors in harmonic progression.
Note: Many students make mistake in calculation part as well as in writing the sine rule. This is the only way, through which we can solve the example in simplest way. Also, it is essential to analyse the result such as \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are in A.P to get the desired result.
In the given question, we need to check whether \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\] are in A.G.P., H.P, G.P., or A.P. For this, we have to draw a figure using the given information. Also, we need to find the area of triangle \[ABC\]. So that we will get the values of \[AD, BE, CF\]. After that, we will show \[a,b,c\] are in A.P. Finally, we will use the sine rule to get the desired result.
Formula Used:
The following formula is used for solving the given question.
In a right-angled triangle, \[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Also, the sine rule is given by
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} = k\]
Here, \[k\] is a constant.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Consider the following figure.

Here, \[AD, BE\] and \[CF\] are the altitudes of a triangle \[ABC\], and also they are in H.P.
Now, we will find the area of triangle \[ABC\].
\[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
\[Area\left( A \right) = \dfrac{1}{2} \times AD \times BC\]
But \[BC = a\]
So, we get \[AD = \dfrac{{2A}}{a}\]
Similarly, we get \[BE = \dfrac{{2A}}{b}\] and \[CF = \dfrac{{2A}}{c}\]
This indicates that \[\dfrac{{2A}}{a}\], \[\dfrac{{2A}}{b}\] and \[\dfrac{{2A}}{c}\] are in H.P.
Thus, we can say that \[\dfrac{1}{a}\], \[\dfrac{1}{b}\] and \[\dfrac{1}{c}\] are in H.P.
Hence, \[a\], \[b\] and \[c\] are in A.P.
Now, we will use the sine rule here.
\[\dfrac{a}{{\sin A}} = \dfrac{b}{{\sin B}} = \dfrac{c}{{\sin C}} = k\]
This gives, \[a = k\sin A,b = k\sin B,\]and \[c = k\sin C\]
But we know that \[a\], \[b\] and \[c\] are in A.P.
So, \[2b = a + c\]
Thus, we get \[2k\sin B = k\sin A + k\sin C\]
By simplifying, we get
\[2\sin B = \sin A + \sin C\]
Hence, \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\], are in A.P.
Thus, if in a triangle \[ABC\], the altitudes from the vertices \[A, B, C\] on opposite sides are in H.P. then \[\sin A,\sin B,\sin C\], are in A.P.
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Additional Information :
A Harmonic Progression (HP) is a series of real numbers formed by calculating the reciprocals of the arithmetic progression that does not include zero. Any element in the sequence is termed the harmonic mean of its two neighbors in harmonic progression.
Note: Many students make mistake in calculation part as well as in writing the sine rule. This is the only way, through which we can solve the example in simplest way. Also, it is essential to analyse the result such as \[a\], \[b\], and \[c\] are in A.P to get the desired result.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




