
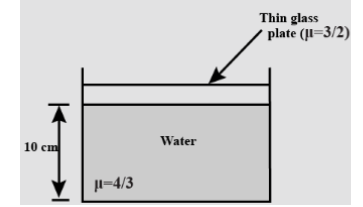
If an observer sees the bottom of the vessel shown in Fig. at 8 cm, find the refractive index of the medium in which the observer is present.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Calculate the apparent depth using the formula \[\mu = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}}\] and now this becomes the real depth for the new case and 8 cm is the apparent depth and using the same formula now calculate required refractive index.
Complete step- by-step solution
When the light is travelling from medium 1 to 2 the refractive index can be written as,
\[_1{\mu _2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{{\mu _1}}}\]
If the object is placed in a different medium then due to refraction, object appears to be displaced from its real position so, when object is in denser medium and observer is in rarer medium,
\[\mu = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}}\]
It is given that real depth is 10 cm and μ can be written as \[{}_g{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{{\mu _w}}}{{{\mu _g}}}\] where, \[{\mu _g} = \dfrac{3}{2};{\mu _w} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Substitute in the formula and we get apparent depth.
\[
_g{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}} \\
\dfrac{{{\mu _w}}}{{{\mu _g}}} = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}} \\
\dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{{\dfrac{3}{2}}} = \dfrac{{10}}{{apparent}} \\
apparent = \dfrac{{45}}{4} \\
\]
Using the same format the refractive index at 8 cm (μr) which is the apparent depth now
$
\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}}}{{{\mu _r}}} = \dfrac{{45}}{{4 \times 8}} \\
{\mu _r} = \dfrac{{16}}{{15}} \\
$
Hence the refractive index at 8 cm is$\dfrac{{16}}{{15}}$ .
Note In case of more immiscible liquids as layers present then refractive index of the combination is
${\mu _c} = \dfrac{{real(d)}}{{app(d)}} = \dfrac{{{d_1} + {d_2}...}}{{\dfrac{{{d_1}}}{{{\mu _1}}} + \dfrac{{{d_2}}}{{{\mu _2}}}...}}$
Complete step- by-step solution
When the light is travelling from medium 1 to 2 the refractive index can be written as,
\[_1{\mu _2} = \dfrac{{{\mu _2}}}{{{\mu _1}}}\]
If the object is placed in a different medium then due to refraction, object appears to be displaced from its real position so, when object is in denser medium and observer is in rarer medium,
\[\mu = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}}\]
It is given that real depth is 10 cm and μ can be written as \[{}_g{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{{\mu _w}}}{{{\mu _g}}}\] where, \[{\mu _g} = \dfrac{3}{2};{\mu _w} = \dfrac{4}{3}\]
Substitute in the formula and we get apparent depth.
\[
_g{\mu _w} = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}} \\
\dfrac{{{\mu _w}}}{{{\mu _g}}} = \dfrac{{real}}{{apparent}} \\
\dfrac{{\dfrac{4}{3}}}{{\dfrac{3}{2}}} = \dfrac{{10}}{{apparent}} \\
apparent = \dfrac{{45}}{4} \\
\]
Using the same format the refractive index at 8 cm (μr) which is the apparent depth now
$
\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{2}}}{{{\mu _r}}} = \dfrac{{45}}{{4 \times 8}} \\
{\mu _r} = \dfrac{{16}}{{15}} \\
$
Hence the refractive index at 8 cm is$\dfrac{{16}}{{15}}$ .
Note In case of more immiscible liquids as layers present then refractive index of the combination is

${\mu _c} = \dfrac{{real(d)}}{{app(d)}} = \dfrac{{{d_1} + {d_2}...}}{{\dfrac{{{d_1}}}{{{\mu _1}}} + \dfrac{{{d_2}}}{{{\mu _2}}}...}}$
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




