
Hemiacetals are usually unstable whereas acetals are stable. Which has the most stable hemiacetal?
A.
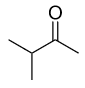
B.
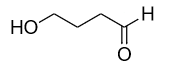
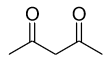
C.
D. \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}-CHO\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When two ether groups are joined to the same carbon, an acetal is created. Additionally, it is made from a hemiacetal, which is an aldehyde with two groups: an ether group and an alcohol group.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Acetals are created when alcohols and aldehydes combine in an acidic environment. These are tetrahedral-shaped functional groups having two alkoxy (\[-OR\]) groups linked to the centre carbon atom. The action begins with the protonation of carbonyl oxygen, which makes the C=O bond highly electrophilic. Alcohol then attacks the C=O bond and creates an intermediate called oxonium as a result. Upon deprotonation, this intermediate transforms into a hemiacetal. In contrast to acetals, which have two alkoxy groups, hemiacetals only have one.
Hemiacetal's OH group is further protonated and converted into a suitable leaving group. The SN2 reaction cannot take place here because carbon is sterically inhibited. As a result, the SN2 process is used in this instance, in which the leaving group is first removed by oxygen lone pairs and then followed by deprotonation of the intermediate oxonium to produce acetal. By creating an ether bond and an OH bond on the same carbon, hemiacetals are created from an aldehyde or ketone and an alcohol. It serves as a tetrahedral intermediary in the acetal synthesis. It moves more quickly when an acid is used as a catalyst, but acid can also cause it to decompose and return to the original substance.
The hemiacetals are generally unstable in nature but they form acetals that are stable in nature. The stability of the acetal depends on the number of carbon chains in the ring. Usually, rings with 5 or 6 members are more stable than the others. So if we look at the given options the only compound that can form a 5 or 6 membered ring structure is option B that is 4-hydroxy butanal. The cyclic form is given as:
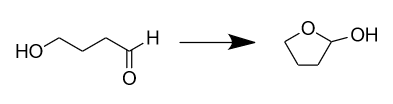
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Because it functions as a reducing sugar, a hemiacetal structure is unstable in nature. Acetals, on the other hand, are non-reducing sugars and are stable because they cannot be changed back into hemiacetals or aldehydes.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Acetals are created when alcohols and aldehydes combine in an acidic environment. These are tetrahedral-shaped functional groups having two alkoxy (\[-OR\]) groups linked to the centre carbon atom. The action begins with the protonation of carbonyl oxygen, which makes the C=O bond highly electrophilic. Alcohol then attacks the C=O bond and creates an intermediate called oxonium as a result. Upon deprotonation, this intermediate transforms into a hemiacetal. In contrast to acetals, which have two alkoxy groups, hemiacetals only have one.
Hemiacetal's OH group is further protonated and converted into a suitable leaving group. The SN2 reaction cannot take place here because carbon is sterically inhibited. As a result, the SN2 process is used in this instance, in which the leaving group is first removed by oxygen lone pairs and then followed by deprotonation of the intermediate oxonium to produce acetal. By creating an ether bond and an OH bond on the same carbon, hemiacetals are created from an aldehyde or ketone and an alcohol. It serves as a tetrahedral intermediary in the acetal synthesis. It moves more quickly when an acid is used as a catalyst, but acid can also cause it to decompose and return to the original substance.
The hemiacetals are generally unstable in nature but they form acetals that are stable in nature. The stability of the acetal depends on the number of carbon chains in the ring. Usually, rings with 5 or 6 members are more stable than the others. So if we look at the given options the only compound that can form a 5 or 6 membered ring structure is option B that is 4-hydroxy butanal. The cyclic form is given as:

Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Because it functions as a reducing sugar, a hemiacetal structure is unstable in nature. Acetals, on the other hand, are non-reducing sugars and are stable because they cannot be changed back into hemiacetals or aldehydes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




