
Glycine may be classed as all of the following except [JIMPER $1997$]
A.A base
B.An acid
C.A zwitterion
D.Optically active acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Glycine is one kind of non-essential amino acid in humans and animals. It is an essential component for all metabolic activities and life processes of animals and human beings. To approach this problem we must have to know the structure of the simplest amino acid, glycine.
Complete step by step solution:An amino acid consists of an amino group $(-N{{H}_{2}})$and a carboxylic group $(-COOH)$. One of the simplest amino acids is glycine with the chemical formula $(N{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH)$. In mammals, glycine is one of the non-essential amino acids. The structure of this amino acid is shown below:
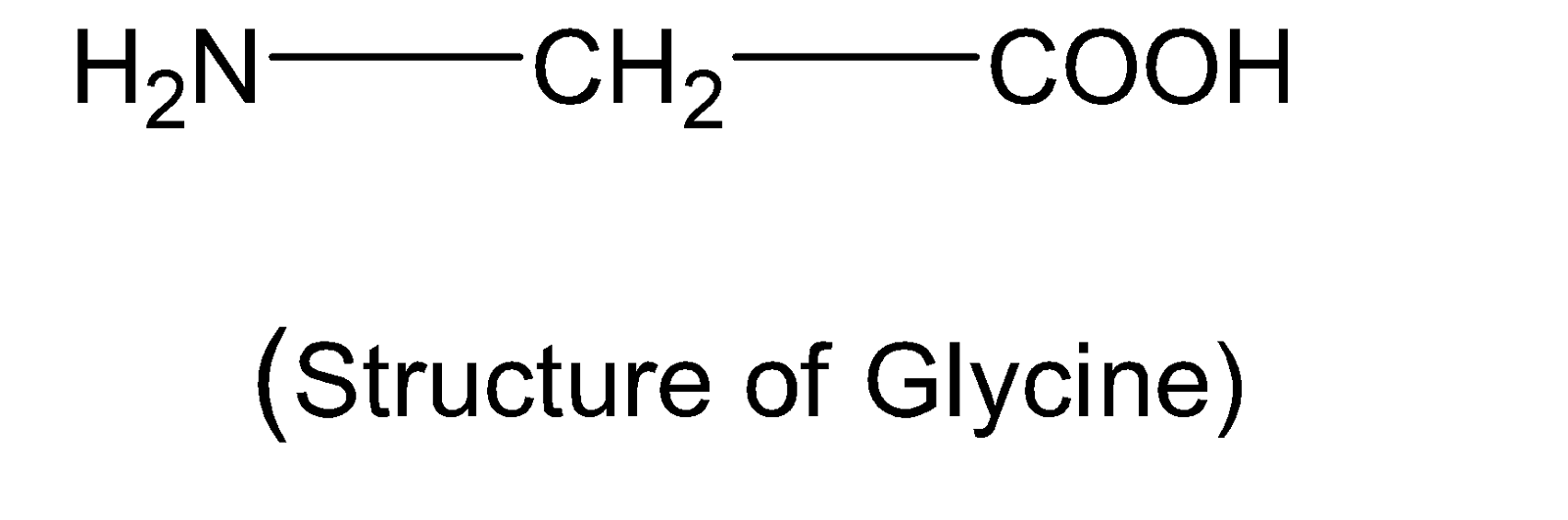
Because of the internal proton transfer of hydrogen ions $({{H}^{+}})$from the carboxylic acid group to the amine group $(-N{{H}_{2}})$ they exist as an ion with both a negative charge on the oxygen of the acid group and a positive charge on the nitrogen of the amine group. This is called zwitterion. This zwitter ionic state is achieved at ${{P}^{H}}=7$. In the basic solution , base abstracts a proton from the $-NH_{3}^{+}$ group of glycine and acts as a base. In an acidic solution, the carboxylic acid group abstracts a proton and thus produces a positively charged amino acid.
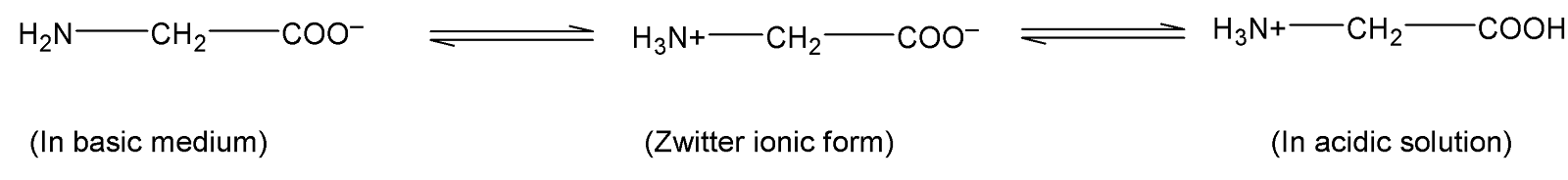
But Glycine is an optically active compound as it does not contain any chiral carbon. Optically active compounds are those which consist of four different substitutions.
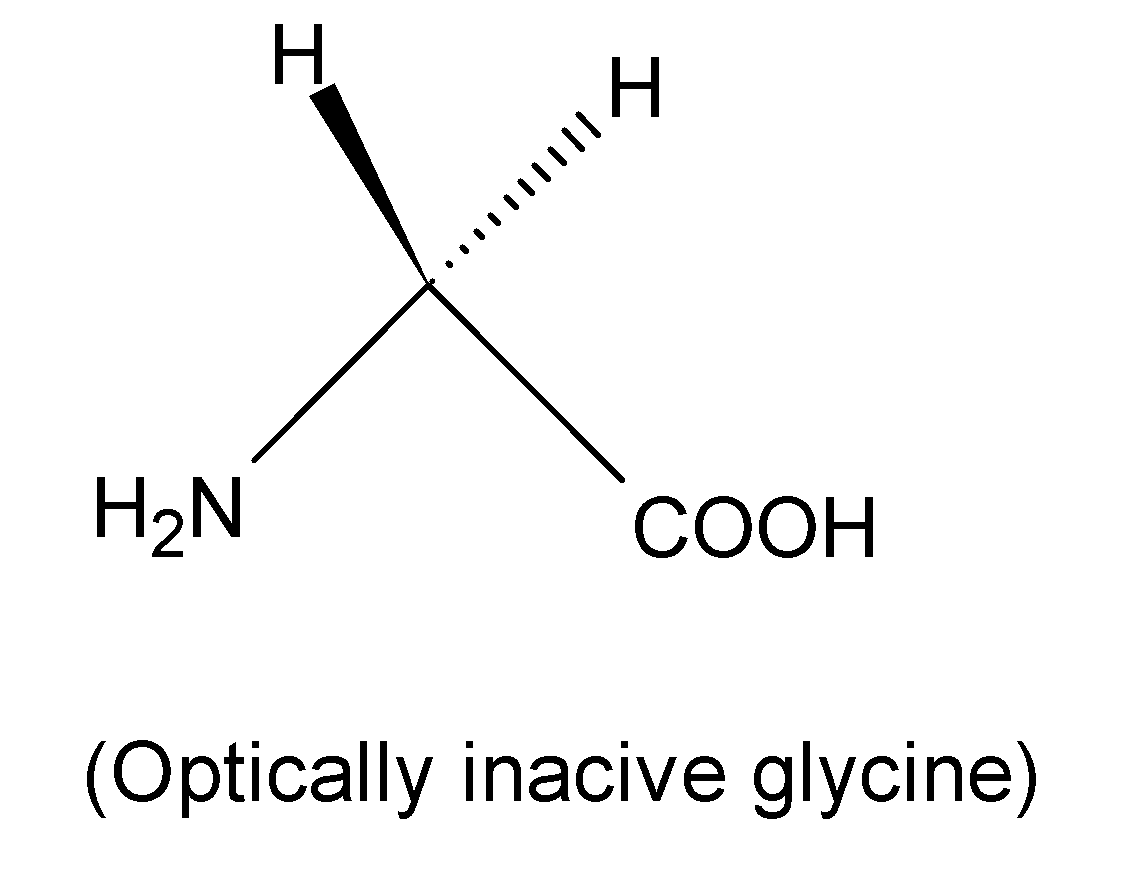
Therefore glycine may be classed as all of the following except optically active acid.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: It is found that there is $20$an amino acid that is essential for all living things. They are building blocks of protein molecules. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body system but can be taken from outside through our diets. Some of them are valine, leucine, lysine, histidine, methionine, etc.
Complete step by step solution:An amino acid consists of an amino group $(-N{{H}_{2}})$and a carboxylic group $(-COOH)$. One of the simplest amino acids is glycine with the chemical formula $(N{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{2}}COOH)$. In mammals, glycine is one of the non-essential amino acids. The structure of this amino acid is shown below:
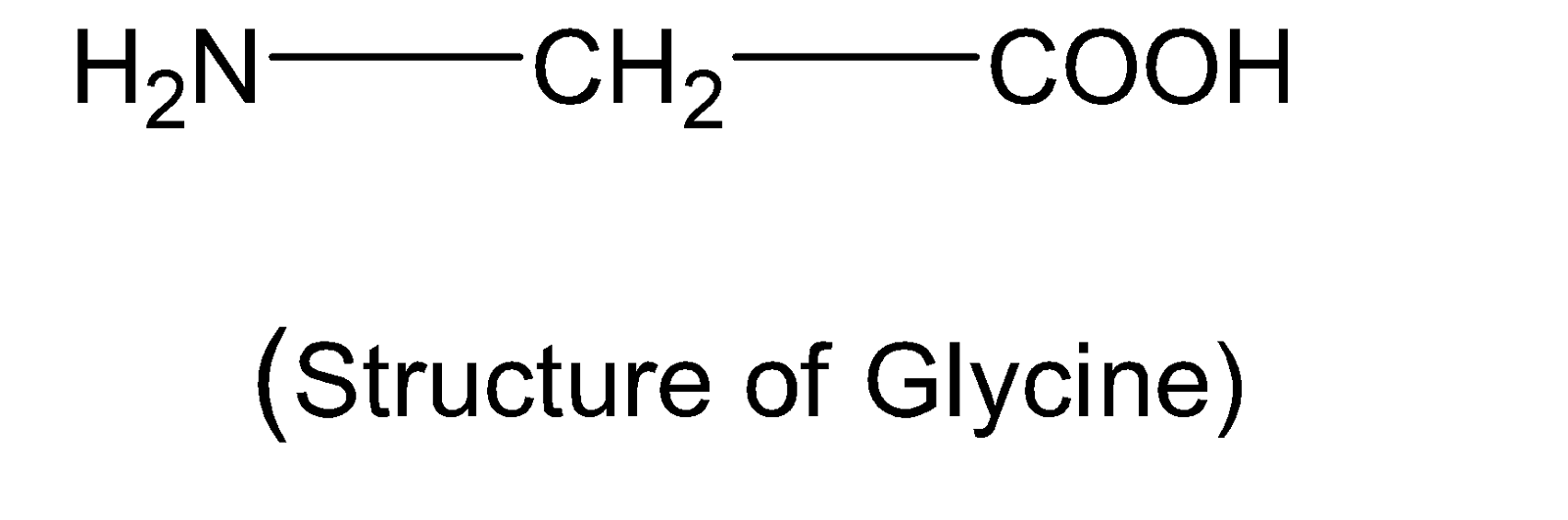
Because of the internal proton transfer of hydrogen ions $({{H}^{+}})$from the carboxylic acid group to the amine group $(-N{{H}_{2}})$ they exist as an ion with both a negative charge on the oxygen of the acid group and a positive charge on the nitrogen of the amine group. This is called zwitterion. This zwitter ionic state is achieved at ${{P}^{H}}=7$. In the basic solution , base abstracts a proton from the $-NH_{3}^{+}$ group of glycine and acts as a base. In an acidic solution, the carboxylic acid group abstracts a proton and thus produces a positively charged amino acid.
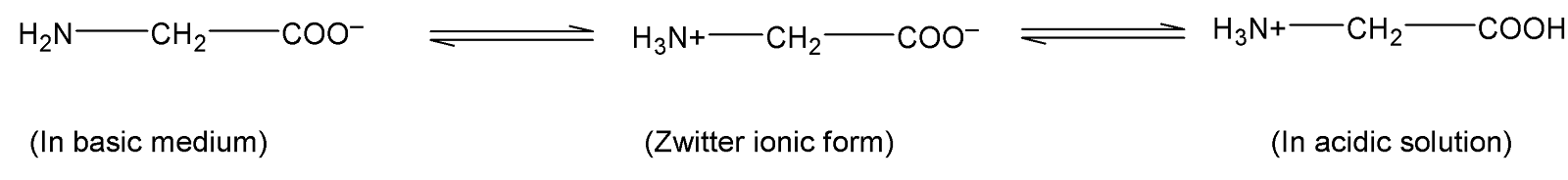
But Glycine is an optically active compound as it does not contain any chiral carbon. Optically active compounds are those which consist of four different substitutions.

Therefore glycine may be classed as all of the following except optically active acid.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: It is found that there is $20$an amino acid that is essential for all living things. They are building blocks of protein molecules. Essential amino acids cannot be synthesized by the human body system but can be taken from outside through our diets. Some of them are valine, leucine, lysine, histidine, methionine, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




