
Find the vertex connectivity of any tree.
A. One
B. Two
C. Three
D. None of the above
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First recall the definition of vertex connectivity of a tree and the definition of a tree, then answer the given question.
Complete step by step solution:
The vertex connectivity of a graph G is the minimum number of vertices whose removal disconnects G.
Now, a tree is an undirected connected graph in which two vertices are connected by exactly one path.
For example let us draw a tree,
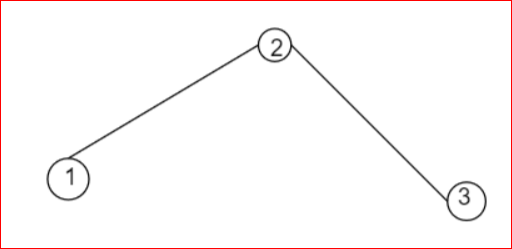
Image: Tree
Now, from the image we can see that if we remove the edge of vertex 1 and 2 then the graph becomes disconnected also if we remove the edge of vertex 2 and 3 this also makes the graph disconnected.
Therefore, the removal of one vertex makes the graph disconnected.
Hence, the vertex connectivity of a tree is always one.
The correct option is A.
Note: Sometimes students draw a tree and shows that when they remove one vertex the graph got disconnected. This is also a good approach to answer this question.
For example,
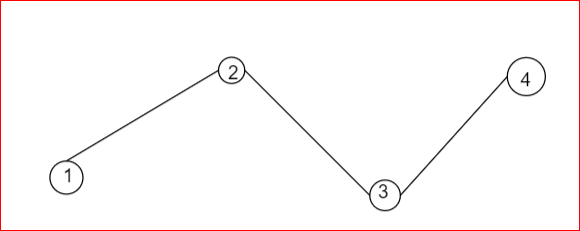
Image: Tree
This diagram is of a tree.
But, if we remove any one edge, suppose we are removing the edge of the vertices 1, 2. Then the graph becomes
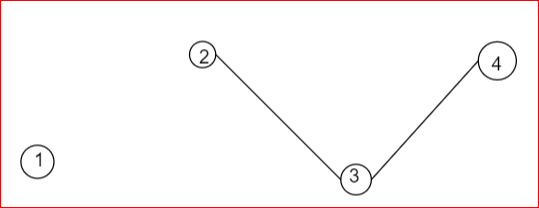
Image: Tree
This is not a connected graph, therefore this is not a tree.
Hence, the vertex connectivity of a tree is 1.
Complete step by step solution:
The vertex connectivity of a graph G is the minimum number of vertices whose removal disconnects G.
Now, a tree is an undirected connected graph in which two vertices are connected by exactly one path.
For example let us draw a tree,

Image: Tree
Now, from the image we can see that if we remove the edge of vertex 1 and 2 then the graph becomes disconnected also if we remove the edge of vertex 2 and 3 this also makes the graph disconnected.
Therefore, the removal of one vertex makes the graph disconnected.
Hence, the vertex connectivity of a tree is always one.
The correct option is A.
Note: Sometimes students draw a tree and shows that when they remove one vertex the graph got disconnected. This is also a good approach to answer this question.
For example,

Image: Tree
This diagram is of a tree.
But, if we remove any one edge, suppose we are removing the edge of the vertices 1, 2. Then the graph becomes

Image: Tree
This is not a connected graph, therefore this is not a tree.
Hence, the vertex connectivity of a tree is 1.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




