
Find the locus of the point which moves so that its distance from x-axis is double of its distance from y-axis.
A. $x = 2y$
B. $y = 2x$
C. $y = 2x + 3$
D. $x = 5y + 1$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Draw a diagram of the stated problem and mark the given information, Then obtain the required relation with the help of the obtained diagram.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,
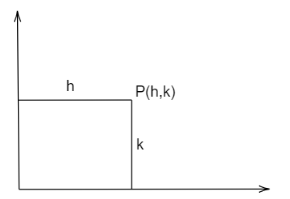
Image: Point P(h,k)
From the diagram we can see that the distance from the x-axis is k and y-axis is h.
It is given that, distance from the x-axis is double of its distance from the y-axis.
Hence,
$k = 2h$ .
Therefore, the required locus is $y = 2x$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Additional information:
Locus of a point is a set of points that satisfy an equation of curve. The curve may be a circle or hyperbola or ellipse or a line etc.
In the given question, we get a linear equation.
If the equation of a locus of a point is linear, then the locus of the point represents a line.
Note: The distance of a point from the x-axis is the ordinate of the point. The distance of a point from the y-axis is the abscissa of the point. Using the concept, we will find the distance of the point from the x-axis and the y-axis. Then equate the ordinate of the point with 2 times the abscissa of the point. At the end of the solution, replace h with x and k with y.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,

Image: Point P(h,k)
From the diagram we can see that the distance from the x-axis is k and y-axis is h.
It is given that, distance from the x-axis is double of its distance from the y-axis.
Hence,
$k = 2h$ .
Therefore, the required locus is $y = 2x$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Additional information:
Locus of a point is a set of points that satisfy an equation of curve. The curve may be a circle or hyperbola or ellipse or a line etc.
In the given question, we get a linear equation.
If the equation of a locus of a point is linear, then the locus of the point represents a line.
Note: The distance of a point from the x-axis is the ordinate of the point. The distance of a point from the y-axis is the abscissa of the point. Using the concept, we will find the distance of the point from the x-axis and the y-axis. Then equate the ordinate of the point with 2 times the abscissa of the point. At the end of the solution, replace h with x and k with y.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




