
Find the equation of the circle touching both axes and passing through ( 1,2).
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: in this Question, we have to find the equation of the circle touching both axes and passing through ( 1,2 ). To solve this question, first we make a circle which touches both the axes and its center be (r,r) then we use the equation of the circle to solve this question. We find out the value of r by putting (1,2) in the equation of circle and using the values of r, we find out the other two equations which passess through (1,2).
Complete Step by step solution:
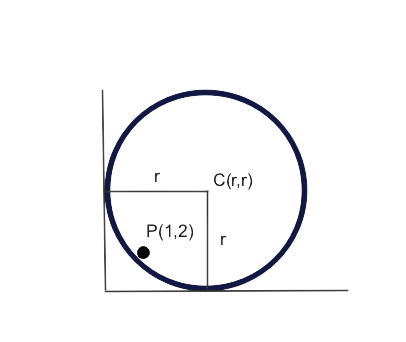
We have to find the equation of circle touching both axes and passing through (1,2)
As shown in the diagram, let CP = r
Then $C{{P}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then ${{(r-1)}^{2}}+{{(r-2)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
By expanding the equation, we get
${{r}^{2}}-2r+1+{{r}^{2}}-4r+4={{r}^{2}}$
We get ${{r}^{2}}-6r+5=0$
Then ( r – 1 ) ( r – 5 ) = 0
Then we get r = 1 ; r = 5
Now we find the equation when r = 1 ; C (1,1)
Then we know equation of circle is ${{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then we get ${{(x-1)}^{2}}+{{(y-1)}^{2}}=1$
We get ${{x}^{2}}-2x+1+{{y}^{2}}-2y+1=1$
That is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x-2y+1=0$
Now we find the equation when r = 5; C ( 5,5 )
We know equation of circle ${{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then we get ${{(x-5)}^{2}}+{{(y-5)}^{2}}=25$
We get ${{x}^{2}}-10x+25+{{y}^{2}}-10y+25=25$
That is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x-10y+25=0$
Hence, the equation of circle touching both axes and passing through ( 1,2 ) is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x-2y+1=0$ and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x-10y+25=0$
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Note: In these types of questions, Students made mistakes in finding out the equations. To clarify the whole question, it is important to make a diagram so that there will be no confusion in the question.
Complete Step by step solution:

We have to find the equation of circle touching both axes and passing through (1,2)
As shown in the diagram, let CP = r
Then $C{{P}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then ${{(r-1)}^{2}}+{{(r-2)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
By expanding the equation, we get
${{r}^{2}}-2r+1+{{r}^{2}}-4r+4={{r}^{2}}$
We get ${{r}^{2}}-6r+5=0$
Then ( r – 1 ) ( r – 5 ) = 0
Then we get r = 1 ; r = 5
Now we find the equation when r = 1 ; C (1,1)
Then we know equation of circle is ${{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then we get ${{(x-1)}^{2}}+{{(y-1)}^{2}}=1$
We get ${{x}^{2}}-2x+1+{{y}^{2}}-2y+1=1$
That is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x-2y+1=0$
Now we find the equation when r = 5; C ( 5,5 )
We know equation of circle ${{(x-h)}^{2}}+{{(y-k)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$
Then we get ${{(x-5)}^{2}}+{{(y-5)}^{2}}=25$
We get ${{x}^{2}}-10x+25+{{y}^{2}}-10y+25=25$
That is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x-10y+25=0$
Hence, the equation of circle touching both axes and passing through ( 1,2 ) is ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x-2y+1=0$ and ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-10x-10y+25=0$
Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Note: In these types of questions, Students made mistakes in finding out the equations. To clarify the whole question, it is important to make a diagram so that there will be no confusion in the question.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




