
Find the equation of the circle in the first quadrant which touches each axis at a distance $5$ from the origin.
A. ${x^2} + {y^2} + 5x + 5y + 25 = 0$
B. ${x^2} + {y^2} - 10x - 10y + 25 = 0$
C. ${x^2} + {y^2} - 5x - 5y + 25 = 0$
D. ${x^2} + {y^2} + 10x + 10y + 25 = 0$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: From the given data we will be drawing a figure which will help us to know the radius and the coordinates of the center from which we can substitute the values in the standard form of a circle.
Formula Used:
We will be using standard form of circle which is ${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$and we will be also using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$ to expand the bracket.
Complete step by step solution:
We will be drawing the figure to understand the terms written in the question,
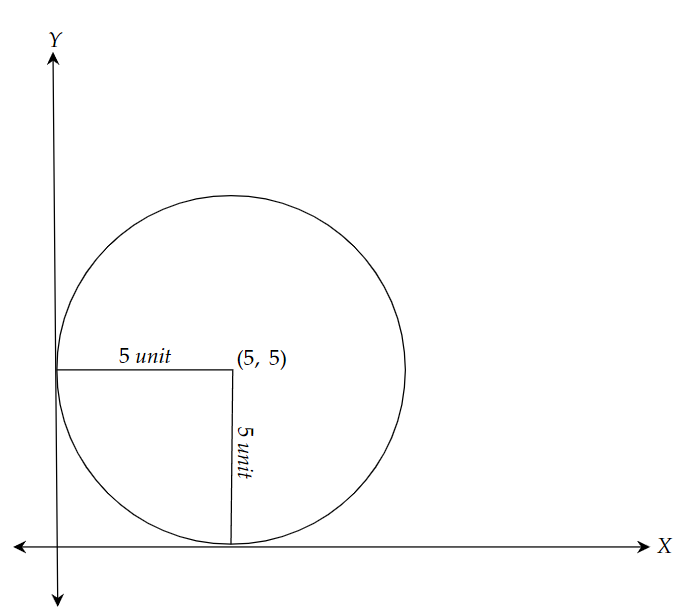
Image: Circle at a distance of 5 units.
According to the figure we can say that the centre of the circle is $\left( {h,k} \right)$ which is equal to,
$\left( {5,5} \right)$ and the radius is equal to $r = 5$
By using the standard form of circle we can substitute the values in it,
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = {5^2}$
Using the formula of ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$
We will open the bracket in the equation.
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = {5^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 25 + {y^2} - 10y + 25 = 25$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 10x - 10y + 25 = 0$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: While drawing the figure student should be very much aware about the distance and the coordinates which will be taken in respect to expand the general form of the circle.
Formula Used:
We will be using standard form of circle which is ${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$and we will be also using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$ to expand the bracket.
Complete step by step solution:
We will be drawing the figure to understand the terms written in the question,

Image: Circle at a distance of 5 units.
According to the figure we can say that the centre of the circle is $\left( {h,k} \right)$ which is equal to,
$\left( {5,5} \right)$ and the radius is equal to $r = 5$
By using the standard form of circle we can substitute the values in it,
${\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = {5^2}$
Using the formula of ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$
We will open the bracket in the equation.
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = {5^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 10x + 25 + {y^2} - 10y + 25 = 25$
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 10x - 10y + 25 = 0$
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note: While drawing the figure student should be very much aware about the distance and the coordinates which will be taken in respect to expand the general form of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
States of Matter Chapter For JEE Main Chemistry

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

[Awaiting the three content sources: Ask AI Response, Competitor 1 Content, and Competitor 2 Content. Please provide those to continue with the analysis and optimization.]

Sign up for JEE Main 2026 Live Classes - Vedantu

JEE Main 2026 Helpline Numbers - Center Contact, Phone Number, Address

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Admit Card Out, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




