
Find the equation of circle of radius 5 and touching the coordinate axes in third quadrant.
A. \[{\left( {x + 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y + 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
B. \[{\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
C. \[{\left( {x - 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y + 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
D. \[{\left( {x + 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Draw a circle with the given conditions. Then write the general equation of a circle. Then substitute the required values of the centre and the radius obtained from the diagram and calculate to obtain the required result.
Formula used:
The general equation of a circle is,
\[{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
Where, \[(h,k)\] is the centre and r is the radius.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,
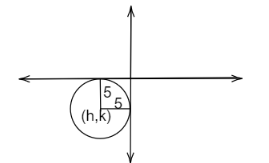
Image: Circle
From the diagram it is clear that the distance of the centre from the x-axis is 5 unit downward and the distance from the y-axis is 5 unit in the left direction.
Hence, the coordinate of the centre is \[( - 5, - 5)\] .
Therefore, the required equation is,
\[{\left( {x - ( - 5)} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - ( - 5)} \right)^2} = {5^2}\]
\[\therefore \]\[{\left( {x + 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y + 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
The correct option is A.
Additional information:
In the first quadrant, ordinate and abscissa are positive integers. In the second quadrant, the abscissa of a coordinate is negative and the ordinate of a coordinate is positive. In the third quadrant, ordinate and abscissa of a coordinate both are negative. In the fourth quadrant, the abscissa of a coordinate is positive and the ordinate of a coordinate is negative.
Note: First draw the diagram for this type of question and then analyze it to compute the required results. From the diagram, it is very much clear that we shifted 5 units left and 5 units downward therefore the required centre is \[( - 5, - 5)\].
Formula used:
The general equation of a circle is,
\[{\left( {x - h} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - k} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
Where, \[(h,k)\] is the centre and r is the radius.
Complete step by step solution:
The diagram of the given problem is,

Image: Circle
From the diagram it is clear that the distance of the centre from the x-axis is 5 unit downward and the distance from the y-axis is 5 unit in the left direction.
Hence, the coordinate of the centre is \[( - 5, - 5)\] .
Therefore, the required equation is,
\[{\left( {x - ( - 5)} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - ( - 5)} \right)^2} = {5^2}\]
\[\therefore \]\[{\left( {x + 5} \right)^2} + {\left( {y + 5} \right)^2} = 25\]
The correct option is A.
Additional information:
In the first quadrant, ordinate and abscissa are positive integers. In the second quadrant, the abscissa of a coordinate is negative and the ordinate of a coordinate is positive. In the third quadrant, ordinate and abscissa of a coordinate both are negative. In the fourth quadrant, the abscissa of a coordinate is positive and the ordinate of a coordinate is negative.
Note: First draw the diagram for this type of question and then analyze it to compute the required results. From the diagram, it is very much clear that we shifted 5 units left and 5 units downward therefore the required centre is \[( - 5, - 5)\].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




