
Find the correct option
The maximum value of \[z = 10x + 6y\] subject to constraints \[x \ge 0\], \[y \ge 0\], \[3x + y \le 12\] and \[2x + 5y \le 34\] is
A.\[72\]
B.\[80\]
C.\[104\]
D.\[56\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First, the graph of the feasible region solved by the given four inequalities represented as constraints is drawn and then the value of \[z\] is calculated at different boundaries of the region from which, the maximum value is found.
Complete step-by-step solution:We have been given the equation of the circle as \[z = 10x + 6y\] subject to constraints \[x \ge 0\], \[y \ge 0\], \[3x + y \le 12\] and \[2x + 5y \le 34\].
Let, \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\]are two lines represented by the two equations \[3x + y = 12\]and \[2x + 5y = 34\]respectively.
Now, we will solve the above two equations.
Multiplying \[5\]with the equation \[3x + y = 12\]
\[15x + 5y = 60\]
Subtracting \[2x + 5y = 34\]from the equation \[15x + 5y = 60\], we have
\[15x + 5y - (2x + 5y) = 60 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow 15x + 5y - 2x - 5y = 26\]
\[ \Rightarrow 13x = 26\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Putting the value of \[x\] in the equation \[3x + y = 12\], we have
\[(3 \times 2) + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6 + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 6\]
So, the two lines \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\] intersect at the point \[B(2,6)\] and \[OABCO\]is the required feasible region as shown in the figure.
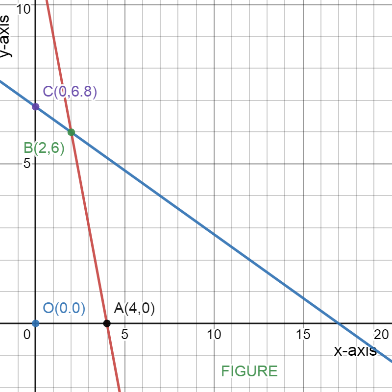
Image: Two lines intersecting
As shown in the figure, the point \[A\]of the region is the point, where, the line \[{L_1}:3x + y = 12\] intersects the X-axis.
Finding the co-ordinates of the point \[A\]
\[3x + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 12\] (Since \[y = 0\] on X-axis)
\[ \Rightarrow x = 4\]
So, the co-ordinates of the point \[A\] is \[(4,0)\].
The co-ordinates of the point \[B\] is \[(2,6)\], which is the intersection point of lines \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\].
As shown in the figure, the point \[C\]of the region is the point, where, the line \[{L_2}:2x + 5y = 34\] intersects the Y-axis.
Finding the co-ordinates of the point \[C\]
\[2x + 5y = 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow 5y = 34\] (Since \[x = 0\]on Y-axis)
\[ \Rightarrow y = 6.8\]
So, the co-ordinates of the point \[C\] is \[(0,6.8)\].
The co-ordinates of the origin \[O\] is \[(0,0)\].
Now, we will calculate the value of \[z = 10x + 6y\]at the four points \[O,A,B\]and \[C\] of the region \[OABCO\]
At \[O(0,0)\], \[z = (10 \times 0) + (6 \times 0) = 0\]
At \[A(4,0)\], \[z = (10 \times 4) + (6 \times 0) = 40\]
At \[B(2,6)\], \[z = (10 \times 2) + (6 \times 6) = 56\]
At \[C(0,6.8)\], \[z = (10 \times 0) + (6 \times 6.8) = 40.8\]
So, the maximum value of \[z = 10x + 6y\]is \[56\]at the point \[B\].
Hence, the option D. \[56\] is the correct answer
Note: The solution set of a system of linear inequation in two variables is the set of all points \[(x,y)\], which satisfies all the inequations in the system simultaneously. So, the region of the plane common to all the portions comprising the solution sets of the given inequalities should be found. When, there is no region common to all the solutions of the given inequations, the solution set of the system is empty.
Complete step-by-step solution:We have been given the equation of the circle as \[z = 10x + 6y\] subject to constraints \[x \ge 0\], \[y \ge 0\], \[3x + y \le 12\] and \[2x + 5y \le 34\].
Let, \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\]are two lines represented by the two equations \[3x + y = 12\]and \[2x + 5y = 34\]respectively.
Now, we will solve the above two equations.
Multiplying \[5\]with the equation \[3x + y = 12\]
\[15x + 5y = 60\]
Subtracting \[2x + 5y = 34\]from the equation \[15x + 5y = 60\], we have
\[15x + 5y - (2x + 5y) = 60 - 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow 15x + 5y - 2x - 5y = 26\]
\[ \Rightarrow 13x = 26\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Putting the value of \[x\] in the equation \[3x + y = 12\], we have
\[(3 \times 2) + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 6 + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 6\]
So, the two lines \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\] intersect at the point \[B(2,6)\] and \[OABCO\]is the required feasible region as shown in the figure.

Image: Two lines intersecting
As shown in the figure, the point \[A\]of the region is the point, where, the line \[{L_1}:3x + y = 12\] intersects the X-axis.
Finding the co-ordinates of the point \[A\]
\[3x + y = 12\]
\[ \Rightarrow 3x = 12\] (Since \[y = 0\] on X-axis)
\[ \Rightarrow x = 4\]
So, the co-ordinates of the point \[A\] is \[(4,0)\].
The co-ordinates of the point \[B\] is \[(2,6)\], which is the intersection point of lines \[{L_1}\]and \[{L_2}\].
As shown in the figure, the point \[C\]of the region is the point, where, the line \[{L_2}:2x + 5y = 34\] intersects the Y-axis.
Finding the co-ordinates of the point \[C\]
\[2x + 5y = 34\]
\[ \Rightarrow 5y = 34\] (Since \[x = 0\]on Y-axis)
\[ \Rightarrow y = 6.8\]
So, the co-ordinates of the point \[C\] is \[(0,6.8)\].
The co-ordinates of the origin \[O\] is \[(0,0)\].
Now, we will calculate the value of \[z = 10x + 6y\]at the four points \[O,A,B\]and \[C\] of the region \[OABCO\]
At \[O(0,0)\], \[z = (10 \times 0) + (6 \times 0) = 0\]
At \[A(4,0)\], \[z = (10 \times 4) + (6 \times 0) = 40\]
At \[B(2,6)\], \[z = (10 \times 2) + (6 \times 6) = 56\]
At \[C(0,6.8)\], \[z = (10 \times 0) + (6 \times 6.8) = 40.8\]
So, the maximum value of \[z = 10x + 6y\]is \[56\]at the point \[B\].
Hence, the option D. \[56\] is the correct answer
Note: The solution set of a system of linear inequation in two variables is the set of all points \[(x,y)\], which satisfies all the inequations in the system simultaneously. So, the region of the plane common to all the portions comprising the solution sets of the given inequalities should be found. When, there is no region common to all the solutions of the given inequations, the solution set of the system is empty.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




