
Find \[A:B\] if A is the area bounded by the curve \[y = \sqrt {3x + 4} \], \[x - axis\] and the lines \[x = - 1\] and \[x = 4\] and B is the area bounded by curve \[{y^2} = 3x + 4\], \[x - axis\], and the lines \[x = - 1\]and \[x = 4\].
A. \[1:1\]
B. \[2:1\]
C. \[1:2\]
D. None of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: For A, we solve it by using substitution and then integrate using substitution. Also, curve B is nothing but the square of curve A, therefore, the answer will come out to be same.
Complete step by step solution
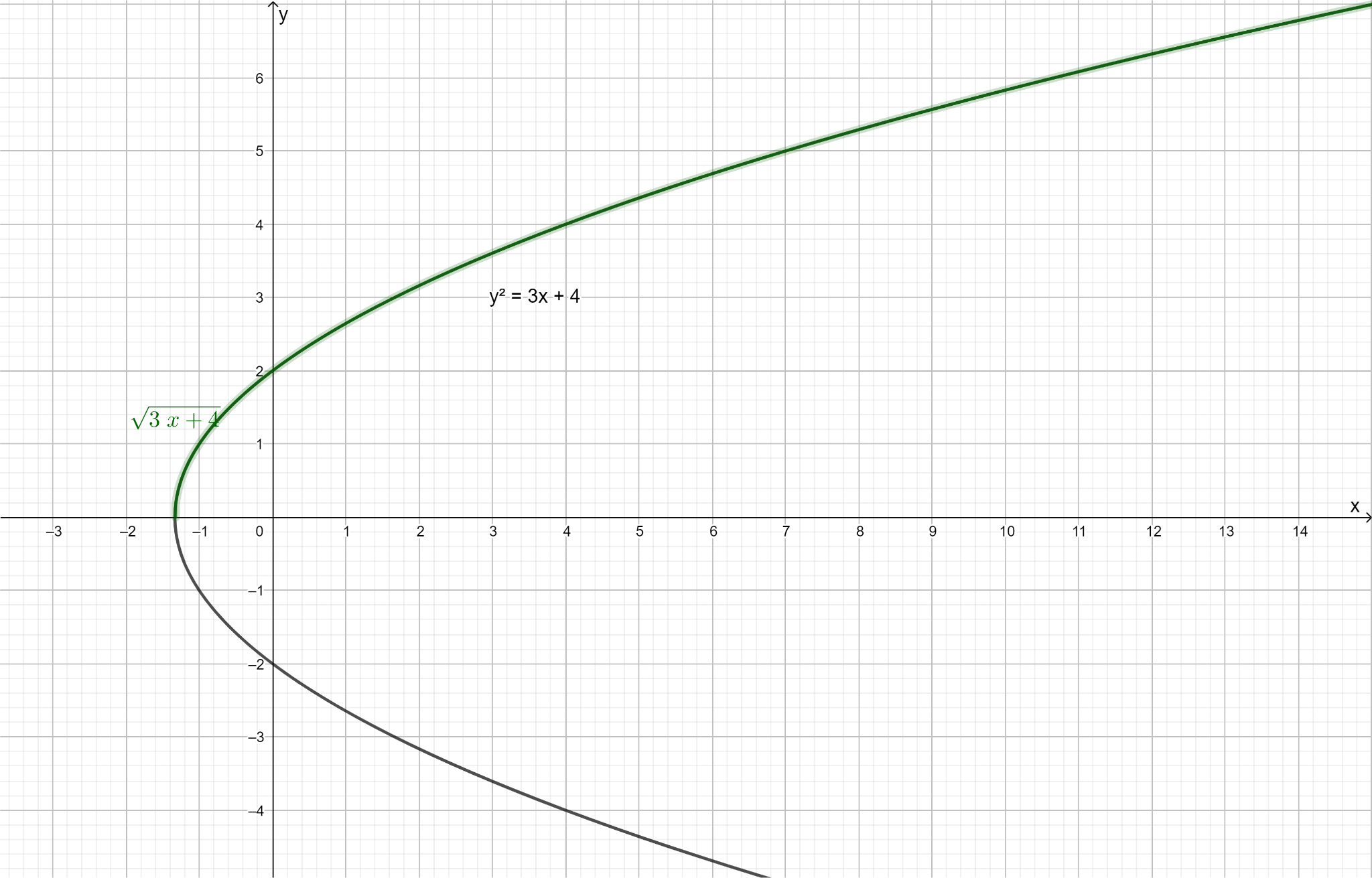
Image: Shown the path of \[y = \sqrt {3x + 4} \] and \[{y^2} = 3x + 4\] in graph paper
We have, first curve as:
\[y = \sqrt {3x + 4} \]
Now, A, area bounded by the curve will be:
\[A = \int\limits_{ - 1}^4 \sqrt {3x + 4} dx\] ……………..(1)
Put \[3x + 4 = {t^2}\] ………..(2)
Then, differentiating both sides of the above equation and we get
\[3dx = 2tdt\]
\[ \Rightarrow dx = \dfrac{2}{3}tdt\] ……..(3)
Substitute (2) and (3) in equation (1), we get
\[A = \int\limits_{ - 1}^4 t \dfrac{2}{3}\, \times tdt\]
Integrating and we get
\[A = \left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_{ - 1}^4\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{2}{9}} \right)\left[ {64 + 1} \right]\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{2}{9}} \right) \times 65\]
\[ = \dfrac{130}{9}uni{t^2}\]
Similarly, We get B as $\dfrac{130}{9}$,
Therefore,
\[A:B\]=\[\dfrac{130}{9}:\dfrac{130}{9}\]= \[1:1\]
The correct answer is option A.
Note:By performing a definite integral between the two locations, one can determine the area under a curve between two points. Integrate \[y = f\left( x \right)\]between the limits of \[a\] and \[b\]to determine the area under the curve \[y = f\left( x \right)\]between \[x = a\] & \[x = b\]. With the aid of integration and the specified constraints, this area can be easily identified.
Complete step by step solution

Image: Shown the path of \[y = \sqrt {3x + 4} \] and \[{y^2} = 3x + 4\] in graph paper
We have, first curve as:
\[y = \sqrt {3x + 4} \]
Now, A, area bounded by the curve will be:
\[A = \int\limits_{ - 1}^4 \sqrt {3x + 4} dx\] ……………..(1)
Put \[3x + 4 = {t^2}\] ………..(2)
Then, differentiating both sides of the above equation and we get
\[3dx = 2tdt\]
\[ \Rightarrow dx = \dfrac{2}{3}tdt\] ……..(3)
Substitute (2) and (3) in equation (1), we get
\[A = \int\limits_{ - 1}^4 t \dfrac{2}{3}\, \times tdt\]
Integrating and we get
\[A = \left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right)\left[ {\dfrac{{{t^3}}}{3}} \right]_{ - 1}^4\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{2}{9}} \right)\left[ {64 + 1} \right]\]
\[ = \left( {\dfrac{2}{9}} \right) \times 65\]
\[ = \dfrac{130}{9}uni{t^2}\]
Similarly, We get B as $\dfrac{130}{9}$,
Therefore,
\[A:B\]=\[\dfrac{130}{9}:\dfrac{130}{9}\]= \[1:1\]
The correct answer is option A.
Note:By performing a definite integral between the two locations, one can determine the area under a curve between two points. Integrate \[y = f\left( x \right)\]between the limits of \[a\] and \[b\]to determine the area under the curve \[y = f\left( x \right)\]between \[x = a\] & \[x = b\]. With the aid of integration and the specified constraints, this area can be easily identified.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole




