
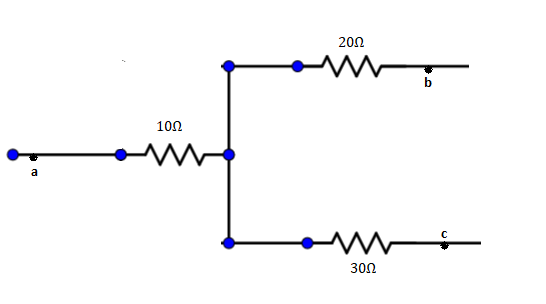
Figure shown a part of an electric circuit, The potentials at the points a, b, and c are \[30V,12V\], and \[2V\] respectively. Find the currents through the three resistors.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: When resistors are connected adjacently in a serial manner, then the circuit will be known as resistor in serial connection. In a serial circuit the same current flows through the resistors. As the resistors connect serially then the common current passes through each resistor and total resistance will be RT.
${R_T} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$ ….
When resistors are connected in a parallel manner, then the circuit is called as resistors in parallel connection. In this parallel circuit current takes multiple paths to flow in the circuit. The reciprocal resistance of all resistance added together to give reciprocal values of equivalent total resistance.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ......$
Formula used:
${i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the potential will be \[Xv\]
From the figure, \[{i_a} = \dfrac{{{V_a} - {V_0}}}{{10}}\]
By putting ${V_a} = 30V,{V_0} = X$
So, ${i_a} = \dfrac{{30 - X}}{{10}}$
Similarly,
${i_b} = \dfrac{{{V_0} - {V_b}}}{{{{20}_{}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{X - 12}}{{20}}$
Also,
${i_3} = \dfrac{{{V_0} - {V_C}}}{{30}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{X - 2}}{{30}}$
From Kirchhoff’s junction law,
${i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3}$
$\dfrac{{30 - X}}{{10}} = \dfrac{{X - 12}}{{20}} + \dfrac{{X - 2}}{{30}}$
By dividing the denominators by 10
$30 - X = \dfrac{{X - 12}}{2} + \dfrac{{X - 2}}{3}$
By taking LCM
$30 - X = \dfrac{{3X - 36 + 2X - 4}}{6}$
Bringing $6$ to LHS and multiply
$180 - 6X = 5X - 40$
Bringing X values one side and constant values other side.
\[X = \dfrac{{220}}{{11}} = 20V\]
\[{i_1} = \dfrac{{30 - 20}}{{10}} = 1A\]
\[{i_2} = \dfrac{{20 - 12}}{{20}} = 0.4A\]
\[{i_3} = \dfrac{{20 - 2}}{{30}} = 0.6A\]
The current through the three resistors are $1A,0.4A,0.6A.$
Note: The resistors are used to reduce current flows in the circuit.
Characteristic of resistors are,
1. Low temperature coefficient of resistance
2. Power rating
3. Electrical resistivity of the material
4. Insulation of the wires

${R_T} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3}$ ….
When resistors are connected in a parallel manner, then the circuit is called as resistors in parallel connection. In this parallel circuit current takes multiple paths to flow in the circuit. The reciprocal resistance of all resistance added together to give reciprocal values of equivalent total resistance.
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_n}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ......$
Formula used:
${i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3}$
Complete step by step answer:
Let the potential will be \[Xv\]
From the figure, \[{i_a} = \dfrac{{{V_a} - {V_0}}}{{10}}\]
By putting ${V_a} = 30V,{V_0} = X$
So, ${i_a} = \dfrac{{30 - X}}{{10}}$
Similarly,
${i_b} = \dfrac{{{V_0} - {V_b}}}{{{{20}_{}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{X - 12}}{{20}}$
Also,
${i_3} = \dfrac{{{V_0} - {V_C}}}{{30}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{X - 2}}{{30}}$
From Kirchhoff’s junction law,
${i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3}$
$\dfrac{{30 - X}}{{10}} = \dfrac{{X - 12}}{{20}} + \dfrac{{X - 2}}{{30}}$
By dividing the denominators by 10
$30 - X = \dfrac{{X - 12}}{2} + \dfrac{{X - 2}}{3}$
By taking LCM
$30 - X = \dfrac{{3X - 36 + 2X - 4}}{6}$
Bringing $6$ to LHS and multiply
$180 - 6X = 5X - 40$
Bringing X values one side and constant values other side.
\[X = \dfrac{{220}}{{11}} = 20V\]
\[{i_1} = \dfrac{{30 - 20}}{{10}} = 1A\]
\[{i_2} = \dfrac{{20 - 12}}{{20}} = 0.4A\]
\[{i_3} = \dfrac{{20 - 2}}{{30}} = 0.6A\]
The current through the three resistors are $1A,0.4A,0.6A.$
Note: The resistors are used to reduce current flows in the circuit.
Characteristic of resistors are,
1. Low temperature coefficient of resistance
2. Power rating
3. Electrical resistivity of the material
4. Insulation of the wires

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




