
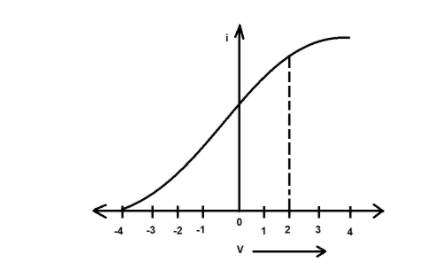
Figure represents the graph of photocurrent $I$ versus applied voltage ($V$). The maximum energy of the emitted photoelectron is-
(A) $2eV$
(B) $4eV$
(C) $0eV$
(D) $3eV$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We are given with the graph of the photocurrent versus the applied voltage and are asked to find out the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron. We will first find out the breakdown voltage of the given situation from the graph. Then we will calculate the kinetic energy with a suitable formula.
Formulae Used:
$K.E{._{Max}} = e{V_o}$
Where, $e$ is the charge on an electron and ${V_o}$ is the breakdown voltage.
Complete step by step solution:
From the graph, it is evident that the photocurrent starts rising from zero when the applied voltage is$ - 4V$.
Thus, by definition, ${V_o} = 4V$.
Now,
We can say,
Maximum Kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron is
$K.E{._{Max}} = e{V_o} = 4eV$
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Additional Information The process we discussed in this question is we can say a special type of photoelectric effect. Fundamentally it works on the principle of photoelectric effect but the catch is that the incident radiation is assisted by an external potential difference.
When a beam of light of certain wavelength is incident on a metal surface, the electrons in the valence shell of the outermost atoms of the surface attain the energy and are emitted out by the surface. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depends on the threshold frequency of the metal which is different for different metals. Now, when the external voltage is applied on the surface, the emitted electrons get some extra energy for its flow. The incidence of the light beam and the applied voltage goes simultaneously.
Note: The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron depends on the breakdown voltage of the system as it is evident from the formula of kinetic energy. If the breakdown voltage of the system changes, then the kinetic energy of the electrons also changes by a certain amount.
Formulae Used:
$K.E{._{Max}} = e{V_o}$
Where, $e$ is the charge on an electron and ${V_o}$ is the breakdown voltage.
Complete step by step solution:
From the graph, it is evident that the photocurrent starts rising from zero when the applied voltage is$ - 4V$.
Thus, by definition, ${V_o} = 4V$.
Now,
We can say,
Maximum Kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectron is
$K.E{._{Max}} = e{V_o} = 4eV$
Hence, the correct answer is (B).
Additional Information The process we discussed in this question is we can say a special type of photoelectric effect. Fundamentally it works on the principle of photoelectric effect but the catch is that the incident radiation is assisted by an external potential difference.
When a beam of light of certain wavelength is incident on a metal surface, the electrons in the valence shell of the outermost atoms of the surface attain the energy and are emitted out by the surface. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depends on the threshold frequency of the metal which is different for different metals. Now, when the external voltage is applied on the surface, the emitted electrons get some extra energy for its flow. The incidence of the light beam and the applied voltage goes simultaneously.
Note: The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electron depends on the breakdown voltage of the system as it is evident from the formula of kinetic energy. If the breakdown voltage of the system changes, then the kinetic energy of the electrons also changes by a certain amount.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




