
Ethylidene dichloride is obtained by the reaction of an excess of HCl with.
(A) Ethylene
(B) Acetylene
(C) Propane
(D) Methane
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: The structure of the Ethylidene dichloride is as follows.
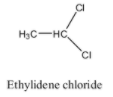
Ethylidene dichloride is also called Gem dihalides. Gem halogens mean the halogen atoms (chlorine) present on the same carbon atom in the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
-Ethylidene chloride is also called 1,1-dichloroethane.
-We have to prepare Ethylidene dichloride by using an excess amount of HCl.
-Coming to the given options, option A, Ethylene. Alkenes generally form only monochloro derivatives with hydrochloric acid.
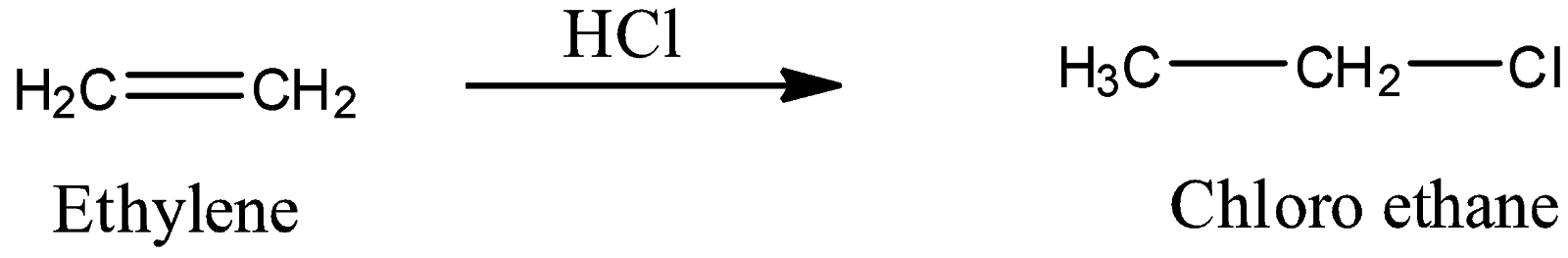
-So, option A is wrong.
-Coming to option B, Acetylene. Acetylene reacts with an excess amount of HCl and forms Ethylidene dichloride as the product. The reaction is as follows.
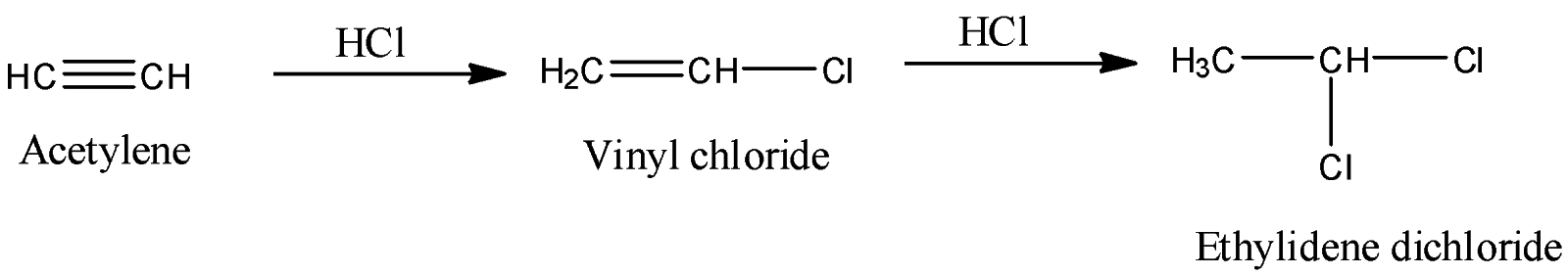
-It is a best example for electrophilic addition reaction.
-Coming to option C, Propane. Propane does not form Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl. So, option C is wrong.
-Coming to option D, Methane. Methane does not form Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl. So, option D is wrong.
-Therefore acetylene forms Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl.
So, the correct option is (B).
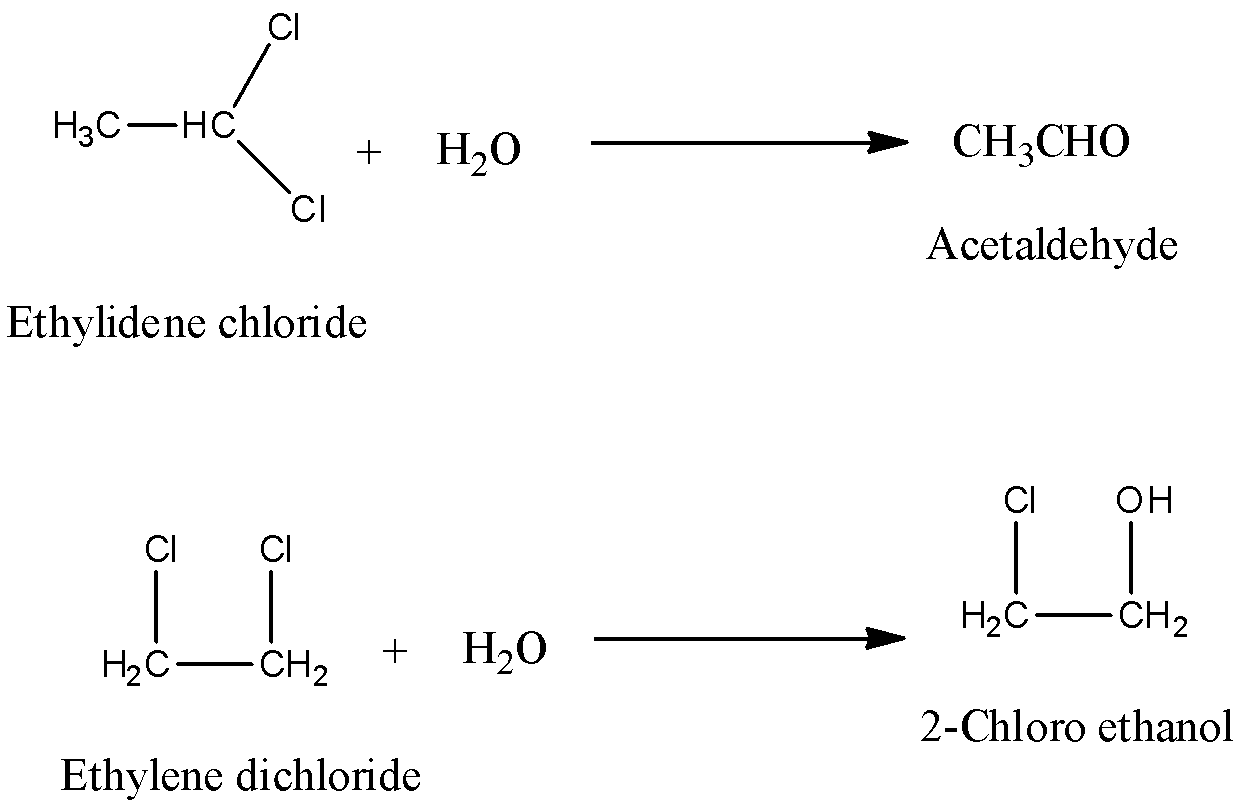
Note: Don’t be confused with Ethylidene chloride and ethylene dichloride. Both are not the same.
Ethylidene chloride and ethylene dichloride can be differentiated by reacting with water.
Ethylidene chloride forms acetaldehyde on reaction with water and ethylene dichloride forms 2-chloro ethanol on reaction with water.

Ethylidene dichloride is also called Gem dihalides. Gem halogens mean the halogen atoms (chlorine) present on the same carbon atom in the molecule.
Complete step by step solution:
-Ethylidene chloride is also called 1,1-dichloroethane.
-We have to prepare Ethylidene dichloride by using an excess amount of HCl.
-Coming to the given options, option A, Ethylene. Alkenes generally form only monochloro derivatives with hydrochloric acid.

-So, option A is wrong.
-Coming to option B, Acetylene. Acetylene reacts with an excess amount of HCl and forms Ethylidene dichloride as the product. The reaction is as follows.
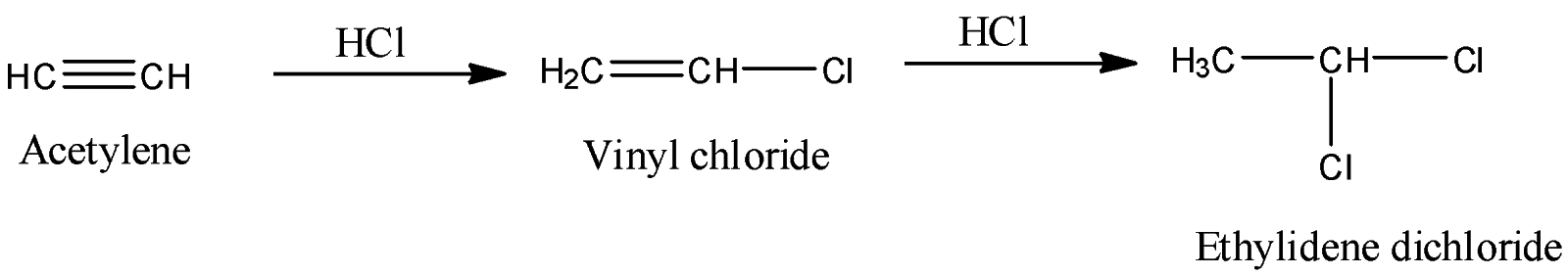
-It is a best example for electrophilic addition reaction.
-Coming to option C, Propane. Propane does not form Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl. So, option C is wrong.
-Coming to option D, Methane. Methane does not form Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl. So, option D is wrong.
-Therefore acetylene forms Ethylidene dichloride with an excess amount of HCl.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note: Don’t be confused with Ethylidene chloride and ethylene dichloride. Both are not the same.
Ethylidene chloride and ethylene dichloride can be differentiated by reacting with water.
Ethylidene chloride forms acetaldehyde on reaction with water and ethylene dichloride forms 2-chloro ethanol on reaction with water.

Recently Updated Pages
WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




