
Ethylene may be obtained by dehydration of which of the following is concentrated \[{H_2}S{O_4}\] at \[160 - 170^\circ C\]?
(a) \[{C_2}{H_5}OH\]
(b) \[C{H_3}OH\]
(c) \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]
(d) \[{(C{H_3})_2}CHC{H_2}OH\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Dehydration reactions are the reaction that involves the removal of water (\[{H_2}O\]) molecules upon heating the molecular compounds. The best example of dehydration reaction is the elimination reaction where the formation of a more stable alkene occurs by the abstraction of a beta-proton via base.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
As we know the dehydration reaction involves the removal of water \[{H_2}O\] molecules.
In a dehydration reaction, a water molecule is generated by the removal of a beta-hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group (\[ - OH\]).
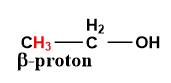
Image: Ethanol
The dehydration of alcohol can be done by the following two methods.
1. By allowing the vapours of alcohols over heated alumina (\[A{l_2}{O_3}\]).
2. By heating alcohols with conc. Sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) and phosphoric acid (\[{H_3}P{O_4}\]).
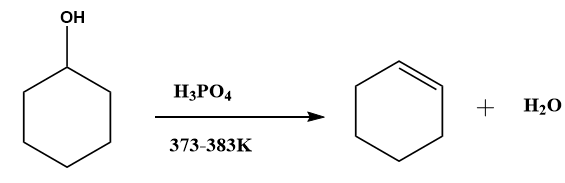
Image: Dehydration of alcohol
Sometimes anhydrous zinc chloride (\[ZnC{l_2}\]) is also used for the dehydration of alcohols.
The dehydration trends of alcohols can be represented as tertiary alcohols > secondary alcohols> primary alcohols.
The tertiary alcohols and secondary alcohols can also be dehydrated by diluting sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]).
In the question, option (b), (c), and (d) will be the incorrect option because the dehydration of \[C{H_3}OH\] , \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]and \[{(C{H_3})_2}CHC{H_2}OH\]do not produce ethylene. For the formation of ethylene, the alcohol must have two carbon atoms.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: During the dehydration of alcohols in the presence of acids the number of carbon atoms remains the same. Sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) is a colourless and corrosive liquid. It is highly miscible with water.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
As we know the dehydration reaction involves the removal of water \[{H_2}O\] molecules.
In a dehydration reaction, a water molecule is generated by the removal of a beta-hydrogen atom and hydroxyl group (\[ - OH\]).

Image: Ethanol
The dehydration of alcohol can be done by the following two methods.
1. By allowing the vapours of alcohols over heated alumina (\[A{l_2}{O_3}\]).
2. By heating alcohols with conc. Sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) and phosphoric acid (\[{H_3}P{O_4}\]).

Image: Dehydration of alcohol
Sometimes anhydrous zinc chloride (\[ZnC{l_2}\]) is also used for the dehydration of alcohols.
The dehydration trends of alcohols can be represented as tertiary alcohols > secondary alcohols> primary alcohols.
The tertiary alcohols and secondary alcohols can also be dehydrated by diluting sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]).
In the question, option (b), (c), and (d) will be the incorrect option because the dehydration of \[C{H_3}OH\] , \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}OH\]and \[{(C{H_3})_2}CHC{H_2}OH\]do not produce ethylene. For the formation of ethylene, the alcohol must have two carbon atoms.
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that option (a) will be the correct answer.
Note: During the dehydration of alcohols in the presence of acids the number of carbon atoms remains the same. Sulfuric acid (\[{H_2}S{O_4}\]) is a colourless and corrosive liquid. It is highly miscible with water.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




