
During the preparation of phenol from benzene sulfonic acid, which of the following reagents is to be used?
(A) NaOH
(B) $NaHS{{O}_{4}}$
(C) $N{{a}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$
(D) $NaCl$
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: Benzene sulphonic acid which is a conjugate base of benzene sulphonate is an organosulfur compound with chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}{{O}_{3}}S$and is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It is a strong acid and dissociates fully in water.
Step by step answer:
-Benzene sulphonic acid is obtained by reacting benzene with oleum. The formed benzene sulphonic acid, when treated with molten sodium hydroxide at high temperature, favours the formation of sodium phenoxide ion which on further acidification gives phenol.
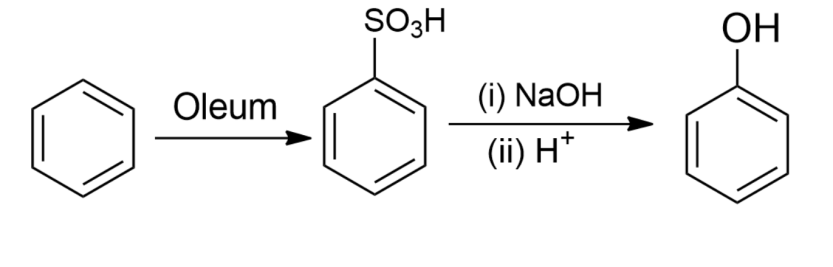
So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:
-Phenol can be prepared by many other processes which are described below-
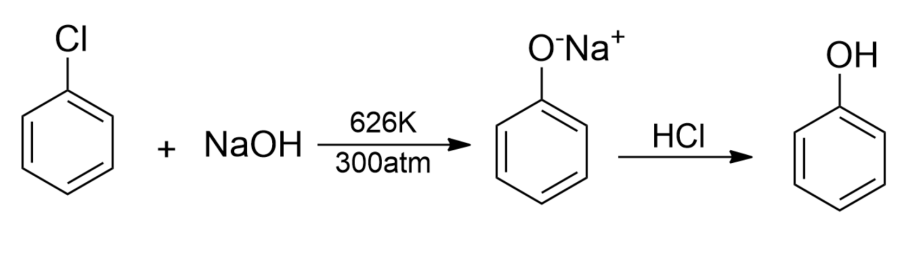
(i) From haloarenes- Chlorobenzene which is formed by the monosubstitution of the benzene ring is an example of haloarene. When chlorobenzene is fused with sodium hydroxide at 626K and 20atm, sodium phenoxide is formed which on acidification gives phenol.
(ii) From Diazonium salts- Diazonium salts are obtained when an aromatic primary amine is treated with nitrous acid $(NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl)$at about 273-278K. These diazonium salts are chemically highly reactive. The diazonium salts upon warming with water hydrolyzes to phenols.

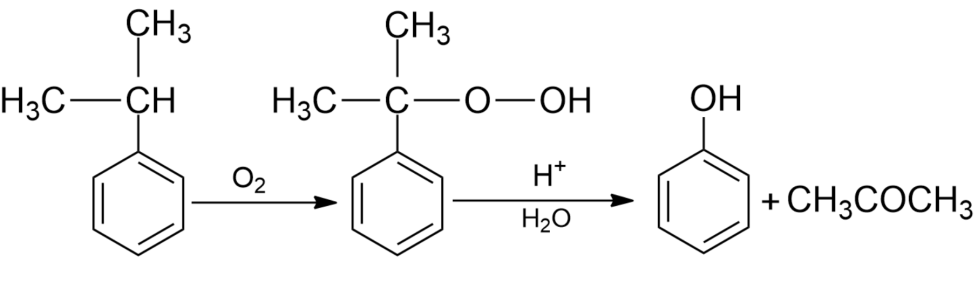
(iii) From cumene- Cumene is an organic compound produced by Friedel Crafts alkylation of benzene with propylene. Oxidation of cumene in the presence of air gives hydroperoxide which on further treatment with dilute acids gives phenol along with acetone as side by-products in large quantities. Hence phenols formed by this method need purifications.
Note: The alkali metal salt of benzene sulphonic acid used in the industrial production of phenol involves the presence of phenoxide salt and produced a lot of water and side products. This process is sometimes known as alkaline fusion. Now, this process is replaced by the Hock process for the production of phenol as it produces less waste.
Step by step answer:
-Benzene sulphonic acid is obtained by reacting benzene with oleum. The formed benzene sulphonic acid, when treated with molten sodium hydroxide at high temperature, favours the formation of sodium phenoxide ion which on further acidification gives phenol.

So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:
-Phenol can be prepared by many other processes which are described below-
(i) From haloarenes- Chlorobenzene which is formed by the monosubstitution of the benzene ring is an example of haloarene. When chlorobenzene is fused with sodium hydroxide at 626K and 20atm, sodium phenoxide is formed which on acidification gives phenol.

(ii) From Diazonium salts- Diazonium salts are obtained when an aromatic primary amine is treated with nitrous acid $(NaN{{O}_{2}}+HCl)$at about 273-278K. These diazonium salts are chemically highly reactive. The diazonium salts upon warming with water hydrolyzes to phenols.

(iii) From cumene- Cumene is an organic compound produced by Friedel Crafts alkylation of benzene with propylene. Oxidation of cumene in the presence of air gives hydroperoxide which on further treatment with dilute acids gives phenol along with acetone as side by-products in large quantities. Hence phenols formed by this method need purifications.

Note: The alkali metal salt of benzene sulphonic acid used in the industrial production of phenol involves the presence of phenoxide salt and produced a lot of water and side products. This process is sometimes known as alkaline fusion. Now, this process is replaced by the Hock process for the production of phenol as it produces less waste.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




