
Draw the Lewis structure for \[IC{l_4}^ - \] and provide the following information.
A. Total number of valence electrons
B. Number of nonbonding electron pairs
C. Electron geometry
D. Molecular geometry
E. Polarity
Answer
239.1k+ views
Hint: VSEPR theory is used to understand the arrangement of electrons. Here the focus is on the arrangements around Iodine in \[IC{l_4}^ - \]. Once the molecular geometry is understood, the Polarity of molecules/species can be calculated.
Lewis’s structure will enable us to determine a stable bonding arrangement for this ion.
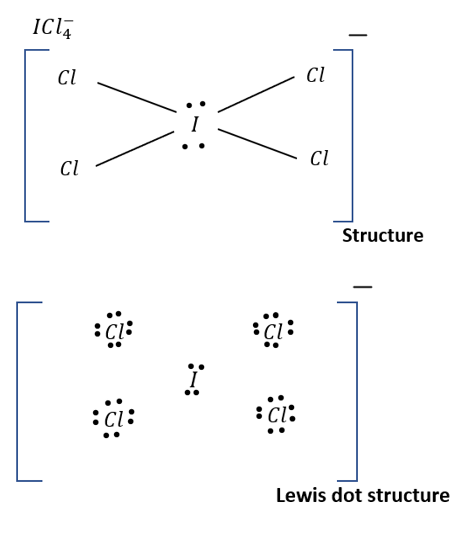
Complete step by step solution:
(a) Total number of valence electrons.
Iodine has 7 valence electrons and chlorine has also 7 electrons in its outermost orbit. One more negative charge on the outside. Hence, total number of valence electrons is:
\[V_e = 7 + 7[4] + 1\\ = 36\]
On the periodic chart, iodine [I] is in Period 3 and may hold more than 8 electrons. The Iodine atom contains 12 valence electrons in the Lewis structure for ICl4-.
(b) Number of nonbonding electron pairs:
As per Lewis structure, chlorine has 6 electrons which does not form bond and iodine has 4 electrons which do not form bond
Therefore, there are 2 non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs on Iodine & \[3\] non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs on each chlorine.
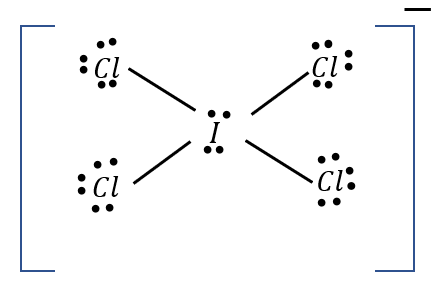
Image: Lewis structure of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
A total of \[14\] non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs are present in this .
(c) Electron geometry
It has octahedral electron geometry.
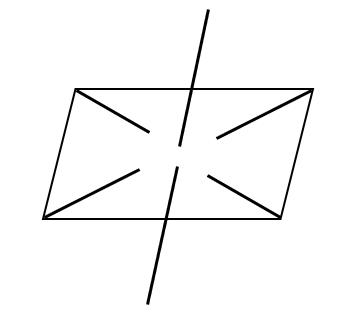
Image: Electron geometry of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
(d) Molecular geometry
It has square planar geometry, because \[2\]non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs of Iodine are occupying \[2\]opposite vertices.
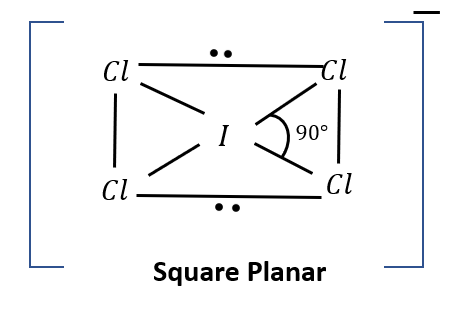
Image: Molecular geometry of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
[e] Polarity:
It is a non-polar compound because it is a square plane. In \[ICl\] bond, \[Cl\] is the most negative, so it attracts the electrons into chemical bonds.
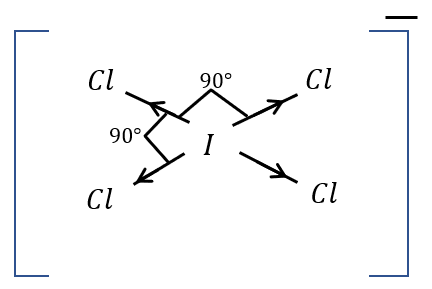
Image: Polarity of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
There is polarity in each \[I - Cl\] bond. But overall polarity is cancelled out due to geometry.
Note: Iron reacting with hydrochloric acid forms iron chloride where iron is in +2 oxidation state whereas when iron reacts with chlorine it also forms iron chloride but here iron is in +3oxidation state. The reaction between iron and chlorine is a type of redox reaction. The reaction between iron and chlorine is shown below:
$2Fe(s) + 3C{l_2}(g) \to 2FeC{l_3}(s)$
Lewis’s structure will enable us to determine a stable bonding arrangement for this ion.

Complete step by step solution:
(a) Total number of valence electrons.
Iodine has 7 valence electrons and chlorine has also 7 electrons in its outermost orbit. One more negative charge on the outside. Hence, total number of valence electrons is:
\[V_e = 7 + 7[4] + 1\\ = 36\]
On the periodic chart, iodine [I] is in Period 3 and may hold more than 8 electrons. The Iodine atom contains 12 valence electrons in the Lewis structure for ICl4-.
(b) Number of nonbonding electron pairs:
As per Lewis structure, chlorine has 6 electrons which does not form bond and iodine has 4 electrons which do not form bond
Therefore, there are 2 non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs on Iodine & \[3\] non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs on each chlorine.

Image: Lewis structure of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
A total of \[14\] non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs are present in this .
(c) Electron geometry
It has octahedral electron geometry.

Image: Electron geometry of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
(d) Molecular geometry
It has square planar geometry, because \[2\]non-bonding \[\bar e\] pairs of Iodine are occupying \[2\]opposite vertices.

Image: Molecular geometry of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
[e] Polarity:
It is a non-polar compound because it is a square plane. In \[ICl\] bond, \[Cl\] is the most negative, so it attracts the electrons into chemical bonds.

Image: Polarity of \[IC{l_4}^ - \]
There is polarity in each \[I - Cl\] bond. But overall polarity is cancelled out due to geometry.
Note: Iron reacting with hydrochloric acid forms iron chloride where iron is in +2 oxidation state whereas when iron reacts with chlorine it also forms iron chloride but here iron is in +3oxidation state. The reaction between iron and chlorine is a type of redox reaction. The reaction between iron and chlorine is shown below:
$2Fe(s) + 3C{l_2}(g) \to 2FeC{l_3}(s)$
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving




