
\[Diazonium~salts + C{u_2}C{l_2} + HCl \to \]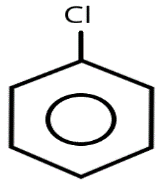 , the reaction is known as
, the reaction is known as
A. Chlorination
B. Sandmeyer’s reaction
C. Perkin reaction
D. Carbyl amine reaction
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint: A group of organic compounds known as diazonium salts have a functional group \[[RN_2]X\] that can have any kind of organic group \[R\], like an aryl or an alkyl, and an inorganic or organic anion, like a halide. It is used in many multiple reactions to form new organic compounds.
Complete step-by-step answer:Diazotization is a chemical reaction in which amine gets converted into diazonium salt with the help of sodium nitrite and HCl at low temperatures of 0-5 degree celsius. The creation of the azo compound is caused by the reaction of benzene-diazonium chloride with another chemical containing a benzene ring known as a coupling specialist, such as phenol or aromatic amine.
By heating aryl azide and cuprous halide, Sandmeyer's reaction produces halobenzene.
Halobenzene is created using Sandmeyer's reaction. For the creation of alkyl fluorides, it cannot be employed. It is an illustration of an aromatic radical-nucleophilic substitution. The Sandmeyer’s reaction for the formation of chlorobenzene is shown below.
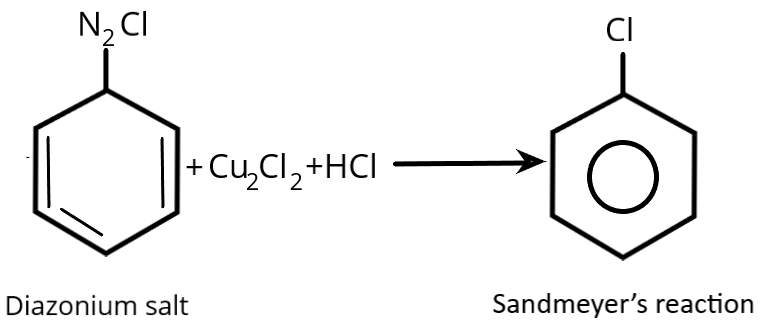
Therefore, the given reaction represents Sandmeyer's reaction.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note:It should be noted that the finding of biaryl byproducts lends support to the radical mechanism of the Sandmeyer reaction. A one-electron transfer mechanism that is catalysed by copper\[(I)\] causes the aromatic diazo group to be replaced with a halogen or pseudohalogen, forming an aryl radical with the loss of nitrogen gas. The substitutes may be produced and the copper\[(I)\] catalyst restored by direct transfer of \[Cl,Br\] or \[OH\] from a copper\[(II)\] species to the aryl radical.
Complete step-by-step answer:Diazotization is a chemical reaction in which amine gets converted into diazonium salt with the help of sodium nitrite and HCl at low temperatures of 0-5 degree celsius. The creation of the azo compound is caused by the reaction of benzene-diazonium chloride with another chemical containing a benzene ring known as a coupling specialist, such as phenol or aromatic amine.
By heating aryl azide and cuprous halide, Sandmeyer's reaction produces halobenzene.
Halobenzene is created using Sandmeyer's reaction. For the creation of alkyl fluorides, it cannot be employed. It is an illustration of an aromatic radical-nucleophilic substitution. The Sandmeyer’s reaction for the formation of chlorobenzene is shown below.

Therefore, the given reaction represents Sandmeyer's reaction.
Option ‘B’ is correct
Note:It should be noted that the finding of biaryl byproducts lends support to the radical mechanism of the Sandmeyer reaction. A one-electron transfer mechanism that is catalysed by copper\[(I)\] causes the aromatic diazo group to be replaced with a halogen or pseudohalogen, forming an aryl radical with the loss of nitrogen gas. The substitutes may be produced and the copper\[(I)\] catalyst restored by direct transfer of \[Cl,Br\] or \[OH\] from a copper\[(II)\] species to the aryl radical.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




