
Cyclohexene on reaction with OsO4 followed by reaction with NaHSO3 gives
A. Cis-diol
B. Trans-diol
C. Epoxy
D. Alcohol
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: The process of conversion of alkene into vicinal diol is called dihydroxylation. It is an oxidation process and for this process, a transition metal with a high oxidation state is needed like osmium or manganese. OsO4 is the most important oxidising agent which is used for the process of dihydroxylation.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The reaction of cyclohexane with OsO4 is a dihydroxylation reaction, dihydroxylation means the addition of two hydroxyl groups in the substituent, and the formation of vicinal diol takes place.
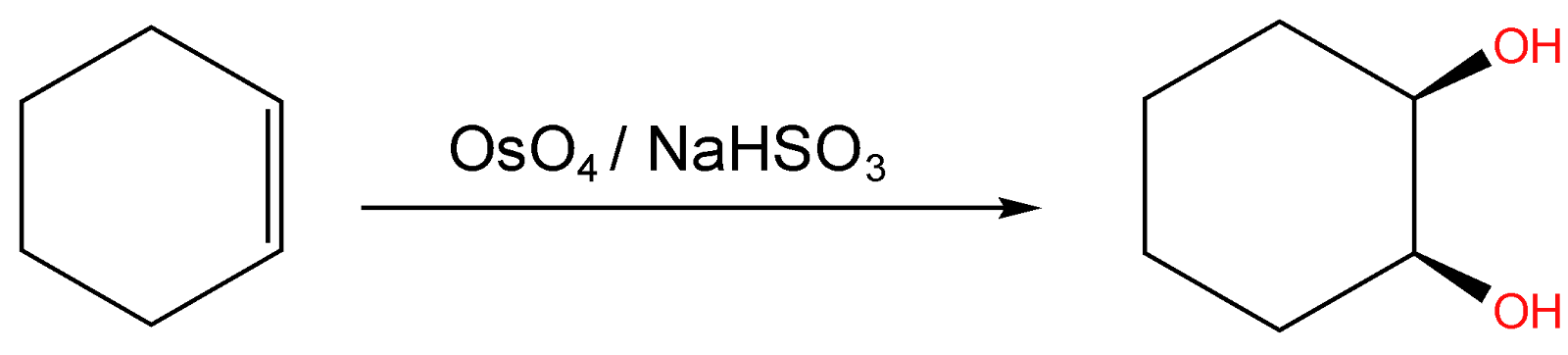
The reaction of Cyclohexene with OsO4 followed by a reaction with NaHSO3 will give a diol-
$C_6H_{10}\xrightarrow[]{OsO_4/NaHSO_3}C_6H_{10}\left ( OH \right )_2$
This is an oxidative addition reaction. And the mechanism of the reaction passes through the transition state and the formation of the transition state requires syn addition thus the product formed will be syn.
The reaction mechanism is
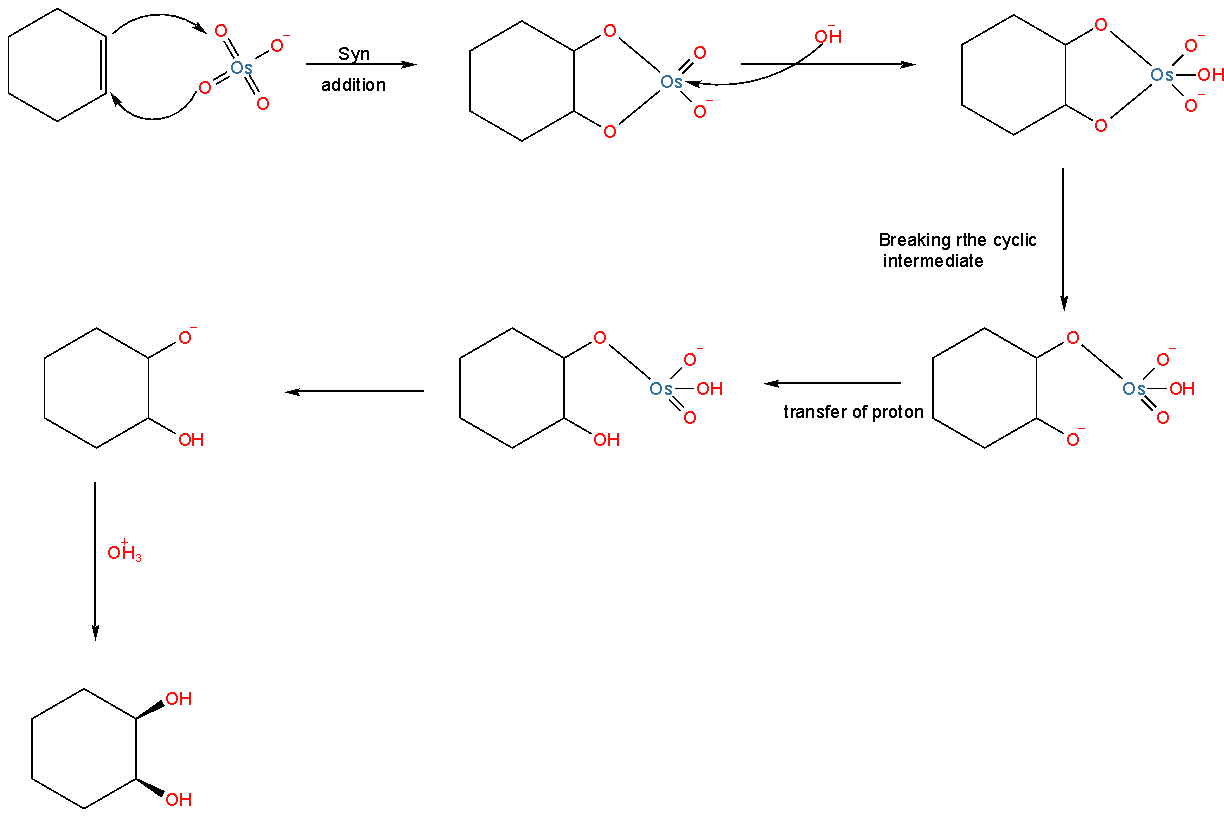
This process follows no rearrangement. The reaction follows syn addition, that is the addition of a new bond will be at the same face of the reactant. In this reaction, NaHSO3 is used to break the five-membered cyclic transition state.
Thus we can see that the Cyclohexene on reaction with OsO4 followed by reaction with NaHSO3 gives cyclohexane cis diol.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Bayer’s reagent which is alkaline potassium permanganate (alkaline) KMnO4 is also a strong oxidising agent which is also used for the formation of vicinal diol. Manganese also has a high oxidation state. It is also used for the determination of unsaturation in a compound.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The reaction of cyclohexane with OsO4 is a dihydroxylation reaction, dihydroxylation means the addition of two hydroxyl groups in the substituent, and the formation of vicinal diol takes place.
The reaction of Cyclohexene with OsO4 followed by a reaction with NaHSO3 will give a diol-
$C_6H_{10}\xrightarrow[]{OsO_4/NaHSO_3}C_6H_{10}\left ( OH \right )_2$

This is an oxidative addition reaction. And the mechanism of the reaction passes through the transition state and the formation of the transition state requires syn addition thus the product formed will be syn.
The reaction mechanism is

This process follows no rearrangement. The reaction follows syn addition, that is the addition of a new bond will be at the same face of the reactant. In this reaction, NaHSO3 is used to break the five-membered cyclic transition state.
Thus we can see that the Cyclohexene on reaction with OsO4 followed by reaction with NaHSO3 gives cyclohexane cis diol.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Bayer’s reagent which is alkaline potassium permanganate (alkaline) KMnO4 is also a strong oxidising agent which is also used for the formation of vicinal diol. Manganese also has a high oxidation state. It is also used for the determination of unsaturation in a compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




