
Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane and 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane are examples of which one of the following?
A. Constitutional isomers
B. Positional isomers
C. Structural isomers
D. Structural as well as positional isomers
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: We know that isomers are different in physical and chemical properties but have the same number of atoms. This phenomenon is termed as isomerism.
Complete step by step answer:
Structural isomers are those isomers where atoms are fully arranged with the same molecular formulae in different order. Molecular formula of Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane and 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}$.
Cyclohexane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of cyclohexane is as follows:
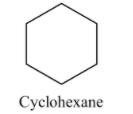
Methylcyclopentane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of methylcyclopentane is as follows:
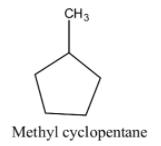
1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane is as follows:
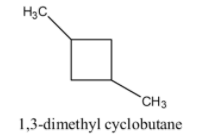
1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane is as follows:
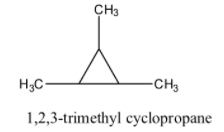
Structural isomers are also termed as constitutional isomers. Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but numbering and IUPAC names are different. Only count the number of each atom in both molecules to see how atoms are organized to decide whether two molecules are constitutional isomers.
Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane and 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane are structural isomers because they have same molecular formula $\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}} \right)$ but different bonding arrangement.
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note:
Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
Structural isomers are those isomers where atoms are fully arranged with the same molecular formulae in different order. Molecular formula of Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane and 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane is ${{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}$.
Cyclohexane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of cyclohexane is as follows:

Methylcyclopentane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of methylcyclopentane is as follows:

1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane is as follows:

1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane has 6 carbon and 12 hydrogen atoms. Now we draw structure of 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane is as follows:

Structural isomers are also termed as constitutional isomers. Constitutional isomers have the same molecular formula but numbering and IUPAC names are different. Only count the number of each atom in both molecules to see how atoms are organized to decide whether two molecules are constitutional isomers.
Position isomers are also structural or constitutional isomers with the same functional group and same carbon skeleton but differing in position of the same functional group on or inside the carbon chain.
Cyclohexane, methylcyclopentane, 1, 3-dimethyl cyclobutane and 1, 2, 3- trimethyl cyclopropane are structural isomers because they have same molecular formula $\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}} \right)$ but different bonding arrangement.
Hence, the correct answer is C.
Note:
Isomers are classified as structural (constitutional) and stereoisomerism. Structural isomers are further classified as chain isomers, position isomers and functional group isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26




