
Conversion of phenol to salicylic acid and to salicyaldehyde are known as? (respectively)
(A) Reimer-Tiemann reaction and Kolbe’s reaction
(B) Williamson’s synthesis and Hydroboration-oxidation
(C) Kolbe’s reaction and Williamson’s synthesis
(D) Kolbe’s reaction and Reimer-Tiemann reaction
Answer
541k+ views
Hint:The conversion of phenol to salicylic acid takes place through a base, and hydrolysis. If we talk about the conversion of phenol of salicylaldehyde takes place through the action of chloroform. So, we identify the naming reactions in which these conversions take place.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will discuss the conversion of phenol to salicylic acid.
The phenol will be deprotonated by strong base i.e. hydroxide ion. There will be addition of phenoxide ions formed to the carbon-dioxide.
So, we can say that the addition further leads to the carboxylate formation. Then, it will further lead to the formation of carboxylic acid, i.e. salicylic acid.
The chemical reaction is
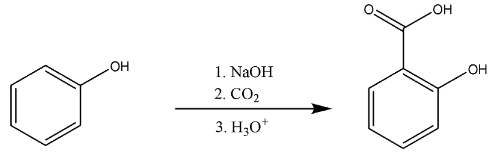
Thus, we know this whole mechanism takes place in Kolbe’s reaction, it is used for the synthesis of aspirin also known as salicylic acid in the industries.
Now, the next we have conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. It was proposed by Karl Riemer, mainly used for the ortho- phenols.
In this reaction too like Kolbe’s reaction, there is deprotonation of chloroform by strong base like KOH.
This reaction takes place through the nucleophilic attack, and the basic hydrolysis is done, leading to the formation of salicylaldehyde.
The chemical reaction is
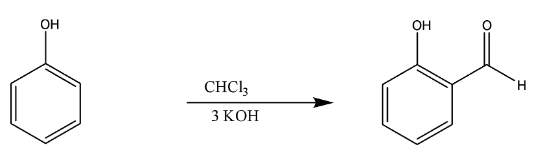
Thus, we can say this whole mechanism takes place in the Riemer –Tiemann reaction.
In the last, we can conclude that conversion of phenol to salicylic acid and to salicylaldehyde are known as Kolbe’ reaction, and Riemer-Tiemann reaction.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: Don’t get confused between both these reactions. These both takes place through deprotonation by a strong base, as we discussed; but the product formation will be different. In case 1 there is addition of carbon-dioxide, and in case 2 there is nucleophilic attack.
Complete step by step solution:
First, we will discuss the conversion of phenol to salicylic acid.
The phenol will be deprotonated by strong base i.e. hydroxide ion. There will be addition of phenoxide ions formed to the carbon-dioxide.
So, we can say that the addition further leads to the carboxylate formation. Then, it will further lead to the formation of carboxylic acid, i.e. salicylic acid.
The chemical reaction is

Thus, we know this whole mechanism takes place in Kolbe’s reaction, it is used for the synthesis of aspirin also known as salicylic acid in the industries.
Now, the next we have conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde. It was proposed by Karl Riemer, mainly used for the ortho- phenols.
In this reaction too like Kolbe’s reaction, there is deprotonation of chloroform by strong base like KOH.
This reaction takes place through the nucleophilic attack, and the basic hydrolysis is done, leading to the formation of salicylaldehyde.
The chemical reaction is

Thus, we can say this whole mechanism takes place in the Riemer –Tiemann reaction.
In the last, we can conclude that conversion of phenol to salicylic acid and to salicylaldehyde are known as Kolbe’ reaction, and Riemer-Tiemann reaction.
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: Don’t get confused between both these reactions. These both takes place through deprotonation by a strong base, as we discussed; but the product formation will be different. In case 1 there is addition of carbon-dioxide, and in case 2 there is nucleophilic attack.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Exam Dates, Session 2 Updates, City Slip, Admit Card & Latest News

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




