
Consider the reaction sequence from P to Q shown below. The overall yield of the major product Q from P is 75%. What is the amount in grams of Q obtained from 9.3 mL of P? (Use density of P \[ = 1.00{\text{ }}g{\text{ }}m{L^{ - 1}}\] ; Molar mass of\[C = 12.0\] , \[H = 1.0\] , \[O = 16.0\] and \[N = 14.0{\text{ }}g{\text{ }}mo{l^{ - 1}}\] )
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The given compound P is aniline. It is reacted with \[NaN{O_2} + HCl\] . Diazonium salt functions as an electrophile. Therefore, it produces diazonium salt. This salt further reacted with beta naphthol and sodium hydroxide. And after that, it will react with acetic acid and water. By using the reaction stoichiometry and molar mass calculations, we have to calculate the amount of Q obtained.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
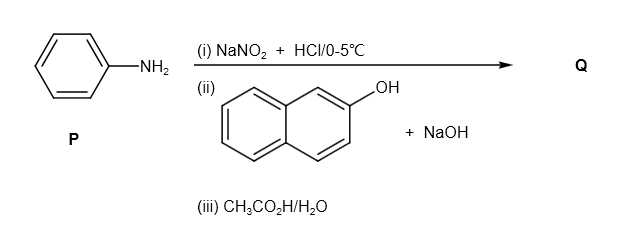
The given compound P is as follows:
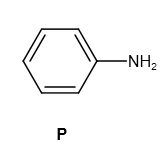
It reacts with \[NaN{O_2} + HCl\] and produces diazonium salt as follows:
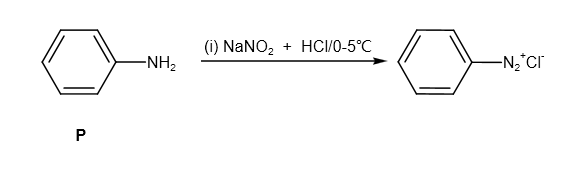
Further, it reacts with \[\beta - \] naphthol and sodium hydroxide as follows:
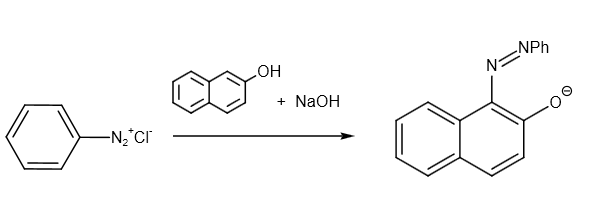
Further, it reacts with \[C{H_3}C{O_2}H/{H_2}O\] as follows:
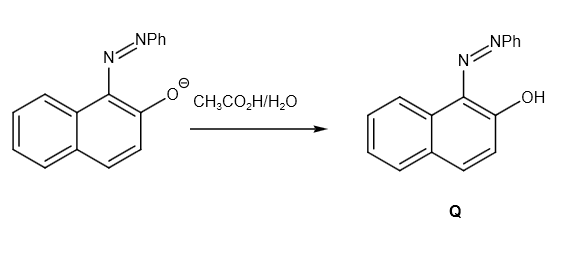
Therefore, the overall reaction can be written as follows:
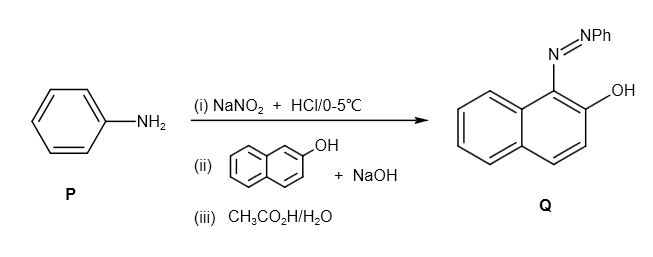
One mole of P produces one mole of Q.
Molar mass of \[{C_6}{H_7}N = 93\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Molar mass of \[{C_{16}}{H_{12}}{N_2}O = 248\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
So, we can say that \[93\,g\] of P produces \[248\,g\] of Q.
The given volume of P is \[9.3\,mL\] .
Density of P \[ = 1.00{\text{ }}g{\text{ }}m{L^{ - 1}}\]
We know that,
\[ m = d \times V \\
\Rightarrow m = 1.0\,g\,m{L^{ - 1}} \times 9.3\,mL \\
\Rightarrow m = 9.3\,g \\ \]
Calculate the number of moles of P as follows:
\[ {\text{No}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{of moles}} = \dfrac{{9.3\,g}}{{93\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{No}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{of moles}} = 0.1\,mol \\ \]
One mole of P produces one mole of Q.
\[0.1\,mol\] of P produces \[0.1\,mol\] of Q.
Now,
\[ {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} = \dfrac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} \times {\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}} \\ \]
Calculate the mass of Q as follows:
\[ {\text{mass}} = {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} \times {\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 0.1 \times 248 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 24.8 \\ \]
The yield of the reaction is \[75\% \] .
Calculate the actual amount of Q as follows:
\[ {\text{mass}} = 24.8 \times \dfrac{{75}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 18.6\,g \\ \]
Therefore, the mass of Q is \[18.6\,g\] .
Note: Molar mass is the amount of mass that makes up one mole of a substance. It may also be referred to as the mass of the substance, measured in grammes, that makes up one mole of the substance. There are \[6.023 \times {10^{23}}\] molecules in a mole. It is known as Avogadro's number. The most significant concept in physical chemistry is molar mass. The molar mass, the molar mass formula, the molecular mass and its formula, the distinction between the molar and molecular masses, and the relative molar mass and its formula are all topics covered in this article.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The given compound P is as follows:

It reacts with \[NaN{O_2} + HCl\] and produces diazonium salt as follows:
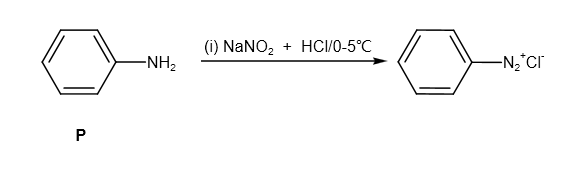
Further, it reacts with \[\beta - \] naphthol and sodium hydroxide as follows:

Further, it reacts with \[C{H_3}C{O_2}H/{H_2}O\] as follows:

Therefore, the overall reaction can be written as follows:

One mole of P produces one mole of Q.
Molar mass of \[{C_6}{H_7}N = 93\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
Molar mass of \[{C_{16}}{H_{12}}{N_2}O = 248\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\]
So, we can say that \[93\,g\] of P produces \[248\,g\] of Q.
The given volume of P is \[9.3\,mL\] .
Density of P \[ = 1.00{\text{ }}g{\text{ }}m{L^{ - 1}}\]
We know that,
\[ m = d \times V \\
\Rightarrow m = 1.0\,g\,m{L^{ - 1}} \times 9.3\,mL \\
\Rightarrow m = 9.3\,g \\ \]
Calculate the number of moles of P as follows:
\[ {\text{No}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{of moles}} = \dfrac{{9.3\,g}}{{93\,g\,mo{l^{ - 1}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{No}}{\text{.}}\,{\text{of moles}} = 0.1\,mol \\ \]
One mole of P produces one mole of Q.
\[0.1\,mol\] of P produces \[0.1\,mol\] of Q.
Now,
\[ {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} = \dfrac{{{\text{mass}}}}{{{\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}}}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} \times {\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}} \\ \]
Calculate the mass of Q as follows:
\[ {\text{mass}} = {\text{No}}{\text{. of moles}} \times {\text{molar}}\,{\text{mass}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 0.1 \times 248 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 24.8 \\ \]
The yield of the reaction is \[75\% \] .
Calculate the actual amount of Q as follows:
\[ {\text{mass}} = 24.8 \times \dfrac{{75}}{{100}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{mass}} = 18.6\,g \\ \]
Therefore, the mass of Q is \[18.6\,g\] .
Note: Molar mass is the amount of mass that makes up one mole of a substance. It may also be referred to as the mass of the substance, measured in grammes, that makes up one mole of the substance. There are \[6.023 \times {10^{23}}\] molecules in a mole. It is known as Avogadro's number. The most significant concept in physical chemistry is molar mass. The molar mass, the molar mass formula, the molecular mass and its formula, the distinction between the molar and molecular masses, and the relative molar mass and its formula are all topics covered in this article.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




