
Consider the below reaction where 6.1 g of benzoic acid is used to get 7.8 g of m-bromobenzoic acid.
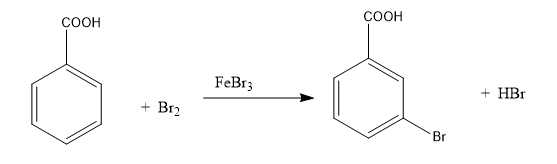
The percentage yield of the product is ______
(Round off to the nearest integer)
(Given: Atomic mass: C:12.0 u, H:1.0 u, O:16 u, Br: 80 u)
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Percentage yield describes the ratio of the percentage of actual yield to the yield that is calculated theoretically. If the values of theoretical and actual yield are the same, then we get a percent yield of 100%.
Formula used:
The formula to find out percentage yield is,
% yield\[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{Actual}}\,{\rm{weight}}}}{{{\rm{Theoretical}}\,{\rm{weight}}}}{\rm{ \times 100}}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of ketone with HBr in excess results in the breaking of the bond. The reaction is as follows:
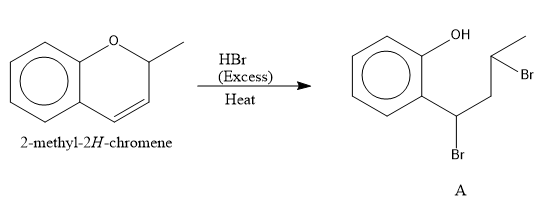
Image: reaction of ketone with HBr
As the HBr is in excess, so, the bromination at the o and p position takes place.
The next step is the reaction of A with alcoholic potassium hydroxide in presence of acid. The reaction of an alkyl halide in alcoholic potassium hydroxide results in the removal of halogen acid to form an alkene.
So, the reaction is,
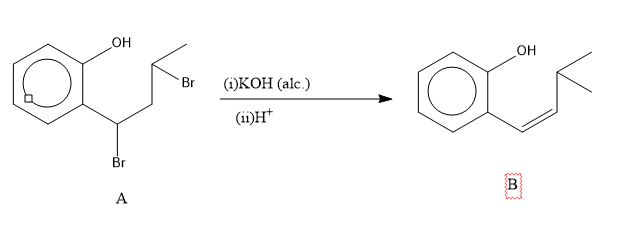
Image: reaction of A with alcoholic potassium hydroxide in presence of acid
The next step is the reaction of B with Ozone in the presence of acid.
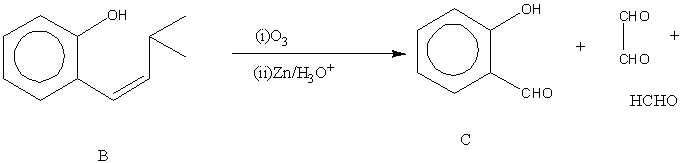
Image: reaction of B with Ozone in presence of acid
This is an ozonolysis reaction. Ozonolysis is a reaction in organic chemistry where the breaking of double or triple bonds of alkynes, alkenes or azo compounds takes place in reaction with ozone. Alkynes and alkenes form organic compounds where the replacement of multiple carbon-carbon bonds takes place by a carbonyl group whereas azo compounds give nitrosamines.
Hence, the product C is in option C.
Note: The higher value of percent yield indicates that there is contamination of the product by excess reactant, water or another substance. A lower value of percent yield signifies that there is mismeasurement of the reactant or there is spilling of a portion of the product.
Formula used:
The formula to find out percentage yield is,
% yield\[{\rm{ = }}\dfrac{{{\rm{Actual}}\,{\rm{weight}}}}{{{\rm{Theoretical}}\,{\rm{weight}}}}{\rm{ \times 100}}\]
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction of ketone with HBr in excess results in the breaking of the bond. The reaction is as follows:

Image: reaction of ketone with HBr
As the HBr is in excess, so, the bromination at the o and p position takes place.
The next step is the reaction of A with alcoholic potassium hydroxide in presence of acid. The reaction of an alkyl halide in alcoholic potassium hydroxide results in the removal of halogen acid to form an alkene.
So, the reaction is,

Image: reaction of A with alcoholic potassium hydroxide in presence of acid
The next step is the reaction of B with Ozone in the presence of acid.

Image: reaction of B with Ozone in presence of acid
This is an ozonolysis reaction. Ozonolysis is a reaction in organic chemistry where the breaking of double or triple bonds of alkynes, alkenes or azo compounds takes place in reaction with ozone. Alkynes and alkenes form organic compounds where the replacement of multiple carbon-carbon bonds takes place by a carbonyl group whereas azo compounds give nitrosamines.
Hence, the product C is in option C.
Note: The higher value of percent yield indicates that there is contamination of the product by excess reactant, water or another substance. A lower value of percent yield signifies that there is mismeasurement of the reactant or there is spilling of a portion of the product.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




