
Compound A $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ is insoluble in water, dilute HCL & aqueous $NaHC{O_3}$ , but it dissolves in dilute $NaOH$ . When A is treated with $B{r_2}$ water it is converted into a compound ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$ rapidly. The structure of A is:
(A)
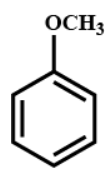
(B)
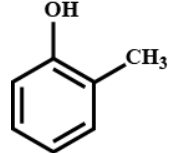
(C)
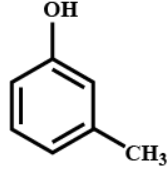
(D)
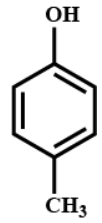
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here is this question, Compound A is given as $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ is insoluble in water is given, where as dilute HCL & aqueous $NaHC{O_3}$ as given but it also dissolves in dilute $NaOH$. After which Compound A is reacted with $B{r_2}$ water and as rapidly it is converted into a compound ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$ . Now we have to justify the structure of Compound A.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here A is given as $({C_7}{H_8}O)$,
AS from we can see that, the Oxygen atom will directly got attached to the benzene ring as from which We have reacted HCL and $NaHC{O_3}$ there is no change taking place in the reaction.
As we react the reactant with $NaOH$ it got reacted and got the following reaction as,
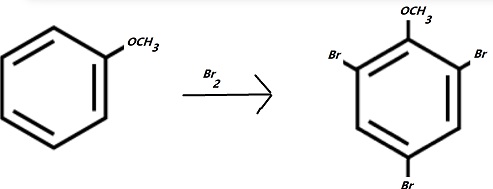
As from the above reaction when $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ as in the presence of $B{r_2}$it is directly converted into ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$.
From which we get the correct structure and positioning of $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ is option (A) as similar to the product of our reaction.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: As we see the importance of nature of any compound in this question when we reacted our main compound A with dilute HCL & aqueous $NaHC{O_3}$ , we got no change as per they are no reactive with each other but when we add dilute $NaOH$ in it got directly soluble in it and got reacted as in the presence of $B{r_2}$ and form a compound as ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$ . Hence, from this we get that the nature of compounds is very important to understand.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Here A is given as $({C_7}{H_8}O)$,
AS from we can see that, the Oxygen atom will directly got attached to the benzene ring as from which We have reacted HCL and $NaHC{O_3}$ there is no change taking place in the reaction.
As we react the reactant with $NaOH$ it got reacted and got the following reaction as,

As from the above reaction when $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ as in the presence of $B{r_2}$it is directly converted into ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$.
From which we get the correct structure and positioning of $({C_7}{H_8}O)$ is option (A) as similar to the product of our reaction.
Hence, the correct option is (A).
Note: As we see the importance of nature of any compound in this question when we reacted our main compound A with dilute HCL & aqueous $NaHC{O_3}$ , we got no change as per they are no reactive with each other but when we add dilute $NaOH$ in it got directly soluble in it and got reacted as in the presence of $B{r_2}$ and form a compound as ${C_7}{H_5}OB{r_3}$ . Hence, from this we get that the nature of compounds is very important to understand.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




