
Chloroform when treated with aniline and alcoholic KOH gives:
a) phenyl cyanide
b) iso-phenyl cyanide
c) chlorobenzene
d) phenol
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint The reaction of Chloroform which is treated with aniline and alcoholic KOH. Look that it is the isocyanide test. From the name we will guess the isocyanide is the product because in between the reactants nobody is isocyanide.
Complete step-by-step solution
The reaction of Chloroform with aniline and alcoholic KOH is called isocyanide test because the product is an iso-cyanide. Let’s know something more about the isocyanide test.
Aniline is an aromatic amine. It is a precursor to various drugs, dyes, and plastics. It is also a pollutant. Aniline is toxic, and it can be harmful to the environment.
The isocyanide test can be used to determine the presence of aniline in a sample. The test uses a reagent that reacts with aniline to form a blue colour. The reaction is not specific for aniline, so other compounds that contain aniline-like structures can also produce a blue colour. Only, primary aliphatic and aromatic amines provide it.
The isocyanide test is a quantitative test. The test can be used to determine the concentration of aniline in a sample. The test is also sensitive to low concentrations of aniline.
Now let’s see the product of the reaction of aniline and chloroform with alcoholic KOH. Obviously, the product is an isocyanide that iso-phenyl cyanide. Let's see the reaction now.
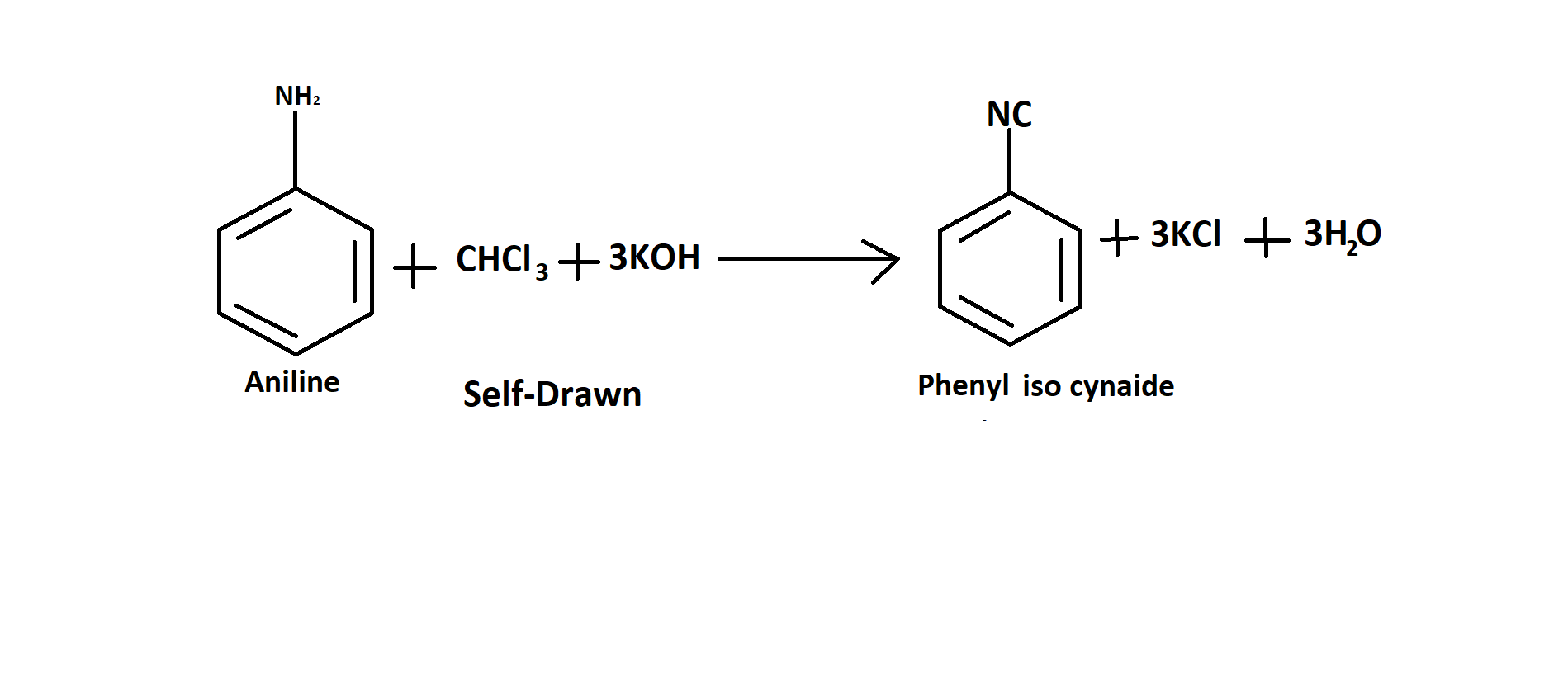
Now let's see the mechanism of the reaction. Chloroform is the first dehydrohalogenation (hydrogen halide is removed from a specific substrate) to produce dichlorocarbene intermediate. This intermediate of the dichlorocarbene is very reactive. The main amine's nucleophilic nitrogen is attacked by the electrophilic dichlorocarbene. Isonitrile is created as a result of the hydrochloric acid being eliminated. Below is a diagram that shows how the carbylamine reaction works.

So, option b is the correct option.
Note: The reaction of Chloroform with aniline and alcoholic KOH is called isocyanide test because the product is an iso-cyanide. Here, the product is an isocyanide that iso-phenyl cyanide. Only, primary aliphatic and aromatic amines provide it.
Complete step-by-step solution
The reaction of Chloroform with aniline and alcoholic KOH is called isocyanide test because the product is an iso-cyanide. Let’s know something more about the isocyanide test.
Aniline is an aromatic amine. It is a precursor to various drugs, dyes, and plastics. It is also a pollutant. Aniline is toxic, and it can be harmful to the environment.
The isocyanide test can be used to determine the presence of aniline in a sample. The test uses a reagent that reacts with aniline to form a blue colour. The reaction is not specific for aniline, so other compounds that contain aniline-like structures can also produce a blue colour. Only, primary aliphatic and aromatic amines provide it.
The isocyanide test is a quantitative test. The test can be used to determine the concentration of aniline in a sample. The test is also sensitive to low concentrations of aniline.
Now let’s see the product of the reaction of aniline and chloroform with alcoholic KOH. Obviously, the product is an isocyanide that iso-phenyl cyanide. Let's see the reaction now.

Now let's see the mechanism of the reaction. Chloroform is the first dehydrohalogenation (hydrogen halide is removed from a specific substrate) to produce dichlorocarbene intermediate. This intermediate of the dichlorocarbene is very reactive. The main amine's nucleophilic nitrogen is attacked by the electrophilic dichlorocarbene. Isonitrile is created as a result of the hydrochloric acid being eliminated. Below is a diagram that shows how the carbylamine reaction works.

So, option b is the correct option.
Note: The reaction of Chloroform with aniline and alcoholic KOH is called isocyanide test because the product is an iso-cyanide. Here, the product is an isocyanide that iso-phenyl cyanide. Only, primary aliphatic and aromatic amines provide it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




