
Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloro acetaldehyde in the presence of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ . The major product formed is:
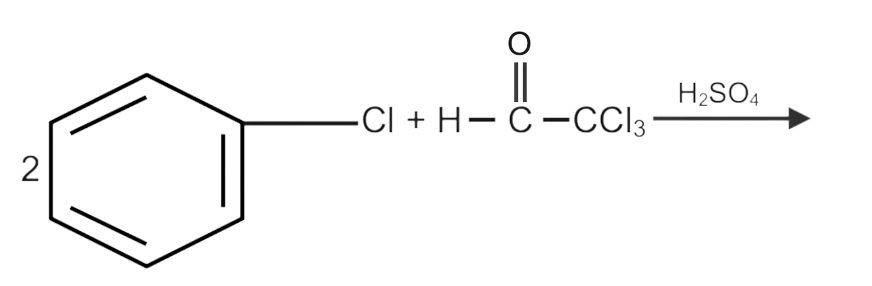
(A)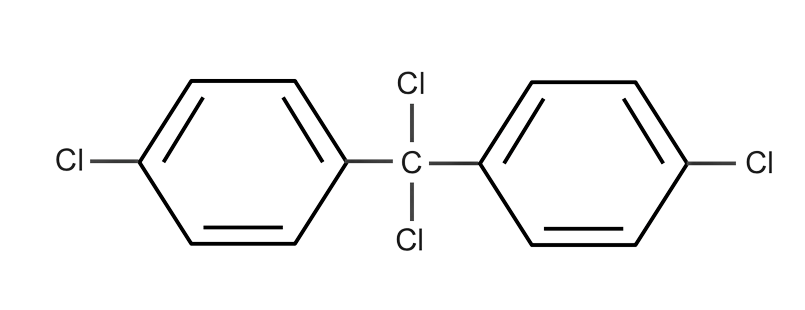
(B) 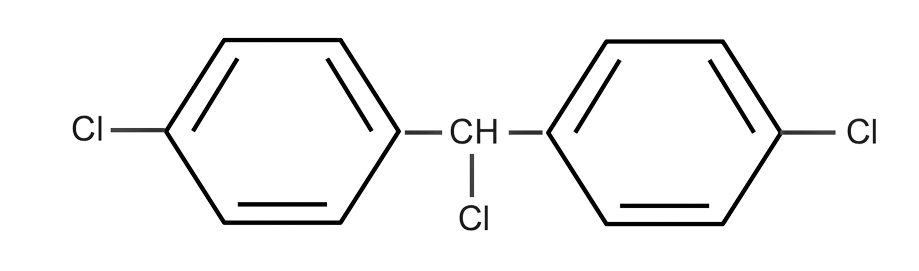
(C) 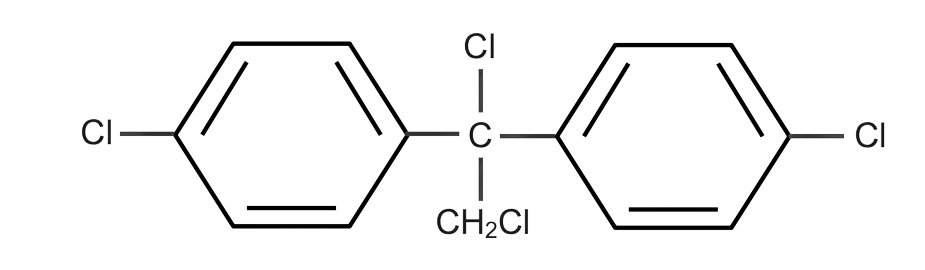
(D) 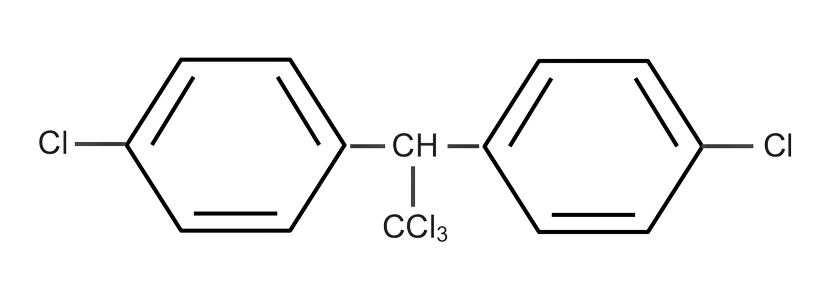
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Trichloroacetaldehyde and chlorobenzene are the reactants, and the carbon centre of the carbonyl group of trichloroacetaldehyde is attacked by chlorobenzene. A dehydrating agent, sulphuric acid aids in the elimination of water molecules.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that when Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloro acetaldehyde(chloral) as with the presence of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ we get the solution as DDT which is also said as Dichloro Diphenyl trichloroethane.
Here in this reaction ${H_2}S{O_4}$ work as a dehydration agent who removes the whole water from the reaction.
The whole reaction is as given below,

Therefore, the correct answer of this reaction is DDT (Dichloro Diphenyl trichloroethane).
Option ‘D’ is correct
Additional Information: DDT is an organochlorine and a crystalline chemical substance that has no colour, no flavour, and nearly no odour.
Although it was initially created as an insecticide, its negative effects on the environment led to its notoriety. Othmar Zeidler was the first to synthesis DDT, while Paul Hermann Müller was the first to recognise its insecticidal properties.
In the second half of World War II, it was employed to prevent the spread of insect-borne illnesses including malaria and typhus among troops and civilians.
Note: In the given reaction, carbonyl nucleophilic addition reaction takes place. The carbonyl carbon of trichloro acetaldehyde has low electron density due to presence of an oxygen atom and $-CCl_3$ group. Due to this low electron density nucleophile attaches to it to form the required product.
Complete step-by-step answer:We know that when Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloro acetaldehyde(chloral) as with the presence of ${H_2}S{O_4}$ we get the solution as DDT which is also said as Dichloro Diphenyl trichloroethane.
Here in this reaction ${H_2}S{O_4}$ work as a dehydration agent who removes the whole water from the reaction.
The whole reaction is as given below,

Therefore, the correct answer of this reaction is DDT (Dichloro Diphenyl trichloroethane).
Option ‘D’ is correct
Additional Information: DDT is an organochlorine and a crystalline chemical substance that has no colour, no flavour, and nearly no odour.
Although it was initially created as an insecticide, its negative effects on the environment led to its notoriety. Othmar Zeidler was the first to synthesis DDT, while Paul Hermann Müller was the first to recognise its insecticidal properties.
In the second half of World War II, it was employed to prevent the spread of insect-borne illnesses including malaria and typhus among troops and civilians.
Note: In the given reaction, carbonyl nucleophilic addition reaction takes place. The carbonyl carbon of trichloro acetaldehyde has low electron density due to presence of an oxygen atom and $-CCl_3$ group. Due to this low electron density nucleophile attaches to it to form the required product.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




