
How many chlorine atoms are present in one mole of DDT?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: DDT stands for dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane which is an organic compound that exists as a tasteless and colourless crystalline solid. It is the chemical used as an insecticide in agriculture and widely used for controlling the pest to prevent malaria and typhus.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The IUPAC name of DDT is 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane and is a chemical compound belonging to the family of organic halogen compounds.
DDT is a low water soluble compound but is soluble in organic solvents, fats and oils. It is readily adsorbed to soil and has long term sources of exposure. DDT is known to be hydrophobic in nature which means the constituents of DDT are absorbed by the aquatic organisms in water.
The indirect exposure of DDT is non-toxic for humans. However, it is highly toxic and carcinogenic and its chronic exposure can cause adverse effects on health like breast cancer, etc.
The molecular formula of DDT is ${C_{14}}{H_{19}}C{l_5}$ and can be structurally represented as follows:
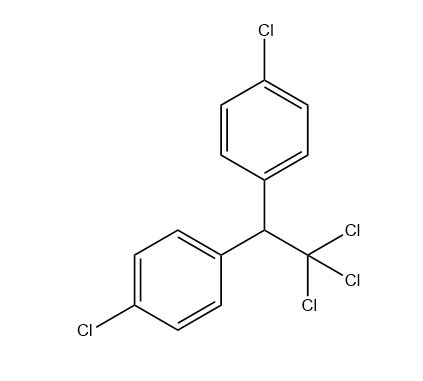
Hence, in one mole of DDT, the number of chlorine atoms present are 5.
Note: It is important to note that many countries banned the use of DDT as an insecticide because of its long term adverse effect. It was observed by the scientists that if DDT persists in the environment, it has the tendency to accumulate in fatty tissues and can cause severe health effects. Also, some insects resist the effect of DDT that means they eventually develop the ability to metabolise DDT, contradicting its main use.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The IUPAC name of DDT is 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane and is a chemical compound belonging to the family of organic halogen compounds.
DDT is a low water soluble compound but is soluble in organic solvents, fats and oils. It is readily adsorbed to soil and has long term sources of exposure. DDT is known to be hydrophobic in nature which means the constituents of DDT are absorbed by the aquatic organisms in water.
The indirect exposure of DDT is non-toxic for humans. However, it is highly toxic and carcinogenic and its chronic exposure can cause adverse effects on health like breast cancer, etc.
The molecular formula of DDT is ${C_{14}}{H_{19}}C{l_5}$ and can be structurally represented as follows:

Hence, in one mole of DDT, the number of chlorine atoms present are 5.
Note: It is important to note that many countries banned the use of DDT as an insecticide because of its long term adverse effect. It was observed by the scientists that if DDT persists in the environment, it has the tendency to accumulate in fatty tissues and can cause severe health effects. Also, some insects resist the effect of DDT that means they eventually develop the ability to metabolise DDT, contradicting its main use.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




