
$CH_3−CH=CH−CH_2−CN \xrightarrow[{{H}_{2}}O]{DIBALH} Product$. Then the product is:
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: DIBALH (Di-isobutyl Aluminium Hydride) is a strong, bulky reducing agent which is used for the partial reduction of esters. It reduces esters to aldehydes. Nitriles are typically converted to aldehydes using the hydride reagent DIBAL-H as well.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction of conversion of nitrile to aldehyde begins with the formation of an iminium anion by adding a hydride to the C-N triple bond. The formed imine salt then hydrolysed to form imine.
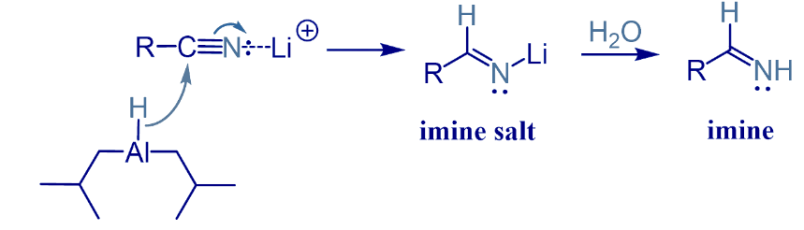
After the first hydride addition, hydrolysis of the imine to amine takes place through the nucleophilic attack of H2O.
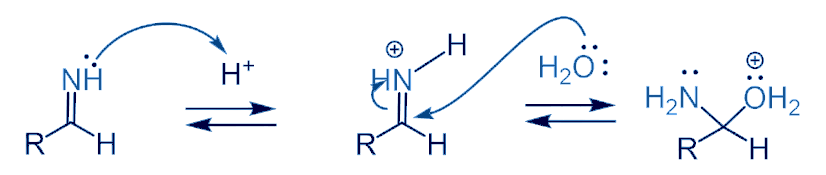
The Amine group leaves the substrate when OH attacks it as a nucleophile and forms a double bond. In the last step H2O takes out the extra H from the substrate and an aldehyde is formed.
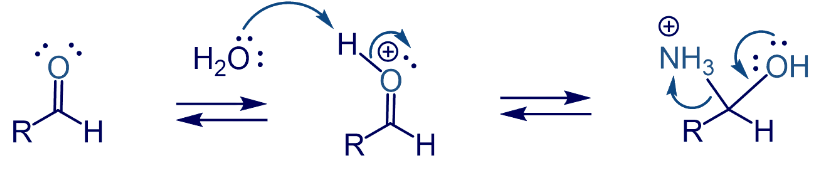
The product is CH3−CH=CH−CH2−CHO.
Additional Information: According to the suggested mechanism, DIBAL joins the nitrile through the creation of an N-Al link to form a Lewis acid-base adduct. The hydride is subsequently transferred to the nitrile's carbon. Aldehyde and ammonia are produced during aqueous workup as desired.
Note: In contrast to lithium aluminium hydride, Di-isobutyl Aluminium Hydride (DIBAL H) won't reduce the aldehyde anymore with the addition of just one equivalent. Other carbonyl substances including amides, aldehydes, ketones, and nitriles will also be reduced by it. DIBAL is most notable for what it does not do, much like Lindlar's catalyst is. It lowers esters but doesn't get all the way to alcohol; it just stops at aldehyde. The temperature is kept very low(-70° C) for the reaction to keep the reactivity in check.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction of conversion of nitrile to aldehyde begins with the formation of an iminium anion by adding a hydride to the C-N triple bond. The formed imine salt then hydrolysed to form imine.

After the first hydride addition, hydrolysis of the imine to amine takes place through the nucleophilic attack of H2O.

The Amine group leaves the substrate when OH attacks it as a nucleophile and forms a double bond. In the last step H2O takes out the extra H from the substrate and an aldehyde is formed.

The product is CH3−CH=CH−CH2−CHO.
Additional Information: According to the suggested mechanism, DIBAL joins the nitrile through the creation of an N-Al link to form a Lewis acid-base adduct. The hydride is subsequently transferred to the nitrile's carbon. Aldehyde and ammonia are produced during aqueous workup as desired.
Note: In contrast to lithium aluminium hydride, Di-isobutyl Aluminium Hydride (DIBAL H) won't reduce the aldehyde anymore with the addition of just one equivalent. Other carbonyl substances including amides, aldehydes, ketones, and nitriles will also be reduced by it. DIBAL is most notable for what it does not do, much like Lindlar's catalyst is. It lowers esters but doesn't get all the way to alcohol; it just stops at aldehyde. The temperature is kept very low(-70° C) for the reaction to keep the reactivity in check.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




