
$(CH_{3})_{2}CO\xrightarrow[HCl]{NaCN}A\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{H_{3}O^{+}}B$ where A and B are
A. \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right){\rm{CN,}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right){\rm{COOH}}\]
B. \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right){\rm{CN,}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}\]
C. \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right){\rm{CN,}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CH}}\left( {{\rm{COOH}}} \right)\]
D. \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}\left( {{\rm{OH}}} \right){\rm{CN,}}{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CO}}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Carbonyl compounds when treated with sodium cyanide in the presence of hydrochloric acid form cyanohydrin.
A cyanohydrin is a functional group of organic compounds having a cyano and a hydroxyl group connected to the same carbon atom.
Cyanohydrin is also called hydroxynitrile.
Complete step-by-step answer: Aldehydes and ketones are highly reactive. These compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.
The carbonyl carbon is quite polar. Due to the greater electronegativity of oxygen, as compared to carbon, the carbon atom possesses a small positive charge.
So, the carbon atom acts as an electrophile.
Therefore, a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the polar carbonyl group.
In the given reaction, acetone is treated with NaCN in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
Here, \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{N}}^{\rm{ - }}}\] acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the acetone molecule.
This step is the slowest.
During this process, the complete transfer of pi-electrons of the carbon-oxygen double bond takes place from the carbon to the oxygen atom.
The hybridization of carbon changes from \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{2}}}\] to \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is formed.
This intermediate then pulls a proton from the hydrochloric acid to give the cyanohydrin product.
Cyanohydrin compound contains a cyanide group and a hydroxyl group attached to the same carbon atom.
In this case, acetone cyanohydrin is formed as the product.
The reaction occurs as follows:
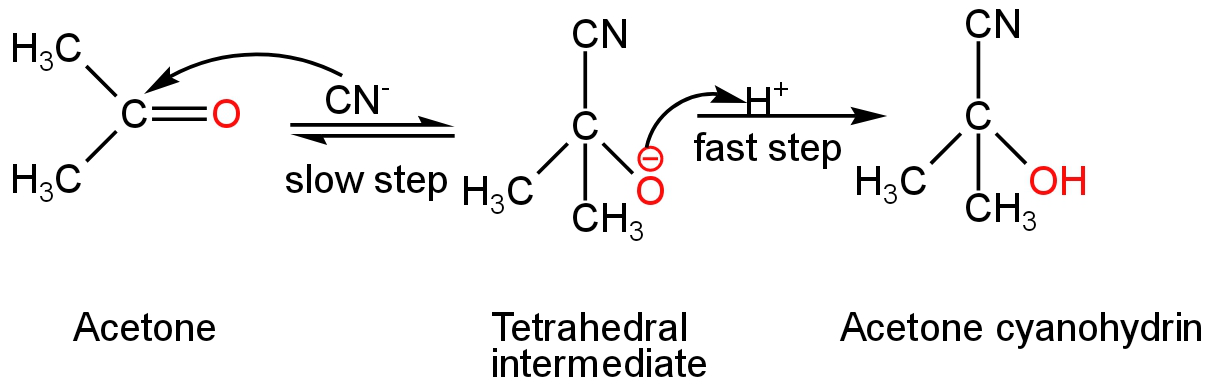
Image: Nucleophilic addition of NaCN to acetone.
Then the acetone cyanohydrin on hydrolysis 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
The reaction will occur as follows: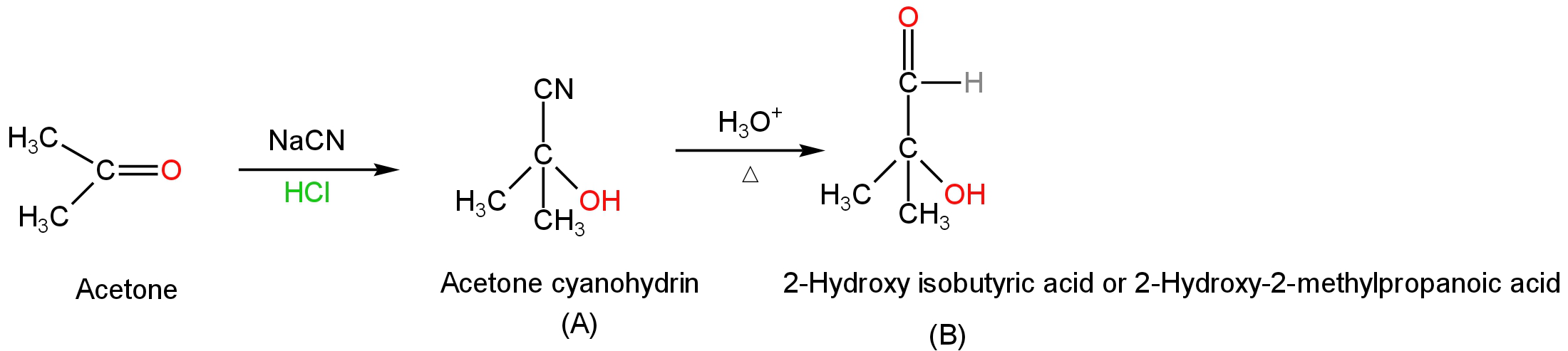
Image: Formation of acetone cyanohydrin followed by hydrolysis.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Acetone on reaction with NaCN in presence of acid forms acetone cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
While attempting the question, one must remember the structure of acetone cyanohydrin and the product it will form on hydrolysis i.e., 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
A cyanohydrin is a functional group of organic compounds having a cyano and a hydroxyl group connected to the same carbon atom.
Cyanohydrin is also called hydroxynitrile.
Complete step-by-step answer: Aldehydes and ketones are highly reactive. These compounds undergo nucleophilic addition reactions.
The carbonyl carbon is quite polar. Due to the greater electronegativity of oxygen, as compared to carbon, the carbon atom possesses a small positive charge.
So, the carbon atom acts as an electrophile.
Therefore, a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbon atom of the polar carbonyl group.
In the given reaction, acetone is treated with NaCN in the presence of hydrochloric acid.
Here, \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{N}}^{\rm{ - }}}\] acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the acetone molecule.
This step is the slowest.
During this process, the complete transfer of pi-electrons of the carbon-oxygen double bond takes place from the carbon to the oxygen atom.
The hybridization of carbon changes from \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{2}}}\] to \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is formed.
This intermediate then pulls a proton from the hydrochloric acid to give the cyanohydrin product.
Cyanohydrin compound contains a cyanide group and a hydroxyl group attached to the same carbon atom.
In this case, acetone cyanohydrin is formed as the product.
The reaction occurs as follows:

Image: Nucleophilic addition of NaCN to acetone.
Then the acetone cyanohydrin on hydrolysis 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
The reaction will occur as follows:

Image: Formation of acetone cyanohydrin followed by hydrolysis.
So, option A is correct.
Note: Acetone on reaction with NaCN in presence of acid forms acetone cyanohydrin which on hydrolysis forms 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
While attempting the question, one must remember the structure of acetone cyanohydrin and the product it will form on hydrolysis i.e., 2-hydroxy isobutyric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




