
Carbolic acid is [AFMC $2005$]
A.${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}CHO$
B.${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}$
C.${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}COOH$
D.${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Carbolic acid is an aromatic and volatile crystalline compound. As it is mildly acidic and it can cause chemical burns, we should handle it very carefully. In aqueous medium carbolic acid loses one proton and thus gains stability due to the delocalization of negative charge throughout the aromatic ring.
Complete answer:Carbolic acid is an organic aromatic acid as it contains a phenyl group bonded to a $-OH$. Phenol is often called carbolic acid. So, the chemical formula of carbolic acid is the same as phenol. That is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$. Thus the structures of carbolic acid can be drawn in the following ways:
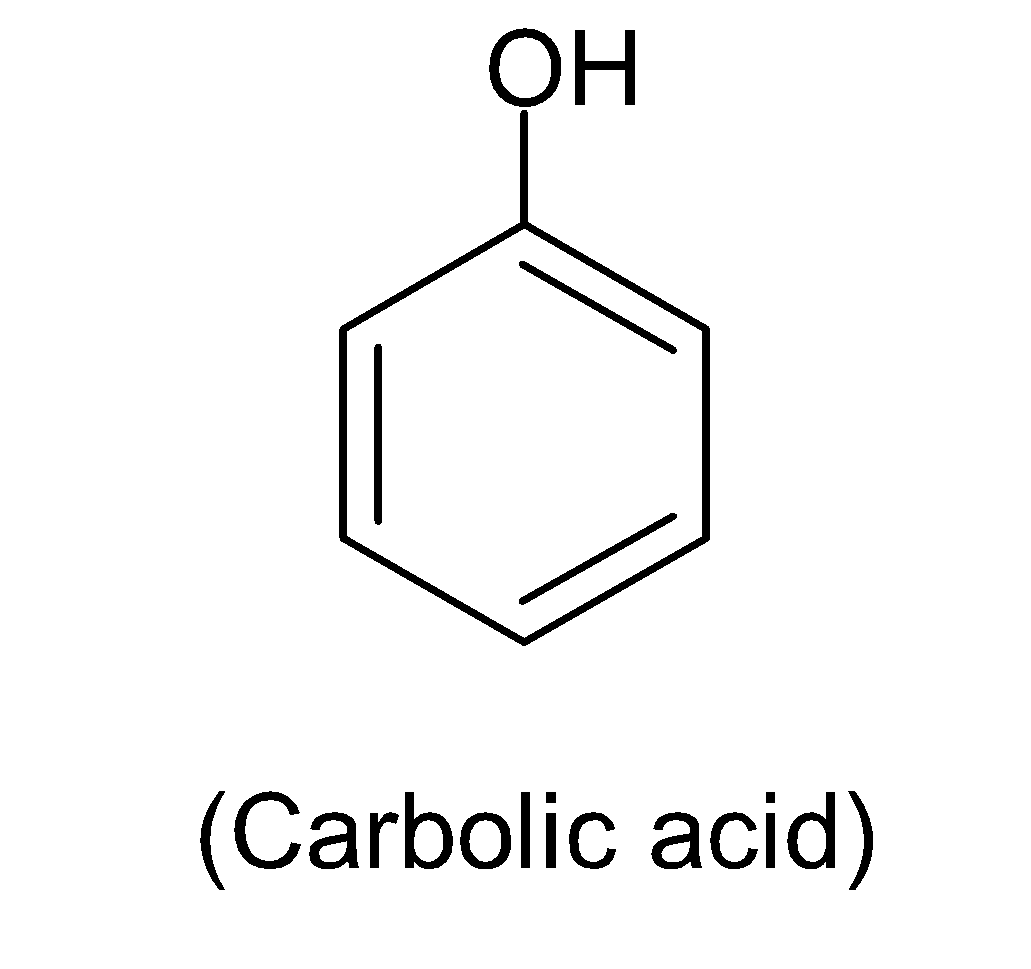
Here in this structure, we can see a $-OH$group is attached to benzene via a single bond. This alcoholic $-OH$group creates a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and due to the high electronegativity of oxygen facilitates the breaking of this polar $O-H$bond, thereby losing one ${{H}^{+}}$ion to form the most stabilized resonance structures which can be shown in below:

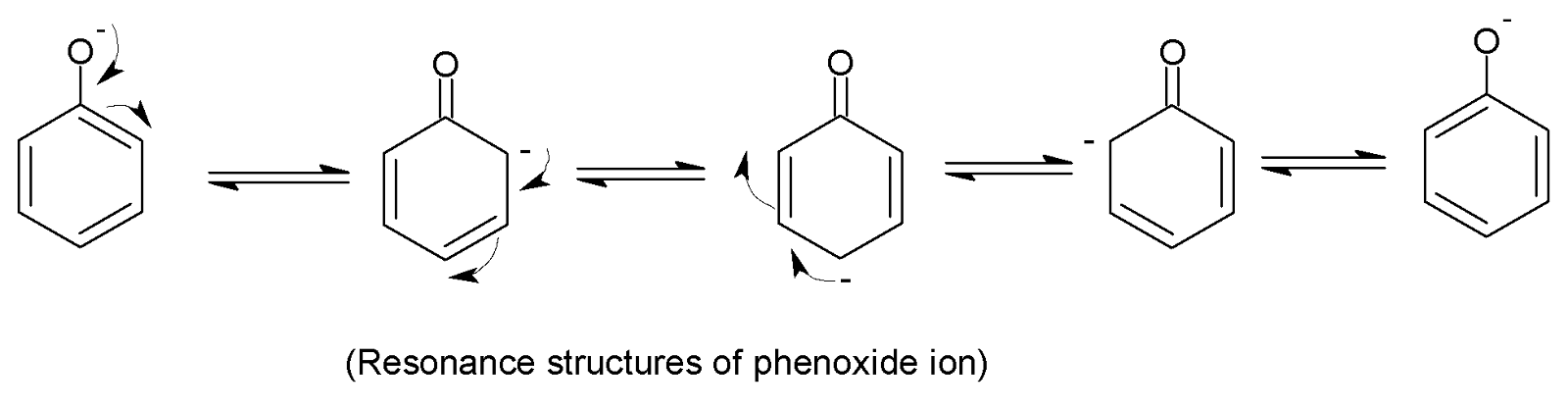
Carbolic acid is an older name for phenol or hydroxy benzene with the chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: Carbolic acid is one of the oldest antiseptic agents. It is widely used in the household to prevent snake infestation and is a versatile precursor to a large collection of drugs for example aspirin as well as many other pharmaceutical herbicides and drugs. Carbolic acid also has many commercial applications for the production of plastics, polycarbonates, epoxides, etc.
Complete answer:Carbolic acid is an organic aromatic acid as it contains a phenyl group bonded to a $-OH$. Phenol is often called carbolic acid. So, the chemical formula of carbolic acid is the same as phenol. That is ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$. Thus the structures of carbolic acid can be drawn in the following ways:

Here in this structure, we can see a $-OH$group is attached to benzene via a single bond. This alcoholic $-OH$group creates a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and due to the high electronegativity of oxygen facilitates the breaking of this polar $O-H$bond, thereby losing one ${{H}^{+}}$ion to form the most stabilized resonance structures which can be shown in below:


Carbolic acid is an older name for phenol or hydroxy benzene with the chemical formula ${{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}OH$.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: Carbolic acid is one of the oldest antiseptic agents. It is widely used in the household to prevent snake infestation and is a versatile precursor to a large collection of drugs for example aspirin as well as many other pharmaceutical herbicides and drugs. Carbolic acid also has many commercial applications for the production of plastics, polycarbonates, epoxides, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




