
\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl + KCN\left( {aq.} \right) \to X + Y\]. Compounds X and Y are
A. \[{C_6}{H_6} + KCl\]
B. \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}CN + KCl\]
C. \[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_3} + KCl\]
D. None of these
Answer
242.7k+ views
Hint: The reaction in question will be a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Potassium cyanide (\[KCN\]) will supply the nucleophile which is the cyanide ion (\[C{N^ - }\]) which will substitute the benzyl chloride (\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]) molecule.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We have been asked to predict the products when potassium cyanide (\[KCN\]) reacts with benzyl chloride (\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]).
Potassium cyanide is a salt and thus, it dissociates in aqueous solutions into potassium ions (\[{K^ + }\]) and cyanide ions (\[C{N^ - }\]) as shown below:
\[KCN(aq) \rightleftharpoons {K^ + }(aq) + C{N^ - }(aq)\]
In benzyl chloride, the chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the benzyl carbon atom. Therefore, the bond between these atoms is polarized toward the chlorine atom. This makes the chlorine atom of benzyl chloride a good leaving group. It can leave as a chloride ion (\[C{l^ - }\]) leaving behind a benzyl carbocation. The chlorine atom being a good leaving group is also aided by the fact that the benzyl carbocation formed is a stable one since the positive charge is delocalized over the ring due to resonance.
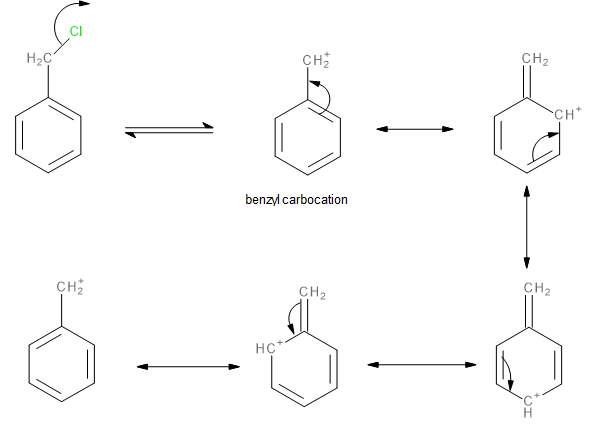
Image: Formation of carbocation
The reaction between\[KCN\] and benzyl chloride is a nucleophilic substitution following the \[{S_N}1\]mechanism.
In the first step of the reaction, the chlorine departs the benzyl chloride molecule as a chloride ion resulting in a benzyl carbocation formation as mentioned previously. The resonance-stabilised benzyl carbocation is attacked by the nucleophilic cyanide ion leading to the formation of 2-phenylacetonitrile. This process is shown below:
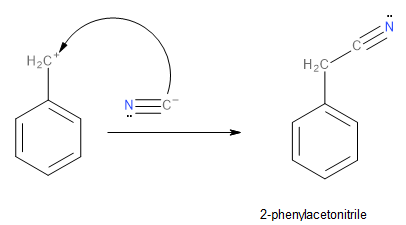
Image: Formation of 2-phenylacetonitrile
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: It is important to remember that this reaction will produce a mixture of products which will be racemic. This is because the benzyl carbocation is planar. Thus, the cyanide ion can attack it from either side of the plane. This leads to the formation of a racemic mixture of 2-phenylacetonitrile. Remember that all\[{S_N}1\] reactions lead to the racemisation of the product.

Image: Racemic mixture
Complete Step by Step Solution:
We have been asked to predict the products when potassium cyanide (\[KCN\]) reacts with benzyl chloride (\[{C_6}{H_5}C{H_2}Cl\]).
Potassium cyanide is a salt and thus, it dissociates in aqueous solutions into potassium ions (\[{K^ + }\]) and cyanide ions (\[C{N^ - }\]) as shown below:
\[KCN(aq) \rightleftharpoons {K^ + }(aq) + C{N^ - }(aq)\]
In benzyl chloride, the chlorine atom is much more electronegative than the benzyl carbon atom. Therefore, the bond between these atoms is polarized toward the chlorine atom. This makes the chlorine atom of benzyl chloride a good leaving group. It can leave as a chloride ion (\[C{l^ - }\]) leaving behind a benzyl carbocation. The chlorine atom being a good leaving group is also aided by the fact that the benzyl carbocation formed is a stable one since the positive charge is delocalized over the ring due to resonance.

Image: Formation of carbocation
The reaction between\[KCN\] and benzyl chloride is a nucleophilic substitution following the \[{S_N}1\]mechanism.
In the first step of the reaction, the chlorine departs the benzyl chloride molecule as a chloride ion resulting in a benzyl carbocation formation as mentioned previously. The resonance-stabilised benzyl carbocation is attacked by the nucleophilic cyanide ion leading to the formation of 2-phenylacetonitrile. This process is shown below:

Image: Formation of 2-phenylacetonitrile
Thus, the correct option is B.
Note: It is important to remember that this reaction will produce a mixture of products which will be racemic. This is because the benzyl carbocation is planar. Thus, the cyanide ion can attack it from either side of the plane. This leads to the formation of a racemic mixture of 2-phenylacetonitrile. Remember that all\[{S_N}1\] reactions lead to the racemisation of the product.

Image: Racemic mixture
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




