
$BrF_3$ is a liquid that considerably undergoes self-ionisation to form cationic and anionic species. Based on VSEPR theory, how many $90^o$ $F-Br-F$ bond angles are there in anionic species?
A. 4
B. 5
C. 3
D. 2
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: $Br{{F}_{3}}$ which is a liquid that considerably undergoes self-ionisation to give a cationic and anionic species in solution. To solve this problem first we have to determine the hybridization of central metal ions in the anionic species by applying the VSEPR theory. Because the bond angle depends upon the hybridization of the central metal ion.
Formula: General according to VSEPR rule the hybridization formula,
$H=\dfrac{V+X-C+A}{2}$
Here H = Hybridisation
V = Number of valence shell electrons of the central atom
X = Number of monovalent atoms around the central atom
C = Positive charge on cation
D = Negative charge on the anion
And the number of lone pairs = $H-$ Total number of bond pairs
Complete Step by Step Answer:
$Br{{F}_{3}}$, bromine trifluoride is a liquid compound of fluoride of bromine and an interhalogen compound. It undergoes self-ionisation to give a cationic species, ${{[Br{{F}_{2}}]}^{+}}$ and an anionic species, ${{[Br{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$.
$2Br{{F}_{3}}\rightleftharpoons {{[Br{{F}_{2}}]}^{+}}+{{[Br{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$
By applying the hybridization formula, we get the hybridization of the central bromine atom in the anionic species.
$H=\dfrac{V+X-C+A}{2}$
Here, V = valence electron of Br atom = $7$
X = Number of fluorine atoms = $4$
C = positive charge = $0$
A = Negative charge on anion = $-1$
$H=\dfrac{7+4-0+1}{2}=6$
Hybridization $6$ means the Br atom has $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization of octahedral geometry.
The number of lone pairs = $(6-4)=2$
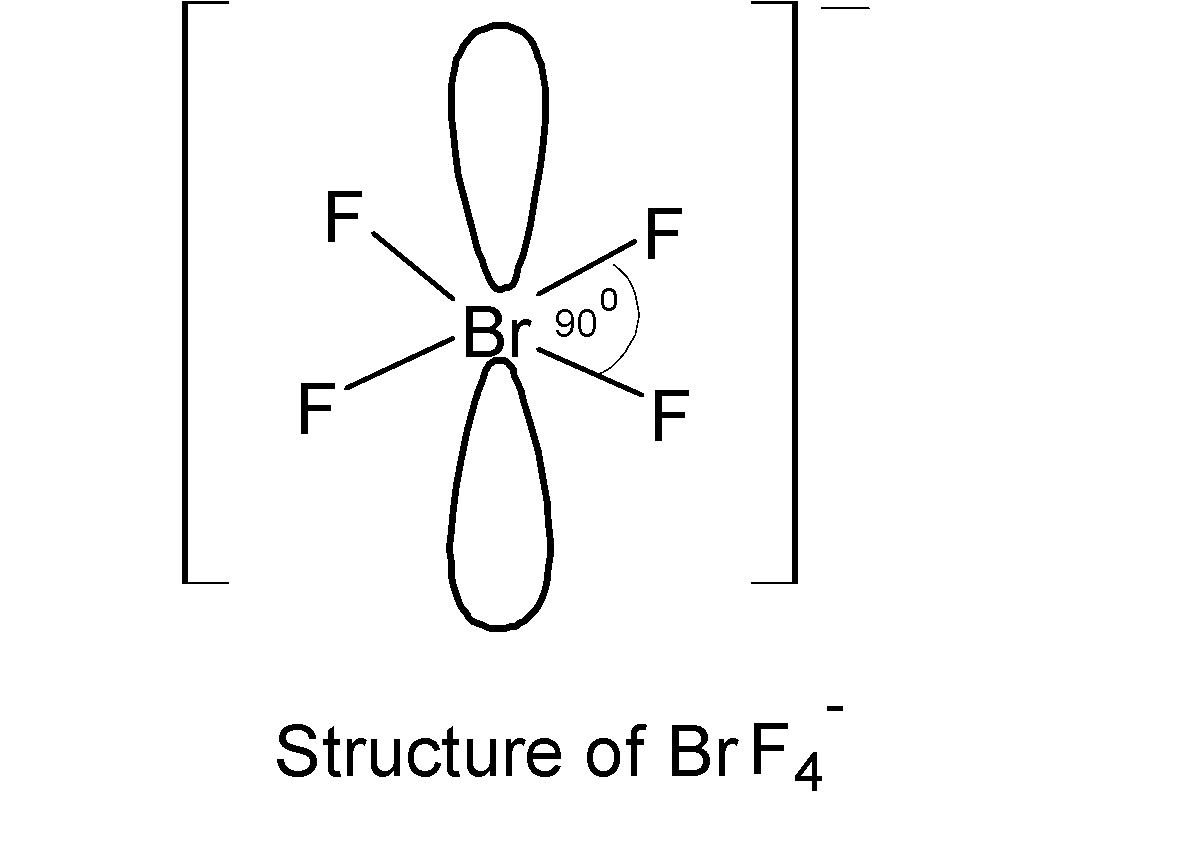
It is found that the anionic species have octahedral geometry and four Br atoms on the plane and thereby making four ${{90}^{{\mathrm O}}}$, $F-Br-F$ equatorial bond angles on the plane.
Therefore based on VSEPR theory, there are four ${{90}^{{\mathrm O}}}$, $F-Br-F$ bond angles are there in anionic species, $BrF_{4}^{-}$.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: According to VSEPR theory the repulsion between the valence electron pair and the outermost shell of the central atom decides the shape of the molecule. The electronegativity of bonded atoms affects bond angle. It is because of changing the distribution of electron pairs around the central atom.
Formula: General according to VSEPR rule the hybridization formula,
$H=\dfrac{V+X-C+A}{2}$
Here H = Hybridisation
V = Number of valence shell electrons of the central atom
X = Number of monovalent atoms around the central atom
C = Positive charge on cation
D = Negative charge on the anion
And the number of lone pairs = $H-$ Total number of bond pairs
Complete Step by Step Answer:
$Br{{F}_{3}}$, bromine trifluoride is a liquid compound of fluoride of bromine and an interhalogen compound. It undergoes self-ionisation to give a cationic species, ${{[Br{{F}_{2}}]}^{+}}$ and an anionic species, ${{[Br{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$.
$2Br{{F}_{3}}\rightleftharpoons {{[Br{{F}_{2}}]}^{+}}+{{[Br{{F}_{4}}]}^{-}}$
By applying the hybridization formula, we get the hybridization of the central bromine atom in the anionic species.
$H=\dfrac{V+X-C+A}{2}$
Here, V = valence electron of Br atom = $7$
X = Number of fluorine atoms = $4$
C = positive charge = $0$
A = Negative charge on anion = $-1$
$H=\dfrac{7+4-0+1}{2}=6$
Hybridization $6$ means the Br atom has $s{{p}^{3}}{{d}^{2}}$ hybridization of octahedral geometry.
The number of lone pairs = $(6-4)=2$

It is found that the anionic species have octahedral geometry and four Br atoms on the plane and thereby making four ${{90}^{{\mathrm O}}}$, $F-Br-F$ equatorial bond angles on the plane.
Therefore based on VSEPR theory, there are four ${{90}^{{\mathrm O}}}$, $F-Br-F$ bond angles are there in anionic species, $BrF_{4}^{-}$.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: According to VSEPR theory the repulsion between the valence electron pair and the outermost shell of the central atom decides the shape of the molecule. The electronegativity of bonded atoms affects bond angle. It is because of changing the distribution of electron pairs around the central atom.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




