
What is the best frequency for FM transmitters?
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A transmitter and receiver are components of every communication system, and the transmitter sends the signal as waves such that the waves being sent have a certain frequency. And the signal with a certain frequency is likewise picked up by the receiver.
Complete step by step solution:
An electronic device known as a radio or FM receiver receives radio waves or signals and transforms the data they carry into a form that may be used. To receive the necessary frequency waves or signals and transform them into information, an antenna is utilised.
The necessary frequency waves or signals will be separated from the other signals using an electrical filter. An electronic amplifier is used to increase the power and the strength of the signal for the next process and finally gets the required information through the demodulation in the receiver.
The most often used radio wave modulation is frequency modulation. The radio waves are frequently broadcast via frequency modulation. Additionally, it is frequently used in telephony, RADAR, multi-way radio systems, musical instruments, magnetic recording systems, and some visual transmission systems, as well as for monitoring newborn babies using electroencephalograms.
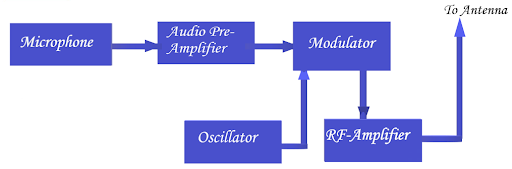
The carrier wave frequency is equivalent to the audio signal of the amplitude and the FM transmitter to produce a VHF band of \[88\] to \[108MHz\].
Therefore, the frequency range best for FM transmission is \[88-108{\text{ }}MHz\] band, this is the frequency range at which all the broadcast radio works.
Note: The radio frequency (RF) amplifier picks up the radio waves or signals and sends them to the mixer, which then sends the signal or waves to the filter, where the required frequency of the wave or signal is separated and given to the demodulator, where it is transformed into audio data.
Complete step by step solution:
An electronic device known as a radio or FM receiver receives radio waves or signals and transforms the data they carry into a form that may be used. To receive the necessary frequency waves or signals and transform them into information, an antenna is utilised.
The necessary frequency waves or signals will be separated from the other signals using an electrical filter. An electronic amplifier is used to increase the power and the strength of the signal for the next process and finally gets the required information through the demodulation in the receiver.
The most often used radio wave modulation is frequency modulation. The radio waves are frequently broadcast via frequency modulation. Additionally, it is frequently used in telephony, RADAR, multi-way radio systems, musical instruments, magnetic recording systems, and some visual transmission systems, as well as for monitoring newborn babies using electroencephalograms.

The carrier wave frequency is equivalent to the audio signal of the amplitude and the FM transmitter to produce a VHF band of \[88\] to \[108MHz\].
Therefore, the frequency range best for FM transmission is \[88-108{\text{ }}MHz\] band, this is the frequency range at which all the broadcast radio works.
Note: The radio frequency (RF) amplifier picks up the radio waves or signals and sends them to the mixer, which then sends the signal or waves to the filter, where the required frequency of the wave or signal is separated and given to the demodulator, where it is transformed into audio data.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




