
Assertion: In photo emissive cells inert gas is used.
Reason: Inert gas in the photo emissive cell gives greater current.
A. If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
B. If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
C. If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
D. If the assertion and reason both are false
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Based on the photoelectric effect, photo-emissive cells emit light. A substance releasing or containing electrically charged particles as a result of absorbing electromagnetic radiation. We first understand about the photocell and its working to answer this question.
Complete step by step solution:
First, understanding what a photoelectric cell is, often known as a photocell, is an electronic gadget that transforms light energy into electrical energy using the photoelectric effect as its basis. The earliest method of converting light into energy is using photoemissive cells.
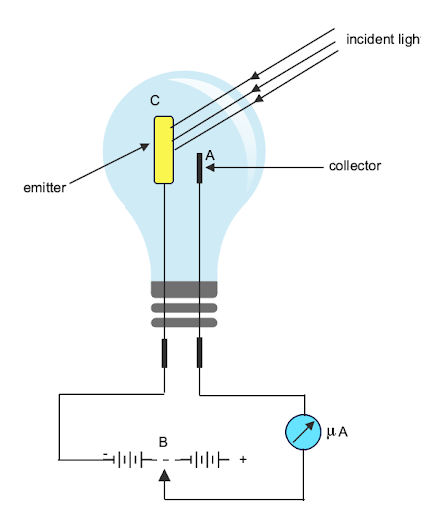
It comprises evacuated glass or quartz bulbs with an anode and cathode made of two metallic electrodes. Anode A is a thin rod or wire held along the axis of semi-cylindrical cathode C, which is semicircular in shape and coated with photosensitive material. Through the galvanometer, the potential difference is applied between cathode and anode.
When the electrons are released, the anode will draw them, which causes the current to move and be detected by the galvanometer. The amount of incident radiation and the potential difference between the cathode and anode will determine how much current is generated.
The photo emissive cell may be evacuated to release a low-pressure inert gas. Greater current is produced by an inert gas inside the cell, but this compromises the cell's ability to react quickly to changes in radiation, which may make it inappropriate for particular applications.
Hence option A is correct.
Note: Photo emissive cells are compact, affordable, low power, simple to operate, and durable. Photovoltaic and photoconductive cells are distinct from phototube and photoelectric cells, which are the same as photoemissive cells. Helium, neon, argon, or another inert gas is used to fill the cell's bulb.
Complete step by step solution:
First, understanding what a photoelectric cell is, often known as a photocell, is an electronic gadget that transforms light energy into electrical energy using the photoelectric effect as its basis. The earliest method of converting light into energy is using photoemissive cells.

It comprises evacuated glass or quartz bulbs with an anode and cathode made of two metallic electrodes. Anode A is a thin rod or wire held along the axis of semi-cylindrical cathode C, which is semicircular in shape and coated with photosensitive material. Through the galvanometer, the potential difference is applied between cathode and anode.
When the electrons are released, the anode will draw them, which causes the current to move and be detected by the galvanometer. The amount of incident radiation and the potential difference between the cathode and anode will determine how much current is generated.
The photo emissive cell may be evacuated to release a low-pressure inert gas. Greater current is produced by an inert gas inside the cell, but this compromises the cell's ability to react quickly to changes in radiation, which may make it inappropriate for particular applications.
Hence option A is correct.
Note: Photo emissive cells are compact, affordable, low power, simple to operate, and durable. Photovoltaic and photoconductive cells are distinct from phototube and photoelectric cells, which are the same as photoemissive cells. Helium, neon, argon, or another inert gas is used to fill the cell's bulb.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




