
Assertion: Bond angle of $P{{F}_{3}}>PC{{l}_{3}}$ but bond angle of $PC{{l}_{3}}<\text{PB}{{\text{r}}_{3}}$
Reason: The bond angles show an increase in decreasing electronegativity of attached other atom on central atom but $P{{F}_{3}}\text{ p}\pi \text{-d}\pi $bonding results in an increase in bond angle.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation for the assertion.
(B) Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation for the assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect
(D) Assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Bond angle of Phosphorus trifluoride is 97 degrees, Bond angle of phosphorous trichloride is 100 degrees and phosphorus tribromide had a bond angle of 101.5 degrees. As we move across the group, bond pair repulsion increases more as compared to lone pair-bond pair repulsion
Complete step by step solution:
Atomic number of phosphorus is 15. Electronic configuration of phosphorus is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$
As phosphorus forms, three bonds, three electrons from 3p orbital are involved in chemical bonding and two electrons from 3s are a lone pair.
Electronegativity of phosphorus is 2.1, Chlorine has electronegativity as 3.2 and for Fluorine, electronegativity is 4.
There are two types of electron repulsion: one is repulsion between Lone pair and bond pair
And second is repulsion between bond pair and bond pair.
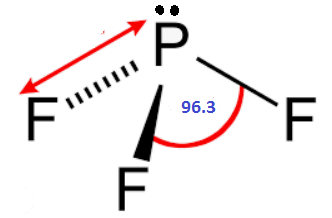
The bond angle of Phosphorus trifluoride is 97 degrees, Bond angle of phosphorus trichloride is 100 degrees and phosphorus tribromide has bond angle of 101.5 degrees.
-Difference in electronegativity between phosphorus and chlorine is lower than that of between phosphorus and Fluorine, so in phosphorus trichloride Bond pair electrons move towards phosphorous which leads to greater repulsion experienced by bond pair-bond pair electrons so the bond angle is greater in phosphorus trichloride as compared to phosphorus trifluoride.
-As size of element increases, electron density also increases, so bond pair-bond pair repulsion also increases.
-As we move across the group, bond pair repulsion increases more as compared to lone pair-bond pair repulsion.
-So the bond angle of phosphorus trifluoride is less than phosphorus trichloride.
Hence, the correct answer is (D) Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Note: There are two types of electron repulsion: one is repulsion between Lone pair and bond pair and second is repulsion between bond pair and bond pair. In phosphorus trichloride Bond pair electrons move towards phosphorus which leads to greater repulsion experienced by bond pair-bond pair electrons so the bond angle is greater in phosphorus trichloride as compared to phosphorus trifluoride.
Complete step by step solution:
Atomic number of phosphorus is 15. Electronic configuration of phosphorus is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{3}}$
As phosphorus forms, three bonds, three electrons from 3p orbital are involved in chemical bonding and two electrons from 3s are a lone pair.
Electronegativity of phosphorus is 2.1, Chlorine has electronegativity as 3.2 and for Fluorine, electronegativity is 4.

There are two types of electron repulsion: one is repulsion between Lone pair and bond pair
And second is repulsion between bond pair and bond pair.
The bond angle of Phosphorus trifluoride is 97 degrees, Bond angle of phosphorus trichloride is 100 degrees and phosphorus tribromide has bond angle of 101.5 degrees.
-Difference in electronegativity between phosphorus and chlorine is lower than that of between phosphorus and Fluorine, so in phosphorus trichloride Bond pair electrons move towards phosphorous which leads to greater repulsion experienced by bond pair-bond pair electrons so the bond angle is greater in phosphorus trichloride as compared to phosphorus trifluoride.
-As size of element increases, electron density also increases, so bond pair-bond pair repulsion also increases.
-As we move across the group, bond pair repulsion increases more as compared to lone pair-bond pair repulsion.
-So the bond angle of phosphorus trifluoride is less than phosphorus trichloride.
Hence, the correct answer is (D) Assertion is incorrect but reason is correct.
Note: There are two types of electron repulsion: one is repulsion between Lone pair and bond pair and second is repulsion between bond pair and bond pair. In phosphorus trichloride Bond pair electrons move towards phosphorus which leads to greater repulsion experienced by bond pair-bond pair electrons so the bond angle is greater in phosphorus trichloride as compared to phosphorus trifluoride.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




