
What are the parts of the transformer?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Transformers works on the principle of mutual induction. It helps in changing the alternating voltage from one to another of greater or smaller value. It mainly consists of two coils insulated from each other and it is usually wound on a soft iron core or magnetic core.
Complete answer:
* The transformers work on the principle of mutual induction, which can be defined as the change in electric current passing through one coil induces an emf in the neighbouring coil and the induced emf is called mutually induced emf.
* The parts of the transformer are the primary coil and the secondary coil which is wound on a soft iron core and insulated from each other. They are either wounded on top of the other or on separate limbs of the soft iron core or magnetic core.
* When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary coil, it produces an alternating magnetic flux that links the secondary coil and induces an emf in it.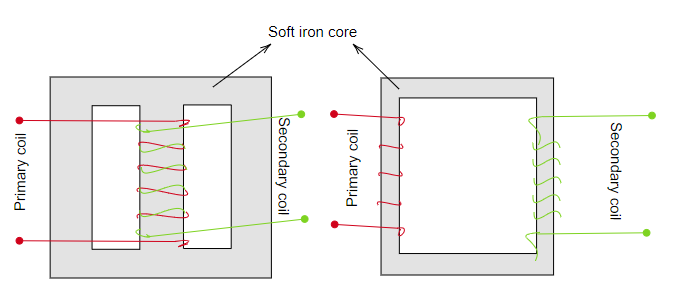
*The transforms are mainly used in the process where it is necessary to change the alternating voltage from one or another of greater or smaller value. So the transformer is of two types.
1. Step-up transformer
2. Step-down transformer
* In the transformer, when the alternating voltage in the primary coil is less than the secondary coil it is called step-up transformer, similarly, when the primary coil has higher alternating voltage than the secondary coil, then it is a step-down transformer.
So the main parts of the transformer are, 1. Primary coil, 2. Secondary coil, 3. Magnetic core. The other parts which are used in the overall process are vents, shafts, brushes, etc,.
Note: Usually the primary coil is used to apply the alternating current and the secondary coil is where the induced emf is measured. The value of this emf is based on the number of turnings of the secondary coil. The number of turns of the primary coil is \[{N_p}\] and the number of turns for the secondary coil is \[{N_s}\] .
Complete answer:
* The transformers work on the principle of mutual induction, which can be defined as the change in electric current passing through one coil induces an emf in the neighbouring coil and the induced emf is called mutually induced emf.
* The parts of the transformer are the primary coil and the secondary coil which is wound on a soft iron core and insulated from each other. They are either wounded on top of the other or on separate limbs of the soft iron core or magnetic core.
* When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary coil, it produces an alternating magnetic flux that links the secondary coil and induces an emf in it.

*The transforms are mainly used in the process where it is necessary to change the alternating voltage from one or another of greater or smaller value. So the transformer is of two types.
1. Step-up transformer
2. Step-down transformer
* In the transformer, when the alternating voltage in the primary coil is less than the secondary coil it is called step-up transformer, similarly, when the primary coil has higher alternating voltage than the secondary coil, then it is a step-down transformer.
So the main parts of the transformer are, 1. Primary coil, 2. Secondary coil, 3. Magnetic core. The other parts which are used in the overall process are vents, shafts, brushes, etc,.
Note: Usually the primary coil is used to apply the alternating current and the secondary coil is where the induced emf is measured. The value of this emf is based on the number of turnings of the secondary coil. The number of turns of the primary coil is \[{N_p}\] and the number of turns for the secondary coil is \[{N_s}\] .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




