
An object is moving towards a stationary plane mirror with a speed of \[2m{s^{ - 1}}\]in left. Velocity of the image w.r.t. the object is:
a. \[2m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards right
b. \[4m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards right
c. \[2m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards left
D. \[4m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards left
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When it comes to solving this type of question from optical physics we must know the concepts clearly that whenever there is any object placed in front of the mirror and it’s moving with any speed then the reflection (image) also moves with same speed in the opposite direction of the movement of the object.
Complete answer:
When the object is kept in front of the mirror which is stationary and plane and that object is moving with the speed of \[2m{s^{ - 1}}\]in left of the mirror.
For this we have to draw a diagram that will explain the situation presented in the question.
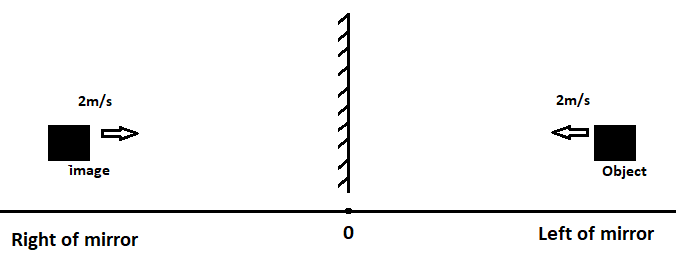
Here, in the above figure we get to know that the object and image are identical and is known as the first law of reflection, size and shape remains same there will be no change. Second thing is that the speed of will remain same in magnitude but different in the direction.
So, let us say \[{v_o}\] be the velocity of the object and \[{v_i}\] be the velocity of the image. Thus according to given condition the left of the mirror represents similarity to the number line that means left side will be positive numbered side and right side will be negative numbered side.
Thus the direction being opposite the velocities are given by:
\[{v_o} = - 2m{s^{ - 1}}\] and \[{v_i} = 2m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Negative because moving in opposite directions.
Thus the speed of the with respect to the object \[ = {v_i} - {v_o}\]
\[ = 2m{s^{ - 1}} - ( - 2m{s^{ - 1}})\]
\[ = 4m{s^{ - 1}}\]
So, the answer is \[4m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards left of the mirror. Correct option is d.
Note: Here, the image velocity is to be considered as positive since its already representing negative number and with addition to the direction it becomes positive that is why we wrote here in positive format.
Complete answer:
When the object is kept in front of the mirror which is stationary and plane and that object is moving with the speed of \[2m{s^{ - 1}}\]in left of the mirror.
For this we have to draw a diagram that will explain the situation presented in the question.
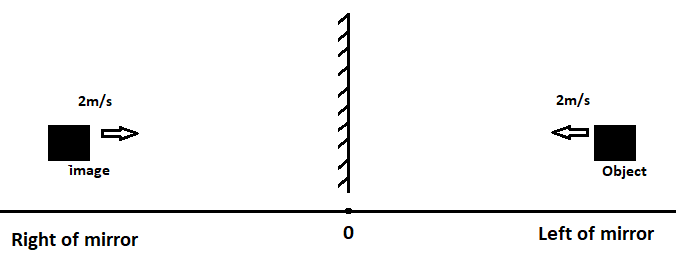
Here, in the above figure we get to know that the object and image are identical and is known as the first law of reflection, size and shape remains same there will be no change. Second thing is that the speed of will remain same in magnitude but different in the direction.
So, let us say \[{v_o}\] be the velocity of the object and \[{v_i}\] be the velocity of the image. Thus according to given condition the left of the mirror represents similarity to the number line that means left side will be positive numbered side and right side will be negative numbered side.
Thus the direction being opposite the velocities are given by:
\[{v_o} = - 2m{s^{ - 1}}\] and \[{v_i} = 2m{s^{ - 1}}\]
Negative because moving in opposite directions.
Thus the speed of the with respect to the object \[ = {v_i} - {v_o}\]
\[ = 2m{s^{ - 1}} - ( - 2m{s^{ - 1}})\]
\[ = 4m{s^{ - 1}}\]
So, the answer is \[4m{s^{ - 1}}\]towards left of the mirror. Correct option is d.
Note: Here, the image velocity is to be considered as positive since its already representing negative number and with addition to the direction it becomes positive that is why we wrote here in positive format.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




