
Ammonium acetate reacts with acetic acid at \[110^\circ {\rm{C}}\] to form
A. Acetamide
B. Formamide
C. Ammonium cyanate
D. Urea
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ammonium acetate is an organic chemical compound. Its appearance is a crystalline solid of white colour. Its odour is acetous-like. This is the salt prepared by the reaction of acetic acid and ammonia.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s draw the structure of ammonium acetate first.
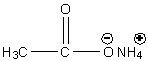
Image: Ammonium acetate
Now, we have to understand the reaction of ammonium acetate with acetic acid at 110 degrees Celsius. When ammonium acetate undergoes a reaction with acetic acid, a loss of water molecules takes place. The chemical reaction is,
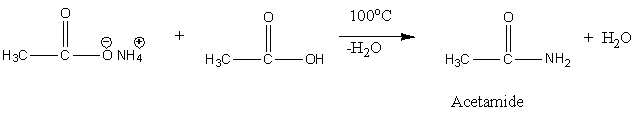
Image: Reaction of ammonium acetate and acetic acid.
Therefore, the reaction of ammonium acetate and acetic acid gives acetamide.
Hence, the option A is right.
Additional Information:
The general name of the compound ethanamide is acetamide. It is chemically represented as\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It is prepared from ethanoic acid. In laboratory preparation, it is prepared from ammonium acetate via the process of dehydration. It smells like ammonia or vinegar.
Note: There is easy solubility of acetamide in water, benzene and chloroform. It belongs to the class of amides that is obtained from the condensation of acetic acid with ammonia. In nature, it is found in beetroot. Some of the uses of acetamides are explosive making, stabiliser, hygroscopic agent etc. It is a substance of combustible nature. The heating of acetamide produces a toxic gas. Exposure to Acetamide is dangerous to health.
Complete step by step solution:
Let’s draw the structure of ammonium acetate first.

Image: Ammonium acetate
Now, we have to understand the reaction of ammonium acetate with acetic acid at 110 degrees Celsius. When ammonium acetate undergoes a reaction with acetic acid, a loss of water molecules takes place. The chemical reaction is,
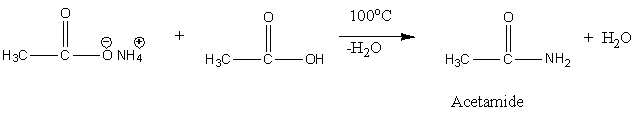
Image: Reaction of ammonium acetate and acetic acid.
Therefore, the reaction of ammonium acetate and acetic acid gives acetamide.
Hence, the option A is right.
Additional Information:
The general name of the compound ethanamide is acetamide. It is chemically represented as\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It is prepared from ethanoic acid. In laboratory preparation, it is prepared from ammonium acetate via the process of dehydration. It smells like ammonia or vinegar.
Note: There is easy solubility of acetamide in water, benzene and chloroform. It belongs to the class of amides that is obtained from the condensation of acetic acid with ammonia. In nature, it is found in beetroot. Some of the uses of acetamides are explosive making, stabiliser, hygroscopic agent etc. It is a substance of combustible nature. The heating of acetamide produces a toxic gas. Exposure to Acetamide is dangerous to health.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




