
A uniform horizontal meter scale of mass m is suspended by two vertical strings attached to its two ends. A body of mass $2m$ is placed on the $75cm$ mark. The tensions in the two strings are in the ratio:
$\left( a \right){\text{ 1:2}}$
$\left( b \right){\text{ 1:3}}$
$\left( c \right){\text{ 2:3}}$
$\left( d \right){\text{ 3:4}}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint So here to solve this type of problem, we should have the basic knowledge of the tension. Firstly we will take out the rotational equilibrium which will be corresponding to the $T1$. And in the same way, we will find them $T2$ , and then we will be able to find the ratio of the tension in the string.
Complete Step By Step Solution First of all we all know, according to the question the net tension produced will be equal to the sum of the two tension applied to it.
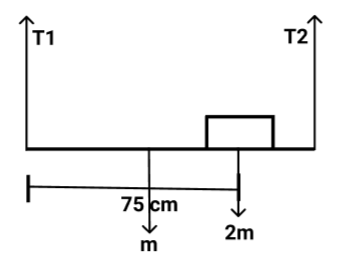
Here,
$ \Rightarrow T1 + T2 = 2mg + 1mg$
So it will be equal to the
$ \Rightarrow T1 + T2 = 3mg$
Now taking tension about the left side of the plank, we will get
$ \Rightarrow 0.5mg + 0.75 \times 2mg = 1 \times T2$
And from here, on solving the above equation we will the values as
$ \Rightarrow T2 = 2mg$
And similarly, another torque will be
$ \Rightarrow T1 = mg$
Now we have to find the ratios, therefore the ratio of the tension will be given by
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{T1}}{{T2}} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2mg}}$
And on solving the above, we will get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{T1}}{{T2}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, we can say that
$\dfrac{1}{2}$, will be the ratio of the tension in the strings.
Hence, the option $\left( a \right)$ is correct.
Note As we know the pressure force is the total force compressed matter exerts longitudinally - i.e. the sum of pressure x cross-section area across all parts of the total cross-section. (In math terms, the integral of pressure across the total cross-section.)
So the tension is just the opposite: The integral of tensile stress across the total cross-section. In other words, the total force that tries to stretch a body of matter.
So we can say that the pressure or, respectively, tensile stress (the difference is only in the sign) in the matter is commonly called stress.
Complete Step By Step Solution First of all we all know, according to the question the net tension produced will be equal to the sum of the two tension applied to it.

Here,
$ \Rightarrow T1 + T2 = 2mg + 1mg$
So it will be equal to the
$ \Rightarrow T1 + T2 = 3mg$
Now taking tension about the left side of the plank, we will get
$ \Rightarrow 0.5mg + 0.75 \times 2mg = 1 \times T2$
And from here, on solving the above equation we will the values as
$ \Rightarrow T2 = 2mg$
And similarly, another torque will be
$ \Rightarrow T1 = mg$
Now we have to find the ratios, therefore the ratio of the tension will be given by
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{T1}}{{T2}} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2mg}}$
And on solving the above, we will get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{T1}}{{T2}} = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore, we can say that
$\dfrac{1}{2}$, will be the ratio of the tension in the strings.
Hence, the option $\left( a \right)$ is correct.
Note As we know the pressure force is the total force compressed matter exerts longitudinally - i.e. the sum of pressure x cross-section area across all parts of the total cross-section. (In math terms, the integral of pressure across the total cross-section.)
So the tension is just the opposite: The integral of tensile stress across the total cross-section. In other words, the total force that tries to stretch a body of matter.
So we can say that the pressure or, respectively, tensile stress (the difference is only in the sign) in the matter is commonly called stress.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




