
When a triode is used as an amplifier the phase difference between the input signal voltage and output is:
A) Zero
B) π
C) π/2
D) π/3
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The low-voltage AC signal connected between the grid and cathode alternately suppresses, then enhances the electron flow between the cathode and plate. This causes a change in voltage on the output of the circuit. The AC voltage and current magnitudes on the tube’s grid are generally quite small compared to the variation of voltage and current in the plate circuit. Thus, the triode functions as an amplifier.
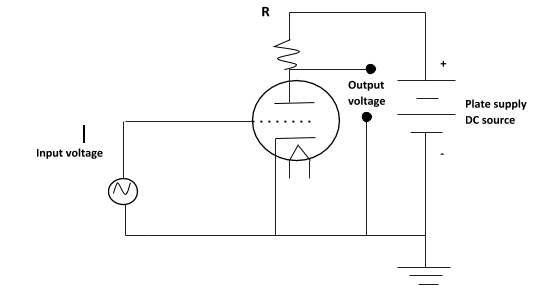
Complete step by step answer:
We know that voltage gain A
$A = \mu {R_L}/({R_L} + {r_p})$……………… (i)
rp =dynamic plate resistance
RL=Load resistance
µ= amplification factor
The amplification factor µ of a triode valve/vacuum tube is a measure of the relative effectiveness of the grid and anode voltages in producing the electrostatic fields at the surface of the cathode.
$\mu = - \dfrac{{\Delta {V_p}}}{{\Delta {V_G}}}$
Substituting the value of $\mu $in eqn(i)
We get $A = - \dfrac{{\Delta {V_p} \times {R_L}}}{{\Delta {V_G} \times ({R_L} + {r_p})}}$
Here,
ΔVp= change in phase voltage
ΔVG= change in grid voltage
The negative sign here shows that input voltage and output voltage are out of phase and out of phase means that the difference between the input voltage signal and the output voltage signal is 180 degrees and we know that in ${180^0} = \pi $radian.
Hence, Option (B) the correct answer.
Note: The triode valve or triode vacuum tube takes the basic concept of the diode and moves it on a significant stage further. A third electrode called a grid or more correctly a control grid is placed between the cathode and anode of the basic diode and by applying a potential to the grid, it is possible to repel or attract the electrons being emitted from the cathode and in this way affect the flow between cathode and anode of the triode vacuum tube.

Complete step by step answer:
We know that voltage gain A
$A = \mu {R_L}/({R_L} + {r_p})$……………… (i)
rp =dynamic plate resistance
RL=Load resistance
µ= amplification factor
The amplification factor µ of a triode valve/vacuum tube is a measure of the relative effectiveness of the grid and anode voltages in producing the electrostatic fields at the surface of the cathode.
$\mu = - \dfrac{{\Delta {V_p}}}{{\Delta {V_G}}}$
Substituting the value of $\mu $in eqn(i)
We get $A = - \dfrac{{\Delta {V_p} \times {R_L}}}{{\Delta {V_G} \times ({R_L} + {r_p})}}$
Here,
ΔVp= change in phase voltage
ΔVG= change in grid voltage
The negative sign here shows that input voltage and output voltage are out of phase and out of phase means that the difference between the input voltage signal and the output voltage signal is 180 degrees and we know that in ${180^0} = \pi $radian.
Hence, Option (B) the correct answer.
Note: The triode valve or triode vacuum tube takes the basic concept of the diode and moves it on a significant stage further. A third electrode called a grid or more correctly a control grid is placed between the cathode and anode of the basic diode and by applying a potential to the grid, it is possible to repel or attract the electrons being emitted from the cathode and in this way affect the flow between cathode and anode of the triode vacuum tube.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




