
A tribasic acid is
A.Oxalic acid
B.Tartaric acid
C.Lactic acid
D.Citric acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: If an acid contains replaceable hydrogen atoms then it is called basicity and a tribasic acid is one that has three replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions. From the given option just we have to find their structure to see that in which acid contains three hydrogen ions to donate to a base in a redox reaction.
Complete answer:When a component is dissolved in water it releases hydrogen ions,${{H}^{+}}$called acid. Generally, basicity is the number of replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions when an acid dissolves in water. If an acid contains one replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ion is called monobasic acid. A dibasic acid contains two replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions and a tribasic acid contains three replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions.
Oxalic acid has a chemical formula $HOOC-COOH$ and it is a polyprotic acid and basicity is equal to $2$. Hence it is a dibasic acid.
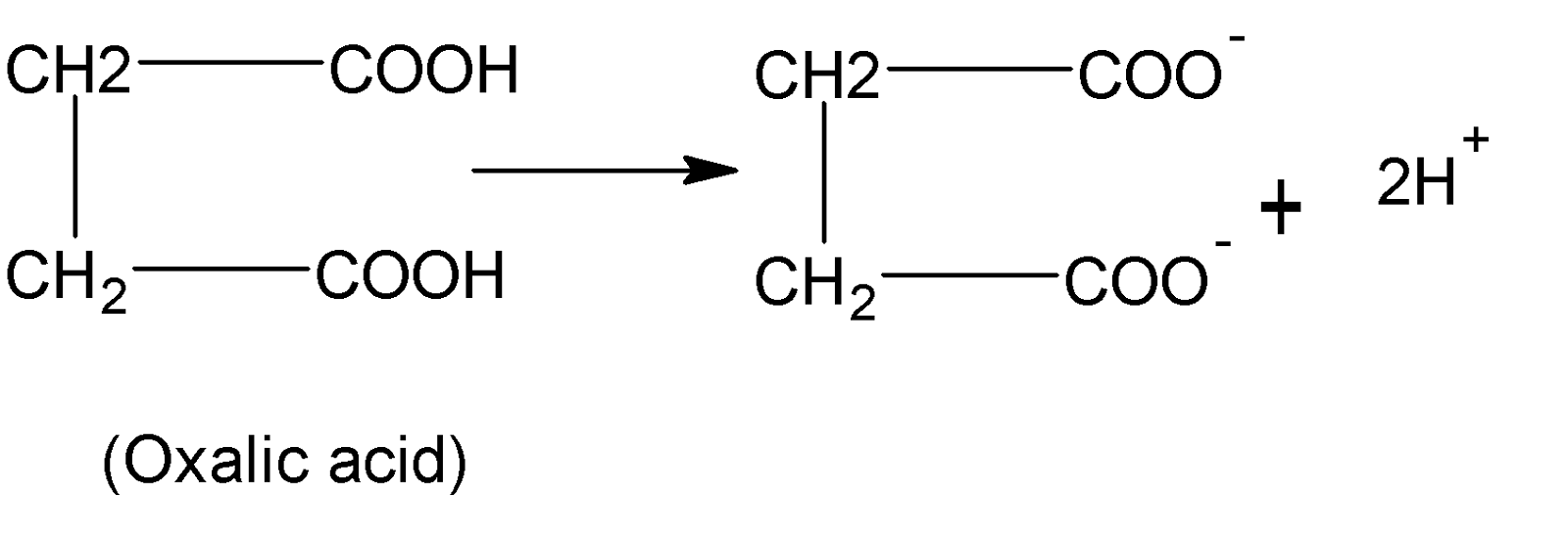
The chemical formula of tartaric acid is ${{[CH(OH)COOH]}_{2}}$. It is also a dibasic acid as it has two replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions.
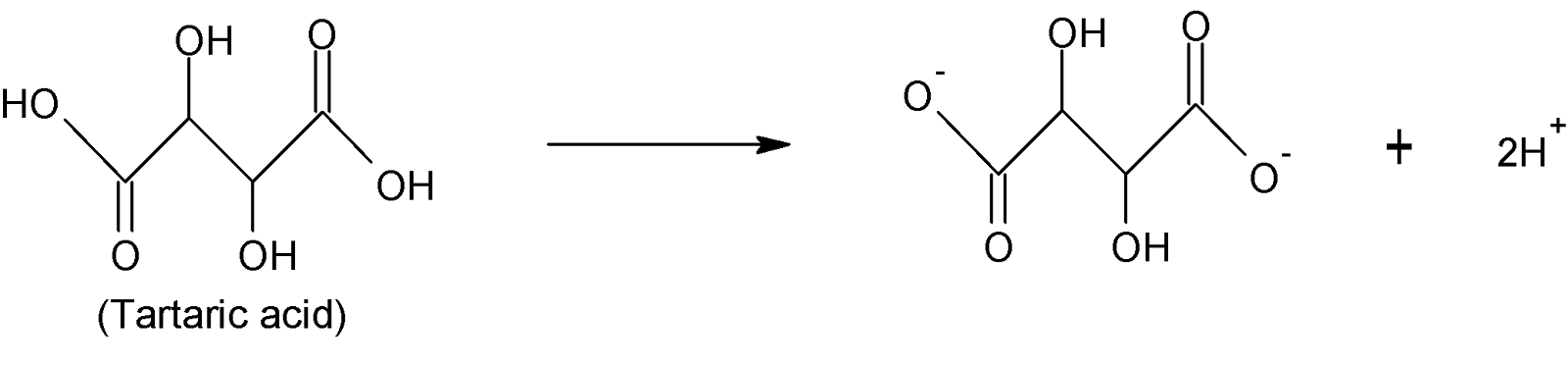
Lactic acid is an organic compound having IUPAC name $2-$hydroxy propanoic acid and chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}CH(OH)COOH$. As it can donate one ${{H}^{+}}$ion to a base thus it is a monobasic acid.
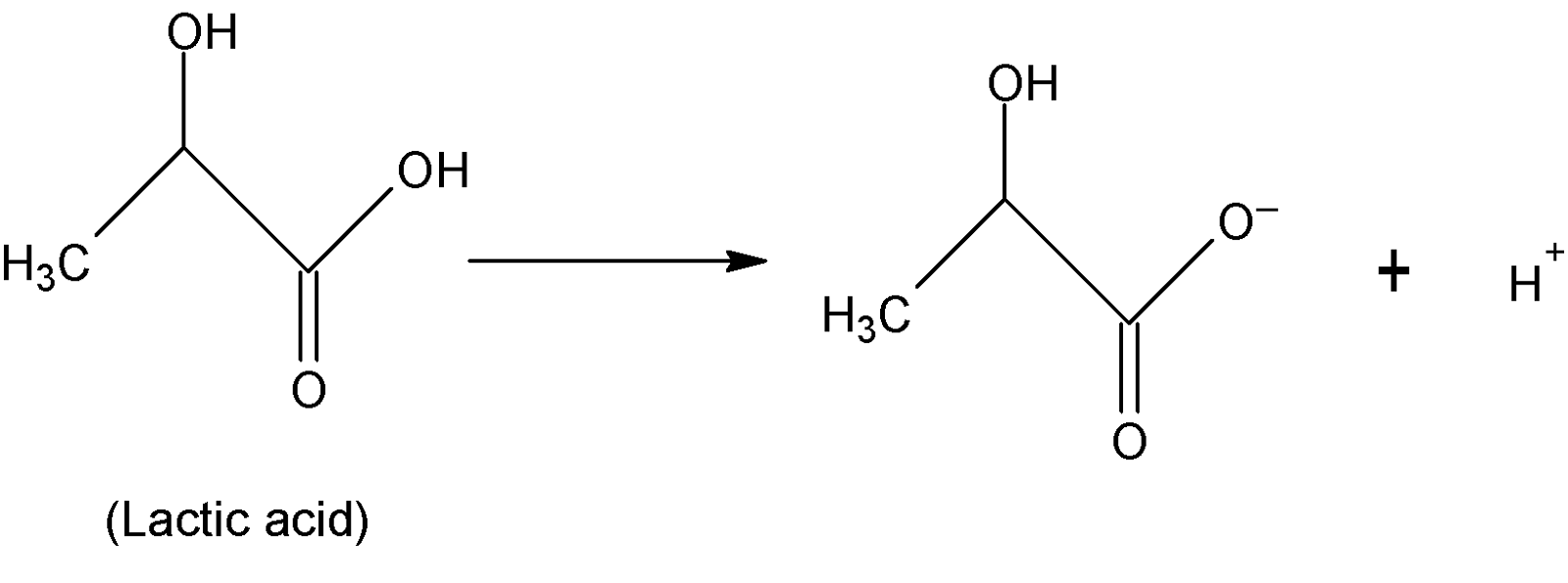
Finally citric acid is an organic compound with a chemical formula $HOOC(HO)C{{(C{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{2}}H)}_{2}}$. Citric acid has basicity $3$ where the number of replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$is three.
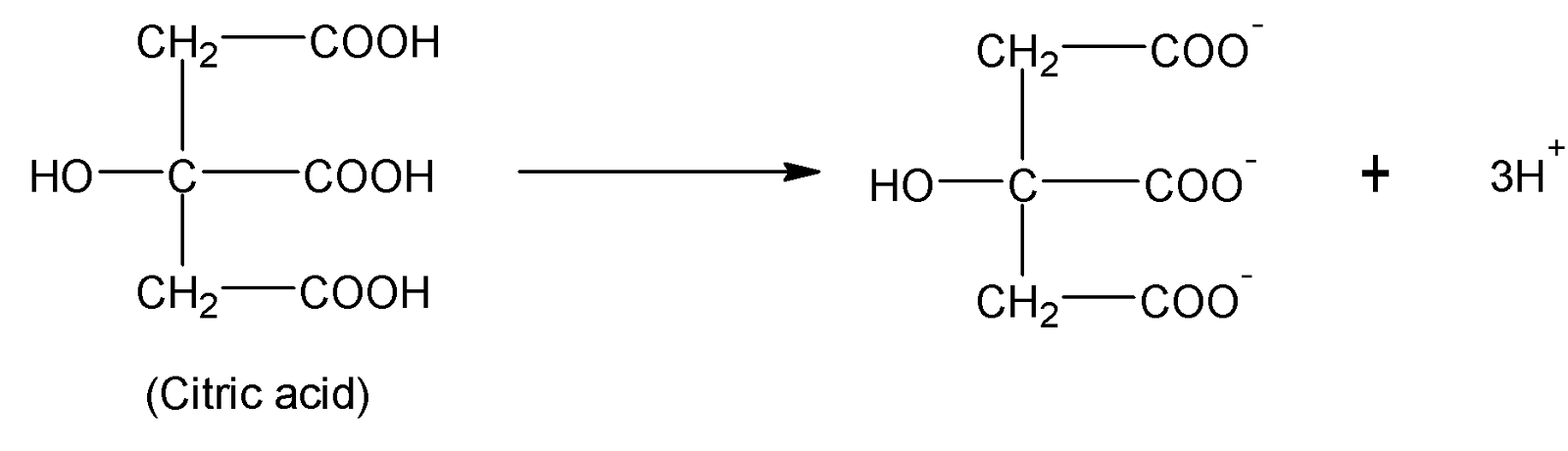
Therefore a tribasic acid is a citric acid.
Thus option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Acidity of a base is equal to the number of $O{{H}^{-}}$ ions present in it or other words, the number of hydroxyl ions produces when one molecule of a base undergoes dissociation is called acidity of a base. $Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}$is an example of a diacid base as it gives two $H{{O}^{-}}$in an aqueous solution.
Complete answer:When a component is dissolved in water it releases hydrogen ions,${{H}^{+}}$called acid. Generally, basicity is the number of replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions when an acid dissolves in water. If an acid contains one replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ion is called monobasic acid. A dibasic acid contains two replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions and a tribasic acid contains three replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions.
Oxalic acid has a chemical formula $HOOC-COOH$ and it is a polyprotic acid and basicity is equal to $2$. Hence it is a dibasic acid.

The chemical formula of tartaric acid is ${{[CH(OH)COOH]}_{2}}$. It is also a dibasic acid as it has two replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$ions.

Lactic acid is an organic compound having IUPAC name $2-$hydroxy propanoic acid and chemical formula $C{{H}_{3}}CH(OH)COOH$. As it can donate one ${{H}^{+}}$ion to a base thus it is a monobasic acid.

Finally citric acid is an organic compound with a chemical formula $HOOC(HO)C{{(C{{H}_{2}}C{{O}_{2}}H)}_{2}}$. Citric acid has basicity $3$ where the number of replaceable ${{H}^{+}}$is three.

Therefore a tribasic acid is a citric acid.
Thus option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: Acidity of a base is equal to the number of $O{{H}^{-}}$ ions present in it or other words, the number of hydroxyl ions produces when one molecule of a base undergoes dissociation is called acidity of a base. $Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}$is an example of a diacid base as it gives two $H{{O}^{-}}$in an aqueous solution.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




