
A ray of light is incident on an equilateral glass prism placed on a horizontal table. For minimum deviation, which of the following is true?
(A) QR is horizontal
(B) PQ is horizontal
(C) Either PQ or QS is horizontal
(D) RS is horizontal
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When the light travels from one medium to another (with different refractive indexes) it’s direction of propagation changes, in other words it is said to be deviated from its original path. The $\delta $gives deviation of light, and is defined as the angle between the incident and the emergent ray.
Complete step by step solution:
When the light travels through a prism, it is deviated two times during its course. First deviation occurs when it is incident on the prism, at point Q. The angle made by incident ray to the normal from the surface is represented by i, this ray is refracted inside by the glass prism.
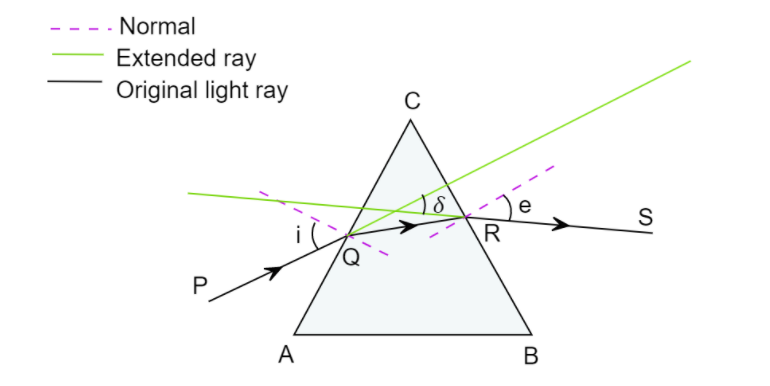
The refracted ray comes out through the point R, and the angle of emergence represented by e. If the incident and the emergence rays are extended , they intersect at a point. The one of the angles produced by the intersection gives the angle of deviation.
At the condition of minimum deviation,
$\angle i = \angle e$
This can only be reached when QR is parallel to AB. This will make the emergence and incident angles equally inclined from the prism, and the light will undergo minimum deviation. The other conditions for minimum deviation can also be derived using the geometry of the prism or the prism formula.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
The angle of incidence can have any value ,but for minimum deviation both of these quantities must be equal, and as another result for this, the line QR should be horizontal. Also, it is to be noted that light gets deviated two times when it travels inside a prism.
Complete step by step solution:
When the light travels through a prism, it is deviated two times during its course. First deviation occurs when it is incident on the prism, at point Q. The angle made by incident ray to the normal from the surface is represented by i, this ray is refracted inside by the glass prism.

The refracted ray comes out through the point R, and the angle of emergence represented by e. If the incident and the emergence rays are extended , they intersect at a point. The one of the angles produced by the intersection gives the angle of deviation.
At the condition of minimum deviation,
$\angle i = \angle e$
This can only be reached when QR is parallel to AB. This will make the emergence and incident angles equally inclined from the prism, and the light will undergo minimum deviation. The other conditions for minimum deviation can also be derived using the geometry of the prism or the prism formula.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note:
The angle of incidence can have any value ,but for minimum deviation both of these quantities must be equal, and as another result for this, the line QR should be horizontal. Also, it is to be noted that light gets deviated two times when it travels inside a prism.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




