
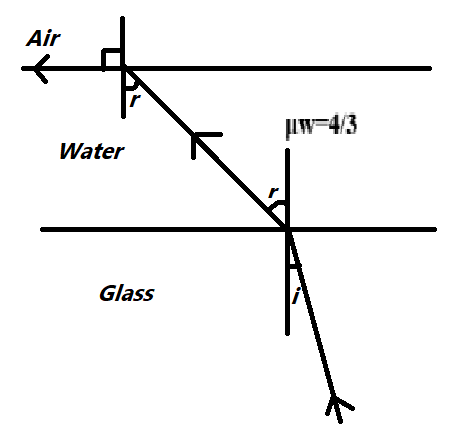
A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i. It merges finally parallel to the surface of the water. Then, the value of ${\mu _g}$ would be (where ${\mu _g}$ is the refractive index of glass with respect to water)
A. $\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)\sin i$
B. $\dfrac{1}{{(\sin i)}}$
C. $\dfrac{4}{3}$
D. $1$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, given that a ray of light is incident through glass medium to the water medium at an angle i and merges parallel to the surface of water. Here we have to find the value of ${\mu _g}$ . As we know that we can easily find the solution using Snell’s law.
Formula used:
Snell’s law
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}}$
Complete answer:
As we know that by applying the Snell’s law, we can easily find the solution of the question,
By applying the Snell’s law at the position of Glass-water surface,
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}}$
Here, $w$ stands for water and $g$ stands for glass,
As by putting the value we get the value as,
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}} = \dfrac{{{}_g\mu }}{{{}_w\mu }}....(i)$
As we take the above equation as equation(i)
Now, Applying the Snell’s law at the position of water-air surface,
${}_w^a\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{\sin r}}$
Here, $a$ stands for air and $w$ stands for water,
By putting the whole value in above equation, we get,
${}_w^a\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{}_w\mu }}{{{}_a\mu }}....(ii)$
Now, by multiplying equation(i) with equation(ii) we get,
$\dfrac{{{}_g\mu }}{{{}_a\mu }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
By taking the whole conclusion we get,
${}_g\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
Therefore, the correct answer for the value of ${}_g\mu $ is $\dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$ .
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Snell's law often applies to isotropic or specular material only (such as glass). The ordinary or o-ray, which obeys Snell's law, and the other extraordinary or e-ray, which may not be co-planar with the incident ray, can be separated by birefringence in anisotropic media, such as certain crystals. So, check the material before using the formula.
Formula used:
Snell’s law
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}}$
Complete answer:
As we know that by applying the Snell’s law, we can easily find the solution of the question,
By applying the Snell’s law at the position of Glass-water surface,
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}}$
Here, $w$ stands for water and $g$ stands for glass,
As by putting the value we get the value as,
${}_g^w\mu = \dfrac{{\sin r}}{{\sin i}} = \dfrac{{{}_g\mu }}{{{}_w\mu }}....(i)$
As we take the above equation as equation(i)
Now, Applying the Snell’s law at the position of water-air surface,
${}_w^a\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{\sin r}}$
Here, $a$ stands for air and $w$ stands for water,
By putting the whole value in above equation, we get,
${}_w^a\mu = \dfrac{{\sin {{90}^ \circ }}}{{\sin r}} = \dfrac{{{}_w\mu }}{{{}_a\mu }}....(ii)$
Now, by multiplying equation(i) with equation(ii) we get,
$\dfrac{{{}_g\mu }}{{{}_a\mu }} = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
By taking the whole conclusion we get,
${}_g\mu = \dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$
Therefore, the correct answer for the value of ${}_g\mu $ is $\dfrac{1}{{\sin i}}$ .
Hence, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Snell's law often applies to isotropic or specular material only (such as glass). The ordinary or o-ray, which obeys Snell's law, and the other extraordinary or e-ray, which may not be co-planar with the incident ray, can be separated by birefringence in anisotropic media, such as certain crystals. So, check the material before using the formula.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




