
A ray gets successively reflection from two mirrors inclined at an angle of \[{40^o}\]. If the angle of incidence for the first mirror is \[{30^o}\], then net deviation of this ray after two reflections:
A) \[{40^o}\]
B) \[{280^o}\]
C) \[{180^o}\]
D) \[{240^o}\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:We can easily solve the question by using laws of reflection. We know that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. Also, we can use the relation between the angle deviation and the angle of incidence. using these two relations we can easily find the answer to the given question.
Complete step-By-Step Answer:
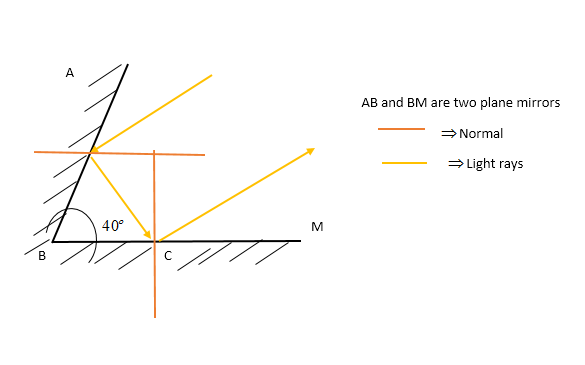
It is given in the question that:
The angle between the two mirrors \[ = {40^o}\]
The angle of incidence on the first mirror \[ = {30^o}\]
We know the laws of reflection states that when a light is reflected off a surface, angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
Let \[\angle i\] be the angle of incidence and\[\angle r\] be the angle of reflection.
Thus, \[\angle i = \angle r\]
The angle of reflection in the first mirror \[ = {30^o}\]
Thus, angle of deviation denoted by \[{\delta _1}\] is \[ = \pi - 2 \times \angle i\]
\[ \Rightarrow {180^o} - {60^o}\]
\[{\delta _1} = {120^o}\]
We also know, from the laws of reflection, the angle of reflection, the angle of incidence and the normal together sums up to\[{180^o}\].
The normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
Now, considering triangle ABC in the diagram:
\[\angle BAC = {90^o} - {30^o} = {60^o}\]Since the normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
\[\angle ABC = {40^o}\](GIVEN)
Using the angle sum property we, obtain:
\[\angle ACB = {80^o}\]
Normal of the second mirror also makes right angle with the plane of the mirror, thus, \[\angle ACD = {90^o} - {80^o} = {10^o}\]
This is the angle of incidence and it equals angle of reflection for the second mirror.
Thus angle of deviation in mirror 2 is given by:
\[{\delta _2} = \pi - 2{i_2}\]
Where, \[{i_2}\] represents the angle of incidence for the second mirror.
\[{\delta _2} = {180^o} - {20^o} = {160^o}\]
Therefore, total angle of deviation is given by:
\[\delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \delta = {120^o} + {160^o} = {280^o}\]
This is our required solution.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Angle of deviation, as we know, is defined as the angle between the straight line path and the reflected ray, which is equal to twice the angle of deviation.
Image formed by the plane mirror is virtual, erect and of the same size as that of the object.
Complete step-By-Step Answer:

It is given in the question that:
The angle between the two mirrors \[ = {40^o}\]
The angle of incidence on the first mirror \[ = {30^o}\]
We know the laws of reflection states that when a light is reflected off a surface, angle of incidence equals angle of reflection.
Let \[\angle i\] be the angle of incidence and\[\angle r\] be the angle of reflection.
Thus, \[\angle i = \angle r\]
The angle of reflection in the first mirror \[ = {30^o}\]
Thus, angle of deviation denoted by \[{\delta _1}\] is \[ = \pi - 2 \times \angle i\]
\[ \Rightarrow {180^o} - {60^o}\]
\[{\delta _1} = {120^o}\]
We also know, from the laws of reflection, the angle of reflection, the angle of incidence and the normal together sums up to\[{180^o}\].
The normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
Now, considering triangle ABC in the diagram:
\[\angle BAC = {90^o} - {30^o} = {60^o}\]Since the normal makes right angles with the plane of the mirror.
\[\angle ABC = {40^o}\](GIVEN)
Using the angle sum property we, obtain:
\[\angle ACB = {80^o}\]
Normal of the second mirror also makes right angle with the plane of the mirror, thus, \[\angle ACD = {90^o} - {80^o} = {10^o}\]
This is the angle of incidence and it equals angle of reflection for the second mirror.
Thus angle of deviation in mirror 2 is given by:
\[{\delta _2} = \pi - 2{i_2}\]
Where, \[{i_2}\] represents the angle of incidence for the second mirror.
\[{\delta _2} = {180^o} - {20^o} = {160^o}\]
Therefore, total angle of deviation is given by:
\[\delta = {\delta _1} + {\delta _2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \delta = {120^o} + {160^o} = {280^o}\]
This is our required solution.
Thus, option (B) is correct.
Note: Angle of deviation, as we know, is defined as the angle between the straight line path and the reflected ray, which is equal to twice the angle of deviation.
Image formed by the plane mirror is virtual, erect and of the same size as that of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




