
A proton moving at constant velocity enters the region between two charged plates, as shown below. Which of the paths shown correctly indicates the proton's trajectory after leaving the region between the charged plates?
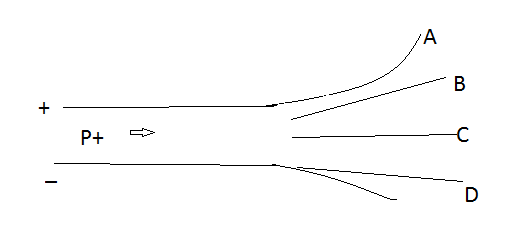
\[A)\;A\]
\[B)\;B\]
\[C)\;C\]
\[D)\;D\]
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Protons are found in the nucleus of the atom. Proton is a stable subatomic particle. Protons are the tiny and dense region at the center of the atom. It is a positively charged particle. Protons are considered elementary particles in particle physics.
Complete step by step solution:
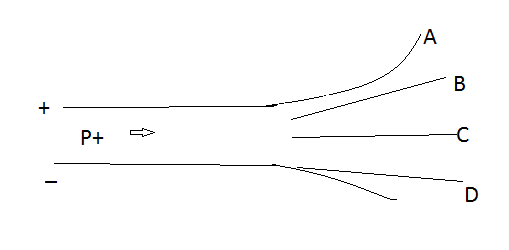
In a given figure, a proton is kept between the two plates. One side of the plate is positively charged and the other side of the plate is negatively charged. It is denoted by the symbol \[p\] . The mass of a proton is $1.6726 \times {10^{ - 27}}$kg. A proton is made up of two ‘’up’’ quarks and one ‘’down’’ quarks. Protons meshed with electrically neutral particles called neutrons.
The antiparticle is antiprotons. The electric charge is $ + 1e$. The number of protons in the nucleus is the property of an element. A proton is moving between the plates and after leaving the region between the two plates the protons are attracted by the negative plates and hit towards the negative plate that is D. This is because the proton is positively charged. Due to attraction between the positive proton and negative plate, the proton moves through the path of D.
Proton is positively charged and thus proton is attracted to the negative plate. Hence it will take a path \[D\] after leaving the region between the charged plates.
Note: Proton was observed by Eugen Goldstein as ${H^ + }$ in $1886$. The word proton was given by Ernest Rutherford in $1920$. The mean lifetime is $ > 2.1 \times {10^{29}}$ years stable. The spin is $\dfrac{1}{2}$(half). It is the building block of nitrogen and all other heavier atomic nuclei.
Complete step by step solution:

In a given figure, a proton is kept between the two plates. One side of the plate is positively charged and the other side of the plate is negatively charged. It is denoted by the symbol \[p\] . The mass of a proton is $1.6726 \times {10^{ - 27}}$kg. A proton is made up of two ‘’up’’ quarks and one ‘’down’’ quarks. Protons meshed with electrically neutral particles called neutrons.
The antiparticle is antiprotons. The electric charge is $ + 1e$. The number of protons in the nucleus is the property of an element. A proton is moving between the plates and after leaving the region between the two plates the protons are attracted by the negative plates and hit towards the negative plate that is D. This is because the proton is positively charged. Due to attraction between the positive proton and negative plate, the proton moves through the path of D.
Proton is positively charged and thus proton is attracted to the negative plate. Hence it will take a path \[D\] after leaving the region between the charged plates.
Note: Proton was observed by Eugen Goldstein as ${H^ + }$ in $1886$. The word proton was given by Ernest Rutherford in $1920$. The mean lifetime is $ > 2.1 \times {10^{29}}$ years stable. The spin is $\dfrac{1}{2}$(half). It is the building block of nitrogen and all other heavier atomic nuclei.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




