
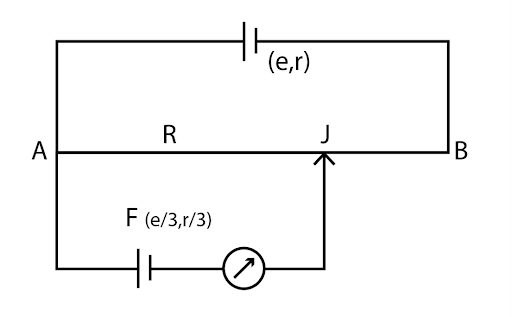
A potentiometer arrangement is shown in fig. The driver cell has emf e and internal resistance r. The resistance of potentiometer wire AB is R. F is the cell of emf e/3 and internal resistance r/3. Balance point (J) can be obtained for all finite values of
A. $R > \dfrac{r}{2}$
B. $R < \dfrac{r}{2}$
C. $R > \dfrac{r}{3}$
D. $R < \dfrac{r}{3}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:The problem is from the current electricity section of physics. We need to know the concepts of the potentiometer to solve this problem. The potentiometer is a device used to measure an unknown voltage by comparing it to a known voltage. It can be used to compare the emf of several cells and to determine the emf and internal resistance of the specified cell.
Complete step by step solution:
Point J is the balance point of the given potentiometer. The current (I) will not flow through the galvanometer. current in wire AB (primary circuit) is given below.
\[I = \dfrac{e}{{R + r}}\]
The potential difference across the wire AB is,
\[{V_{AB}} = IR = \dfrac{{eR}}{{R + r}}\]
In order to obtain a balanced point of the potentiometer, the potential drop across wire should be greater than the emf of the cell in the secondary circuit.
\[\dfrac{{eR}}{{R + r}} > \dfrac{e}{3}\]
\[\therefore R > \dfrac{r}{2}\]
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional Information: A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or revolving contact that serves as a voltage divider that may be adjusted. It functions as a variable resistor or rheostat when only two terminals are employed. Potentiometers are frequently used in the manufacture of electronic equipment that allows users to change electrical circuits to get the desired outputs. Although volume controls on radios and other audio-related electrical equipment are the most used applications
Note: The smallest change in the potential difference that a potentiometer can detect is its sensitivity. By lowering the potential gradient, the potentiometer's sensitivity can be improved. That is done by extending the potentiometer wire's length.
Complete step by step solution:
Point J is the balance point of the given potentiometer. The current (I) will not flow through the galvanometer. current in wire AB (primary circuit) is given below.
\[I = \dfrac{e}{{R + r}}\]
The potential difference across the wire AB is,
\[{V_{AB}} = IR = \dfrac{{eR}}{{R + r}}\]
In order to obtain a balanced point of the potentiometer, the potential drop across wire should be greater than the emf of the cell in the secondary circuit.
\[\dfrac{{eR}}{{R + r}} > \dfrac{e}{3}\]
\[\therefore R > \dfrac{r}{2}\]
Hence, the correct option is option A.
Additional Information: A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or revolving contact that serves as a voltage divider that may be adjusted. It functions as a variable resistor or rheostat when only two terminals are employed. Potentiometers are frequently used in the manufacture of electronic equipment that allows users to change electrical circuits to get the desired outputs. Although volume controls on radios and other audio-related electrical equipment are the most used applications
Note: The smallest change in the potential difference that a potentiometer can detect is its sensitivity. By lowering the potential gradient, the potentiometer's sensitivity can be improved. That is done by extending the potentiometer wire's length.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




