
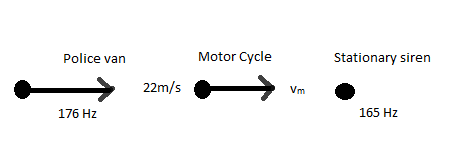
A police car moving at 22 m/s, chases a motorcyclist. The policeman sounds his horn at 176 Hz, while both of them move towards a stationary siren of frequency 165 Hz as shown in the figure. If the motorcyclist does not observe any beats, his speed must be: (take the speed of sound = 330 m/s)
A) 33 m/s
B) 22 m/s
C) zero
D) 11 m/s
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Frequency is defined as the number of waves that pass through a fixed point in the unit of time. It is also defined as the number of oscillations per unit of time. The unit of frequency is Hertz.
Complete step by step solution:
Given data:
Speed of a police car, ${v_s} = 22m/s$
Frequency of the sound horn, ${n_{car}} = 176Hz$
Frequency of the siren, ${n_{siren}} = 165Hz$
Speed of the sound, v = 330 m/s
Speed of the motorcyclist, ${v_m}$ =?
It is given that in the first case the police car which is a source of sound is moving at a speed ${v_s}$and is approaching a motorcycle (observer) which in turn is moving away from the police car with a speed of ${v_m}$.
Thus the apparent frequency of the sound heard by the motorcyclist is given by,
$\Rightarrow n' = {n_{car}}\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
Again in the second case the motorcyclist, an observer is approaching a stationary siren, source at a speed of ${v_m}$
Thus the apparent frequency of the sound heard by the motorcyclist is given by,
$\Rightarrow n'' = {n_{siren}}\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{v}} \right)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 2 \right)$
It is given that the motorcyclist does not observe any beats and this is possible only when the difference in the frequencies heard by the motorcyclist is zero.
Thus $n' - n'' = 0$
$ \Rightarrow n' = n''$
Substituting the values of $n'$ and $n''$ from the equations 1 and 2, we get,
$\Rightarrow {n_{car}}\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right) = {n_{siren}}\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{v}} \right)$
Thus substituting the values of ${n_{car}},{v_m},{v_s},{n_{siren}},v,$ we get
$\Rightarrow 176\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{330 - 22}}} \right) = 165\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{{330}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v + {v_m}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{165}}{{176}} \times \dfrac{{308}}{{330}} = \dfrac{7}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow 8v - 8{v_m} = 7v + 7{v_m}$
$ \Rightarrow 15{v_m} = v$
$ \Rightarrow {v_m} = \dfrac{v}{{15}} = \dfrac{{330}}{{15}} = 22m/s$
Thus the speed of the motorcyclist $ = 22m/s$
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: The sound source generates the sound waves and creates the vibrations in the surrounding medium. As this continues the vibrations propagate away at the speed of the sound.
Complete step by step solution:
Given data:
Speed of a police car, ${v_s} = 22m/s$
Frequency of the sound horn, ${n_{car}} = 176Hz$
Frequency of the siren, ${n_{siren}} = 165Hz$
Speed of the sound, v = 330 m/s
Speed of the motorcyclist, ${v_m}$ =?
It is given that in the first case the police car which is a source of sound is moving at a speed ${v_s}$and is approaching a motorcycle (observer) which in turn is moving away from the police car with a speed of ${v_m}$.
Thus the apparent frequency of the sound heard by the motorcyclist is given by,
$\Rightarrow n' = {n_{car}}\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 1 \right)$
Again in the second case the motorcyclist, an observer is approaching a stationary siren, source at a speed of ${v_m}$
Thus the apparent frequency of the sound heard by the motorcyclist is given by,
$\Rightarrow n'' = {n_{siren}}\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{v}} \right)\_\_\_\_\_\_\_\left( 2 \right)$
It is given that the motorcyclist does not observe any beats and this is possible only when the difference in the frequencies heard by the motorcyclist is zero.
Thus $n' - n'' = 0$
$ \Rightarrow n' = n''$
Substituting the values of $n'$ and $n''$ from the equations 1 and 2, we get,
$\Rightarrow {n_{car}}\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v - {v_s}}}} \right) = {n_{siren}}\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{v}} \right)$
Thus substituting the values of ${n_{car}},{v_m},{v_s},{n_{siren}},v,$ we get
$\Rightarrow 176\left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{330 - 22}}} \right) = 165\left( {\dfrac{{v + {v_m}}}{{330}}} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{v - {v_m}}}{{v + {v_m}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{165}}{{176}} \times \dfrac{{308}}{{330}} = \dfrac{7}{8}$
$ \Rightarrow 8v - 8{v_m} = 7v + 7{v_m}$
$ \Rightarrow 15{v_m} = v$
$ \Rightarrow {v_m} = \dfrac{v}{{15}} = \dfrac{{330}}{{15}} = 22m/s$
Thus the speed of the motorcyclist $ = 22m/s$
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: The sound source generates the sound waves and creates the vibrations in the surrounding medium. As this continues the vibrations propagate away at the speed of the sound.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




